Photosynth-Cellular Respiration
... of cellular respiration, glycolysis, takes place in the cell cytoplasm. The two remaining pathways—the Krebs Cycle and electron transport—take place inside the mitochondria of the cell. ...
... of cellular respiration, glycolysis, takes place in the cell cytoplasm. The two remaining pathways—the Krebs Cycle and electron transport—take place inside the mitochondria of the cell. ...
Cellular Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... must first be broken down into glucose before entering glycolysis ...
... must first be broken down into glucose before entering glycolysis ...
Key enzymes in glycolysis
... 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
... 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
Glycolysis
... 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
... 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 10. In which of the following situations would you least expect to find anaerobic respiration occurring? a) a vat in which beer is being manufactured b) a human brain engaged in writing this test c) the inside of a bacterium living inside a human intestine d) a runner's leg muscle during a 400-m das ...
... 10. In which of the following situations would you least expect to find anaerobic respiration occurring? a) a vat in which beer is being manufactured b) a human brain engaged in writing this test c) the inside of a bacterium living inside a human intestine d) a runner's leg muscle during a 400-m das ...
AP Biology
... 1. Krebs cycle reactions occur in matrix of mitochondria. 2. Cycle is named for Sir Hans Krebs, who received Noel Prize for identifying these reactions. Cycle begins by adding C2 acetyl group to C4 molecule, forming citrate; also called the citric acid cycle. The acetyl group is then oxidized to two ...
... 1. Krebs cycle reactions occur in matrix of mitochondria. 2. Cycle is named for Sir Hans Krebs, who received Noel Prize for identifying these reactions. Cycle begins by adding C2 acetyl group to C4 molecule, forming citrate; also called the citric acid cycle. The acetyl group is then oxidized to two ...
Chapter 5 Capturing and releasing Energy
... energy of carbohydrates to chemical energy of ATP by oxygen-requiring aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration • Aerobic pathway that breaks down carbohydrates to produce ATP • Pathway finishes in mitochondria ...
... energy of carbohydrates to chemical energy of ATP by oxygen-requiring aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration • Aerobic pathway that breaks down carbohydrates to produce ATP • Pathway finishes in mitochondria ...
Study Guide
... which carbon fixation takes place. 7. The stage of cell respiration that takes in the products of glycolysis and produces two ATP molecules. 9. A small, high-energy molecule that can be used by cells. It is the by-product of glucose breakdown. 10. A series of reactions used by all living things that ...
... which carbon fixation takes place. 7. The stage of cell respiration that takes in the products of glycolysis and produces two ATP molecules. 9. A small, high-energy molecule that can be used by cells. It is the by-product of glucose breakdown. 10. A series of reactions used by all living things that ...
Where is energy stored in biomolecules like sugars, carbs, lipids, etc.
... What is the first stage of cellular respiration called? ...
... What is the first stage of cellular respiration called? ...
Chapter 9 - John A. Ferguson Senior High School
... the CAC, the acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme Enzymes of CAC: ...
... the CAC, the acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme Enzymes of CAC: ...
Slide 1
... lower center of the diagram.) Probably most important, and placed centrally in this diagram, is carbohydrate metabolism, which will be discussed in detail in the next three lectures. ...
... lower center of the diagram.) Probably most important, and placed centrally in this diagram, is carbohydrate metabolism, which will be discussed in detail in the next three lectures. ...
Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations
... After a balanced meal, the body handles the nutrients as follows. The digestion of carbohydrate yields glucose (and other monosaccharides); some is stored as glycogen, and some is broken down to pyruvate and acetyl CoA to provide energy. The acetyl CoA can then enter the TCA cycle and electron trans ...
... After a balanced meal, the body handles the nutrients as follows. The digestion of carbohydrate yields glucose (and other monosaccharides); some is stored as glycogen, and some is broken down to pyruvate and acetyl CoA to provide energy. The acetyl CoA can then enter the TCA cycle and electron trans ...
BIO 101 Blinderman Mercer County Community College Division of
... 12. Examine cellular location of smooth ER and rough ER and compare synthetic functions of each. 13. Explain why RER is both a membrane factory, a protein modifier, and a maker of vesicles 14. Examine cisternae, and cis and trans faces of the Golgi apparatus. View the Golgi and a protein modifier an ...
... 12. Examine cellular location of smooth ER and rough ER and compare synthetic functions of each. 13. Explain why RER is both a membrane factory, a protein modifier, and a maker of vesicles 14. Examine cisternae, and cis and trans faces of the Golgi apparatus. View the Golgi and a protein modifier an ...
Glyconeogenesis
... • Gluconeogenesis requires both mitochondrial & cytosolic enzymes (exception: if gluconeogenesis starts by Glycerol, it will need only the cytosol) • Gluconeogenesis is an energy consuming. i.e. anabolic process. ...
... • Gluconeogenesis requires both mitochondrial & cytosolic enzymes (exception: if gluconeogenesis starts by Glycerol, it will need only the cytosol) • Gluconeogenesis is an energy consuming. i.e. anabolic process. ...
Alternative ways of monosaccharides metabolism
... • Red blood cells steadily produce lactate • Lactate produced by active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs • The plasma membranes of some cells, particularly cells in cardiac muscle, contain carriers that make them highly permeable to lactate and pyruvate. ...
... • Red blood cells steadily produce lactate • Lactate produced by active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs • The plasma membranes of some cells, particularly cells in cardiac muscle, contain carriers that make them highly permeable to lactate and pyruvate. ...
of Glycolysis
... Regulation of glycolysis • Glycolytic flux is controlled by need for ATP and/or for intermediates formed by the pathway (e.g., for fatty acid synthesis). • Control occurs at sites of irreversible reactions • Hexokinase or glucokinase • Phosphofructokinase‐ major control point; first enzyme “unique ...
... Regulation of glycolysis • Glycolytic flux is controlled by need for ATP and/or for intermediates formed by the pathway (e.g., for fatty acid synthesis). • Control occurs at sites of irreversible reactions • Hexokinase or glucokinase • Phosphofructokinase‐ major control point; first enzyme “unique ...
Communication, Homeostasis
... Helps dehydrogenase enzymes to carry out oxidation reactions Contains 2 ribose sugars, 1 nitrogenous base adenine 2 phosphate groups and a nictinamide molecule. When NAD accepts two hydrogen atoms with their electrons it becomes reduced. NAD operates during Glycolysis, the link reaction, Krebs c ...
... Helps dehydrogenase enzymes to carry out oxidation reactions Contains 2 ribose sugars, 1 nitrogenous base adenine 2 phosphate groups and a nictinamide molecule. When NAD accepts two hydrogen atoms with their electrons it becomes reduced. NAD operates during Glycolysis, the link reaction, Krebs c ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... source will also observe niacin deficiency if niacin uptake is not being watched carefully. • Sorghum contains large amount of leucine, which will inhibit quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRT), an enzyme involved in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. • Vitamin B6 deficiency can also lead to ...
... source will also observe niacin deficiency if niacin uptake is not being watched carefully. • Sorghum contains large amount of leucine, which will inhibit quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRT), an enzyme involved in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. • Vitamin B6 deficiency can also lead to ...
Ecological speciation model
... • Examples: Glucose (C6H12O6): 6O is +6, 12 H's is -6, 6-6=0 Lactate (C3H6O3): 3O is +3, 6H's is -3, 3-3=0 Acetate (C2H4O2): 2O is +2, 4H's is -2, 2-2=0 Glycerol (C3H8O3): 3O is +3, 8 H's is -4, 3-4 = -1 Ethanol (C2H6O): 1O is +1, 6 H is -3, 1-3= -2 Carbon dioxide (CO2): 2 O's = +2 ...
... • Examples: Glucose (C6H12O6): 6O is +6, 12 H's is -6, 6-6=0 Lactate (C3H6O3): 3O is +3, 6H's is -3, 3-3=0 Acetate (C2H4O2): 2O is +2, 4H's is -2, 2-2=0 Glycerol (C3H8O3): 3O is +3, 8 H's is -4, 3-4 = -1 Ethanol (C2H6O): 1O is +1, 6 H is -3, 1-3= -2 Carbon dioxide (CO2): 2 O's = +2 ...
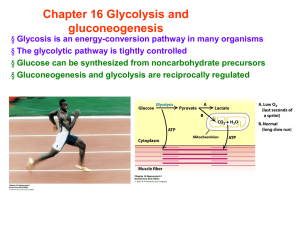
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
Cellular respiration - Jocha
... to NAD+(4) and FAD(1) been processed: (1) all the original C atoms from the glucose have been converted to CO2 2 Pyruvic acid 3 carbons Enzyme 1 (2) all the original H atoms from the glucose have been transferred to NAD+ NADH CO 2 Acetyl CoA 2 carbons or FAD coenzymes ...
... to NAD+(4) and FAD(1) been processed: (1) all the original C atoms from the glucose have been converted to CO2 2 Pyruvic acid 3 carbons Enzyme 1 (2) all the original H atoms from the glucose have been transferred to NAD+ NADH CO 2 Acetyl CoA 2 carbons or FAD coenzymes ...
Cellular-Respiration Student
... Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation • Pyruvate oxidation is a chemical pathway connecting glycolysis in cytoplasm with the Kreb’s cycle in the mitochondrial matrix – The 2 pyruvate molecules must be transported through the two mitochondrial membranes into the matrix ...
... Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation • Pyruvate oxidation is a chemical pathway connecting glycolysis in cytoplasm with the Kreb’s cycle in the mitochondrial matrix – The 2 pyruvate molecules must be transported through the two mitochondrial membranes into the matrix ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.