Campbell Ch 14 Reading guide
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 13. How does codominance compare to incomplete dominance? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 13. How does codominance compare to incomplete dominance? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
Quiz 4
... Which of the following cannot be an example of evolution? a. As a consequence of legislation promoting cleaner air, the frequency of black peppered moths in Europe has decreased in the last half century. b. After repeated exposure to high temperatures, an individual turtle can tolerate heat more suc ...
... Which of the following cannot be an example of evolution? a. As a consequence of legislation promoting cleaner air, the frequency of black peppered moths in Europe has decreased in the last half century. b. After repeated exposure to high temperatures, an individual turtle can tolerate heat more suc ...
Document
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
Huntington`s disease is an example of a genetic disorder caused by
... 3. Michelle and Keith are apparently normal, but their daughter was born with alkaptonuria, an inherited metabolic disorder. a. What inheritance pattern is described above? b. What term would be used to describe the parents? c. If alkaptonuria is like most other human hereditary disorders, what is p ...
... 3. Michelle and Keith are apparently normal, but their daughter was born with alkaptonuria, an inherited metabolic disorder. a. What inheritance pattern is described above? b. What term would be used to describe the parents? c. If alkaptonuria is like most other human hereditary disorders, what is p ...
Chemistry Revision
... Pure Breeding- An organism that will be either homozygous dominant or recessive for a particular trait Somatic mutation- a mutation that cannot be inherited because these cells only reproduce via mitosis Gamete mutation- a mutation that can be inherited because these cells will produce via mei ...
... Pure Breeding- An organism that will be either homozygous dominant or recessive for a particular trait Somatic mutation- a mutation that cannot be inherited because these cells only reproduce via mitosis Gamete mutation- a mutation that can be inherited because these cells will produce via mei ...
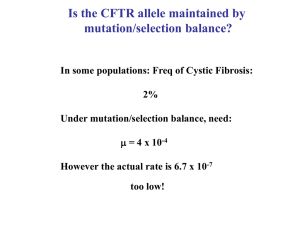
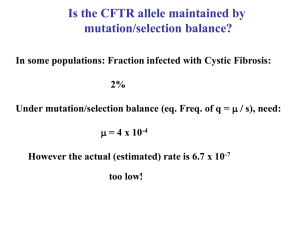
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
Genetic Variation and Equilibrium
... 3. Sexual Selection (nonrandom mating): occurs when certain traits increase mating success ...
... 3. Sexual Selection (nonrandom mating): occurs when certain traits increase mating success ...
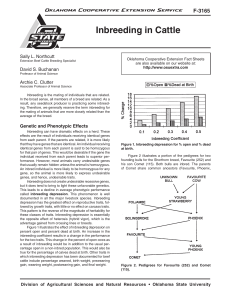
Inbreeding in Cattle
... from each parent. If the parents are related, it is more likely that they have genes that are identical. An individual receiving identical genes from each parent is said to be homozygous for that pair of genes. This would be desirable if the gene the individual received from each parent leads to sup ...
... from each parent. If the parents are related, it is more likely that they have genes that are identical. An individual receiving identical genes from each parent is said to be homozygous for that pair of genes. This would be desirable if the gene the individual received from each parent leads to sup ...
Traditional (historical) Breeding
... selection for a specific trait • EBV = ave. of animals selected minus the ave. of all animals X heritability • EPD = EBV X .5 ...
... selection for a specific trait • EBV = ave. of animals selected minus the ave. of all animals X heritability • EPD = EBV X .5 ...
Introduction to Genetics Study Guide
... Genetics scientific study of heredity True-breeding describes organisms that if allowed to self-pollinate, they would produce offspring identical to themselves Trait a distinguishing characteristic that can be inherited and varies from one individual to another Hybrid offspring of crosses between pa ...
... Genetics scientific study of heredity True-breeding describes organisms that if allowed to self-pollinate, they would produce offspring identical to themselves Trait a distinguishing characteristic that can be inherited and varies from one individual to another Hybrid offspring of crosses between pa ...
Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring
... Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics- study of heredity Gregor Mendel-“Father of Genetics” Dominant- a trait that ALWAYS shows up & it covers up the recessive trait CAPITAL letters Recessive- trait that only shows up when there is NO dominant trait Lowercase letters G ...
... Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics- study of heredity Gregor Mendel-“Father of Genetics” Dominant- a trait that ALWAYS shows up & it covers up the recessive trait CAPITAL letters Recessive- trait that only shows up when there is NO dominant trait Lowercase letters G ...
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems 1. The frequency of two
... 891 are white and 9 are black. Calculate the allelic frequencies within this population, assuming that the population is in H-W equilibrium. 3. In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the frequency of the recessive homozygote genotype of a certain trait is 0.09. Calculate the percenta ...
... 891 are white and 9 are black. Calculate the allelic frequencies within this population, assuming that the population is in H-W equilibrium. 3. In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the frequency of the recessive homozygote genotype of a certain trait is 0.09. Calculate the percenta ...
The Hardy-Weinberg Principles
... Hardy-Weinberg Equation • This equation shows the frequency of each genotype we would expect to see based on the allele frequencies in the population. • p2 + 2pq + q2= 1 Ex. What would the genotype proportions be in the flower population? ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Equation • This equation shows the frequency of each genotype we would expect to see based on the allele frequencies in the population. • p2 + 2pq + q2= 1 Ex. What would the genotype proportions be in the flower population? ...
q 2 - cloudfront.net
... • To see what forces lead to evolutionary change, we must examine the circumstances in which the Hardy-Weinberg law may fail to apply. There are five: • mutation • gene flow • genetic drift • nonrandom mating • natural selection ...
... • To see what forces lead to evolutionary change, we must examine the circumstances in which the Hardy-Weinberg law may fail to apply. There are five: • mutation • gene flow • genetic drift • nonrandom mating • natural selection ...
Individuals are Selected for But Populations Evolve
... Six Fingers is dominant…why do most of us have 5? Why do many Northern Europeans carry the lethal recessive CF allele? ...
... Six Fingers is dominant…why do most of us have 5? Why do many Northern Europeans carry the lethal recessive CF allele? ...
Intro to Genetics notes
... • Alleles are separated during reproduction; one from each parent. –Ex. BB (mom) bb (dad) »Child (Bb) ...
... • Alleles are separated during reproduction; one from each parent. –Ex. BB (mom) bb (dad) »Child (Bb) ...
Egg Genetics Vocab. Notes
... • Recall that most organisms have two sets of chromosomes (each chromosome has a matching pair. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 chromosomes total.) • Pairs of chromosomes have matching genes, therefore, genes also come in pairs, (2). • Not all genes in a pair are identical! – Ex.) There i ...
... • Recall that most organisms have two sets of chromosomes (each chromosome has a matching pair. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 chromosomes total.) • Pairs of chromosomes have matching genes, therefore, genes also come in pairs, (2). • Not all genes in a pair are identical! – Ex.) There i ...
1. Offspring that are the result of mating between two genetically
... inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. A 19th century central European monk scientist who published his ideas about genetics in 1866 but largely went unrecognized until 1900, which was long after his death. He acquired his understanding of genetics mostly through pea plant breeding experime ...
... inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. A 19th century central European monk scientist who published his ideas about genetics in 1866 but largely went unrecognized until 1900, which was long after his death. He acquired his understanding of genetics mostly through pea plant breeding experime ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 15. There are five conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Enter the conditions on the left side of the chart and a brief explanation of the condition on the right side. ...
... 15. There are five conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Enter the conditions on the left side of the chart and a brief explanation of the condition on the right side. ...
popandecojeopardyREVISED
... 7. An allele whose trait always is seen in the organism when the allele is present in either of the two gene locations. __________________________ 8. A genotype that has 2 different alleles for a gene. ________________________ 9. An allele whose trait is covered up whenever the dominant allele is pr ...
... 7. An allele whose trait always is seen in the organism when the allele is present in either of the two gene locations. __________________________ 8. A genotype that has 2 different alleles for a gene. ________________________ 9. An allele whose trait is covered up whenever the dominant allele is pr ...
inheritance and Mendelian genetics
... in inherited characters (eg., for flower color gene, two alleles - purple trait and white trait – for each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent (eg., homologous chromosones) – If the two alleles differ, one is fully expressed (dominant allele, denoted in upper case, eg., ...
... in inherited characters (eg., for flower color gene, two alleles - purple trait and white trait – for each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent (eg., homologous chromosones) – If the two alleles differ, one is fully expressed (dominant allele, denoted in upper case, eg., ...