Section 2: Building A Muslim Empire.
... Successor to Muhammad In 632 Abu Bakr became the first Caliph. ▪ United all Arab tribes as Muslims. ...
... Successor to Muhammad In 632 Abu Bakr became the first Caliph. ▪ United all Arab tribes as Muslims. ...
Conquest and Faith WHAP/Napp “When the Prophet died leaving no
... umma and its political organization would break up. To preserve them, the Muslim leadership elected Abu Bakr (r. 632-634), one of Muhammad’s closest associates and the father of his wife Aisha, as caliph – that is, successor to the Prophet and head of the Muslim community. The next three caliphs [th ...
... umma and its political organization would break up. To preserve them, the Muslim leadership elected Abu Bakr (r. 632-634), one of Muhammad’s closest associates and the father of his wife Aisha, as caliph – that is, successor to the Prophet and head of the Muslim community. The next three caliphs [th ...
Condemning the Islamic State and the `caliphate`
... The name is significant. The group changed its name from the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria to simply the Islamic State. For them, the underlying vision is something found in Muslim history: the caliphate. And they don't want to be geographically limited; they want to fashion the world in their ima ...
... The name is significant. The group changed its name from the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria to simply the Islamic State. For them, the underlying vision is something found in Muslim history: the caliphate. And they don't want to be geographically limited; they want to fashion the world in their ima ...
Expansion of the Early Caliphates 632–750 CE
... which angered many and resulted in his death in 656. • Alib ibn Abi Talib, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, reluctantly became the 4th caliph but was challenged by members of the Umayyad Dynasty. After settling a Muslim civil war, he was murdered by a supporter that disagreed with his actions. • Th ...
... which angered many and resulted in his death in 656. • Alib ibn Abi Talib, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, reluctantly became the 4th caliph but was challenged by members of the Umayyad Dynasty. After settling a Muslim civil war, he was murdered by a supporter that disagreed with his actions. • Th ...
File
... Non-Muslims, who were “Peoples of the Book,” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes. ...
... Non-Muslims, who were “Peoples of the Book,” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes. ...
The Rise and Fall of the Caliphates
... (Muhammad’s cousin & son-in-law) was chosen as natural successor Ali’s rule was challenged by Muawiya (governor of Syria) 661, Ali assassinated Umayyad (led by Muawiya’s son) come to power & move capital to Damascus Arabs upset that capital was so far away Began to live a life of luxury ...
... (Muhammad’s cousin & son-in-law) was chosen as natural successor Ali’s rule was challenged by Muawiya (governor of Syria) 661, Ali assassinated Umayyad (led by Muawiya’s son) come to power & move capital to Damascus Arabs upset that capital was so far away Began to live a life of luxury ...
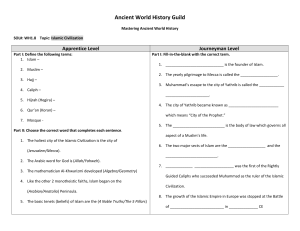
Ancient World History Guild
... 3. The mathematician Al-Khwarizmi developed (Algebra/Geometry) Guided Caliphs who succeeded Muhammad as the ruler of the Islamic 4. Like the other 2 monotheistic faiths, Islam began on the Civilization. (Arabian/Anatolia) Peninsula. 8. The growth of the Islamic Empire in Europe was stopped at the Ba ...
... 3. The mathematician Al-Khwarizmi developed (Algebra/Geometry) Guided Caliphs who succeeded Muhammad as the ruler of the Islamic 4. Like the other 2 monotheistic faiths, Islam began on the Civilization. (Arabian/Anatolia) Peninsula. 8. The growth of the Islamic Empire in Europe was stopped at the Ba ...
Ancient World History Guild
... 3. The mathematician Al-Khwarizmi developed (Algebra/Geometry) Guided Caliphs who succeeded Muhammad as the ruler of the Islamic 4. Like the other 2 monotheistic faiths, Islam began on the Civilization. (Arabian/Anatolia) Peninsula. 8. The growth of the Islamic Empire in Europe was stopped at the Ba ...
... 3. The mathematician Al-Khwarizmi developed (Algebra/Geometry) Guided Caliphs who succeeded Muhammad as the ruler of the Islamic 4. Like the other 2 monotheistic faiths, Islam began on the Civilization. (Arabian/Anatolia) Peninsula. 8. The growth of the Islamic Empire in Europe was stopped at the Ba ...
The Schism of Islam Directions: Read the following account
... growing Muslim Empire in Saudi Arabia. However, upon his death, he did not leave instructions for how the next Caliph, or community leader, should be chosen. Some Muslims believe that the Caliph should be a direct descendant of Muhammad; others believed that the community should elect the Caliph. Th ...
... growing Muslim Empire in Saudi Arabia. However, upon his death, he did not leave instructions for how the next Caliph, or community leader, should be chosen. Some Muslims believe that the Caliph should be a direct descendant of Muhammad; others believed that the community should elect the Caliph. Th ...
10.2 The Spread of Islam
... The reign of a caliph was known as a caliphate. Example: Caliph Abu-Bakr • During caliphate of Abu-Bakr, there were many uprisings that were quickly subdued (put down). ...
... The reign of a caliph was known as a caliphate. Example: Caliph Abu-Bakr • During caliphate of Abu-Bakr, there were many uprisings that were quickly subdued (put down). ...
Power Point 4 Caliphs
... expanded the lands under their rule despite struggles over leadership and even civil wars. ...
... expanded the lands under their rule despite struggles over leadership and even civil wars. ...
The Rise of Islam - Fabius
... – These disagreements led to the development of three rival sects in the Muslim community. The ___________ supported Ali’s claim to the caliphate and believed that the position of caliph rightly belonged to the descendants of Ali. Those known as the ______________ believed that the first three calip ...
... – These disagreements led to the development of three rival sects in the Muslim community. The ___________ supported Ali’s claim to the caliphate and believed that the position of caliph rightly belonged to the descendants of Ali. Those known as the ______________ believed that the first three calip ...
Chapter 6-2: The Arab Empire and Its Successors
... empire in the thirteenth century? The Mongols were fierce nomads who created such terror that people would not fight back. They seized Persia and Mesopotamia, bringing the Abbasid caliphate to an end. What changes occurred with Mongol rulers over ...
... empire in the thirteenth century? The Mongols were fierce nomads who created such terror that people would not fight back. They seized Persia and Mesopotamia, bringing the Abbasid caliphate to an end. What changes occurred with Mongol rulers over ...
H - The Schism within Islam
... • Strong support from many Muslims • Also faced resistance – especially from Syrian Gov. Muawiya (from the Umayyad Clan), Uthman’s cousin • Results in Battle of Siffin ...
... • Strong support from many Muslims • Also faced resistance – especially from Syrian Gov. Muawiya (from the Umayyad Clan), Uthman’s cousin • Results in Battle of Siffin ...
Chapter Six The First Global Civilization
... • Caliph = Islamic religious and political leader • Caliphate = dynasty of Islamic caliphs • Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs (632-661) • Abu Bakr; Umar; Uthman; Ali ...
... • Caliph = Islamic religious and political leader • Caliphate = dynasty of Islamic caliphs • Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs (632-661) • Abu Bakr; Umar; Uthman; Ali ...
File
... In a short space of 10 years, Sayyiduna Umar (radi Allahu anhu) had been well-known for his outstanding achievements and reforms in Islam. Some of these reforms were:1. He established the "Baitul Maal" (People's treasury for the state and ...
... In a short space of 10 years, Sayyiduna Umar (radi Allahu anhu) had been well-known for his outstanding achievements and reforms in Islam. Some of these reforms were:1. He established the "Baitul Maal" (People's treasury for the state and ...
The Rise and Spread of Islam
... • People resent extravagance of Umayyads, see them as corrupt and decadent. • Abbasid family/army rebels and challenges Umayyad army at the Battle of the River Zab in ...
... • People resent extravagance of Umayyads, see them as corrupt and decadent. • Abbasid family/army rebels and challenges Umayyad army at the Battle of the River Zab in ...
Topic 6: Caravans and Conquest: Song to Mongols.
... 1. The Rise of Islam, 600-1000 ca. 570 CE Birth of Muhammad in Mecca 610 Muhammad’s first revelations 613 Muhammad begins public preaching 622 Hijrah: 1st year of Islamic calendar 630 Occupation of Mecca by Muslims 632 Death of Muhammad 661 Establishment of Umayyad Caliphate in Damascus [Origin of S ...
... 1. The Rise of Islam, 600-1000 ca. 570 CE Birth of Muhammad in Mecca 610 Muhammad’s first revelations 613 Muhammad begins public preaching 622 Hijrah: 1st year of Islamic calendar 630 Occupation of Mecca by Muslims 632 Death of Muhammad 661 Establishment of Umayyad Caliphate in Damascus [Origin of S ...
The Rise of Islam 632 - 1200
... in 1258, the Abbasid caliphate remained a purely formal institution After the dissolution of the Buyids in the mideleventh century, their place was filled by the Turkish Seljuks, who took the title of Sultan. ...
... in 1258, the Abbasid caliphate remained a purely formal institution After the dissolution of the Buyids in the mideleventh century, their place was filled by the Turkish Seljuks, who took the title of Sultan. ...
Muslim Civilizations 10.2-10.3
... • Shiites believed that Muhammad had designated his son-in-law Ali to be his successor. “Followers of Ali”. • Sunni’s believed that the caliph should be a pious member of Muhammad’s tribe, not necessarily one of his relatives. • Shiites believed that the new leader should serve as a religious leader ...
... • Shiites believed that Muhammad had designated his son-in-law Ali to be his successor. “Followers of Ali”. • Sunni’s believed that the caliph should be a pious member of Muhammad’s tribe, not necessarily one of his relatives. • Shiites believed that the new leader should serve as a religious leader ...
Islam after Muhammad Arabian Caliphate
... Ottomans: powerful army; began in Turkey in 1200. Ottoman Empire a. Conquered Byzantine Empire, pushed north into Constantinople, capital city b. Then in Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and parts of Arabia c. Sultan Suleiman Ottoman Gov’t lasted until WWI in 1916 a. Laws for Muslims, Christians, and Jews i ...
... Ottomans: powerful army; began in Turkey in 1200. Ottoman Empire a. Conquered Byzantine Empire, pushed north into Constantinople, capital city b. Then in Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and parts of Arabia c. Sultan Suleiman Ottoman Gov’t lasted until WWI in 1916 a. Laws for Muslims, Christians, and Jews i ...
Behrman movie recommendation
... Osborne, leader of the Turks in Asia o Kicks the greeks out of Byzantium o The Ottoman Empire o Sultan took the title of Caliph, til 1924 o WWI end; powers dismember the Ottoman empire o Civil war in Turkey, no more worldwide Ummah leader now - Ibm Tamiyah (1268-1328) is inspired by the Kharijites o ...
... Osborne, leader of the Turks in Asia o Kicks the greeks out of Byzantium o The Ottoman Empire o Sultan took the title of Caliph, til 1924 o WWI end; powers dismember the Ottoman empire o Civil war in Turkey, no more worldwide Ummah leader now - Ibm Tamiyah (1268-1328) is inspired by the Kharijites o ...