Fractionation of the isotopes of carbon and hydrogen in biosynthetic
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
11. Archaea and Bacteria
... unsaturated CDP-archaeol with phytanyl or geranylgeranyl chains. An enzyme that reduces double bonds of geranylgeranyl chains bound in phospholipids is found in Archaea [7]. Because the substrate specificity of the enzyme is not so tight, the exact point of reduction (saturation) of unsaturated isop ...
... unsaturated CDP-archaeol with phytanyl or geranylgeranyl chains. An enzyme that reduces double bonds of geranylgeranyl chains bound in phospholipids is found in Archaea [7]. Because the substrate specificity of the enzyme is not so tight, the exact point of reduction (saturation) of unsaturated isop ...
actiona actionation of FFFFFrrrrractiona
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
Genomics Insights esTs from seeds to Assist the selective Breeding
... is catalyzed repeatedly by fatty acid synthase until a C16 fatty acid (palmitate) is synthesized. Fatty acids chains longer than palmitate are formed by elongation reactions catalyzed by enzymes on the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. These reactions add two carbon units (Malo ...
... is catalyzed repeatedly by fatty acid synthase until a C16 fatty acid (palmitate) is synthesized. Fatty acids chains longer than palmitate are formed by elongation reactions catalyzed by enzymes on the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. These reactions add two carbon units (Malo ...
Exploring Yeast as a Cell Factory for the Production of Carboxylic
... time. A number of genetic modifications were then implemented resulting in increased PHB formation, especially in the absence of oxygen, a condition that is desirable in industry since it reduces the need for aeration, and therefore the overall process cost. ix ...
... time. A number of genetic modifications were then implemented resulting in increased PHB formation, especially in the absence of oxygen, a condition that is desirable in industry since it reduces the need for aeration, and therefore the overall process cost. ix ...
The Industrial Age of Biocatalytic Transamination
... A first efficient method for equilibrium displacement was the removal of pyruvate – the co-product formed from the amine donor alanine – by use of a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).[7] The LDH converts the pyruvate into lactic acid at the expense of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). For the recy ...
... A first efficient method for equilibrium displacement was the removal of pyruvate – the co-product formed from the amine donor alanine – by use of a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).[7] The LDH converts the pyruvate into lactic acid at the expense of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). For the recy ...
Fatty acid metabolism in adipose tissue, muscle and liver in health
... at this time, again by the action of insulin. Both the liver and skeletal muscle take up fatty acids largely according to their availability. The rate of removal of plasma NEFA is, under most conditions, fairly closely proportional to their plasma concentration. The removal by the liver of remnant-p ...
... at this time, again by the action of insulin. Both the liver and skeletal muscle take up fatty acids largely according to their availability. The rate of removal of plasma NEFA is, under most conditions, fairly closely proportional to their plasma concentration. The removal by the liver of remnant-p ...
Aromatic Chemistry - heckgrammar.co.uk
... equilibrium constant (Kc) is related to reaction stoichiometry (a, b, c etc) and is a constant at constant temperature the value of Kc is an indicator of the position of equilibrium (reverse reaction = inverse value) the value of Kc is not indicative of how fast the reaction proceeds you must be abl ...
... equilibrium constant (Kc) is related to reaction stoichiometry (a, b, c etc) and is a constant at constant temperature the value of Kc is an indicator of the position of equilibrium (reverse reaction = inverse value) the value of Kc is not indicative of how fast the reaction proceeds you must be abl ...
Full-Text PDF
... which Cu is bound to one amino acid via coordination with its N and O sites, to another amino acid by its carboxylic group, while also interacting with a Cl− ion, derived from NaCl, with Na+ (when occurring with an underpopulated water shell) acting as a dehydration agent. Under such circumstances ( ...
... which Cu is bound to one amino acid via coordination with its N and O sites, to another amino acid by its carboxylic group, while also interacting with a Cl− ion, derived from NaCl, with Na+ (when occurring with an underpopulated water shell) acting as a dehydration agent. Under such circumstances ( ...
phys chapter 78 [2-9
... Insulin has direct effect in promoting amino acid uptake by cells and conversion of amino acids into protein; inhibits breakdown of proteins already in cells Insulin composed of 2 amino acid chains connected by disulfide linkages; when amino acid chains split apart, functional activity of insuli ...
... Insulin has direct effect in promoting amino acid uptake by cells and conversion of amino acids into protein; inhibits breakdown of proteins already in cells Insulin composed of 2 amino acid chains connected by disulfide linkages; when amino acid chains split apart, functional activity of insuli ...
Amino Acid Sequences containing Cysteine or Cystine Residues in
... contaminant was probably ovomucoid which elutes in the earliest fractions from carboxymethy1cellulose columns, and is known to have a high cystine content. No stringent repurification was applied to the samples used for sequence work and no peptide amino acid sequences were found in recovered peptid ...
... contaminant was probably ovomucoid which elutes in the earliest fractions from carboxymethy1cellulose columns, and is known to have a high cystine content. No stringent repurification was applied to the samples used for sequence work and no peptide amino acid sequences were found in recovered peptid ...
Amino acid fluxes to and from seawater in axenic veliger larvae of a
... concentration of 250 nM. Samples (500 111) of the medium were removed from the experimental culture vessels (40 or 50 ml) at various time intervals. These samples were immediately passed through a 0.2 bcm polycarbonate filter held in a Pop-Top 13 mm filter holder (Nuclepore). All filter holders had ...
... concentration of 250 nM. Samples (500 111) of the medium were removed from the experimental culture vessels (40 or 50 ml) at various time intervals. These samples were immediately passed through a 0.2 bcm polycarbonate filter held in a Pop-Top 13 mm filter holder (Nuclepore). All filter holders had ...
A Theoretical Analysis of NADPH Production and
... plant and fungal mitochondria (Palmer & Msller, 1982). The quantitative importance of this process in vivo is unknown. N A DPH-producing processes in yeasts The localization of NADPH-producing processes in the yeast cell is an important parameter since, as mentioned above, most NADPH-consuming proce ...
... plant and fungal mitochondria (Palmer & Msller, 1982). The quantitative importance of this process in vivo is unknown. N A DPH-producing processes in yeasts The localization of NADPH-producing processes in the yeast cell is an important parameter since, as mentioned above, most NADPH-consuming proce ...
DNA and Amino Acid Comparisons
... perfectly. When a mutation occurs, a new allele is created. These mutations are random (can occur at any location along the DNA). The rate of these mutations is relatively constant within a given species. If the mutation occurs in a critical location the result is usually disastrous. Other areas w ...
... perfectly. When a mutation occurs, a new allele is created. These mutations are random (can occur at any location along the DNA). The rate of these mutations is relatively constant within a given species. If the mutation occurs in a critical location the result is usually disastrous. Other areas w ...
Short-Chain-Length Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Synthesis in
... in fed-batch culture [32, 36]. It was proposed by metabolic flux analysis of recombinant E. coli producing P(3HB) that more acetyl-CoA was generated via pyruvate, which were generated by the additional flux of pyruvate formate lyase reaction without any decrease in the flux of pyruvate dehydrogenase ...
... in fed-batch culture [32, 36]. It was proposed by metabolic flux analysis of recombinant E. coli producing P(3HB) that more acetyl-CoA was generated via pyruvate, which were generated by the additional flux of pyruvate formate lyase reaction without any decrease in the flux of pyruvate dehydrogenase ...
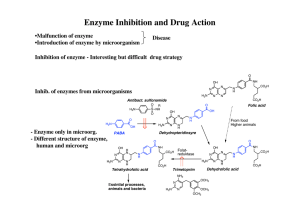
ENZYMES at Lew Port`s Biology Place
... 2. Without enzymes, many of the important processes of life could not happen. Enzymes are very __________ in their functions. Each enzyme has only __________ reaction that it can help. (ANIMATION b) 3. Enzymes are __________ __________ when they perform their function. This means that the same enzym ...
... 2. Without enzymes, many of the important processes of life could not happen. Enzymes are very __________ in their functions. Each enzyme has only __________ reaction that it can help. (ANIMATION b) 3. Enzymes are __________ __________ when they perform their function. This means that the same enzym ...
Science Course Outline Template
... environment, which they cause to become more disordered in consequence. They are essentially an ‘open’ chemical system existing in a steady-state condition and must therefore extract energy, generally as chemical fuel, from their surroundings. Viewed as a machine, they must obey the same thermodynam ...
... environment, which they cause to become more disordered in consequence. They are essentially an ‘open’ chemical system existing in a steady-state condition and must therefore extract energy, generally as chemical fuel, from their surroundings. Viewed as a machine, they must obey the same thermodynam ...
All fatty acids are not equal: discrimination in plant membrane lipids
... been described in seed oils1,2, and it has been estimated that thousands more could be present throughout the plant kingdom. The structures of these fatty acids can vary in chain length from 8 to 24 carbons, they can have double bonds in unusual positions, or novel functional groups, such as hydroxy ...
... been described in seed oils1,2, and it has been estimated that thousands more could be present throughout the plant kingdom. The structures of these fatty acids can vary in chain length from 8 to 24 carbons, they can have double bonds in unusual positions, or novel functional groups, such as hydroxy ...
NAD (H) Linked Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions using Coupled
... zirconium nanoparticles. No detectable activity was observed in either the supernatant or in the particles by adsorption method when enzymes were added to alumina. This suggests that direct contact with the surface of the alumina particles denatures the enzyme completely. Unsuccessful direct couplin ...
... zirconium nanoparticles. No detectable activity was observed in either the supernatant or in the particles by adsorption method when enzymes were added to alumina. This suggests that direct contact with the surface of the alumina particles denatures the enzyme completely. Unsuccessful direct couplin ...
waxes - staging.files.cms.plus.com
... Marine waxes. Many marine animals from invertebrates to whales contain appreciable amounts of waxes in the form mainly of hydrocarbons and wax esters. In addition, glycerol ethers and sterols could be classified as wax components in some species. They are found in a variety of tissues from fish roe, ...
... Marine waxes. Many marine animals from invertebrates to whales contain appreciable amounts of waxes in the form mainly of hydrocarbons and wax esters. In addition, glycerol ethers and sterols could be classified as wax components in some species. They are found in a variety of tissues from fish roe, ...
Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate
... common step in all pyridoxal phosphate catalyzed reactions is the formation of an external aldimine intermediate with the substrate. This occurs through a series of steps in which the unprotonated amino group of the substrate attacks the protonated Schiff base formed between a lysine side chain in t ...
... common step in all pyridoxal phosphate catalyzed reactions is the formation of an external aldimine intermediate with the substrate. This occurs through a series of steps in which the unprotonated amino group of the substrate attacks the protonated Schiff base formed between a lysine side chain in t ...
Compartmentation of the Metabolism of Lactose
... thus preventing the latter from achieving true equilibrium with the compound at all its locations within the cell. Experimentally, the study of compartmentation in living cells presents certain problems arising from the difficulty of distinguishing between several reservoirs of a substance without f ...
... thus preventing the latter from achieving true equilibrium with the compound at all its locations within the cell. Experimentally, the study of compartmentation in living cells presents certain problems arising from the difficulty of distinguishing between several reservoirs of a substance without f ...
Design, Synthesis, and Antibacterial Properties of Dual
... been nothing but beneficial and advantageous to my growth as a scientist. I would also like to thank Dr. Carol Taylor for her understanding, assistance, and help in molding a biologist into an organic chemist. I would also like to thank my other committee members, Dr. Aaron Smith and Dr. David Donze ...
... been nothing but beneficial and advantageous to my growth as a scientist. I would also like to thank Dr. Carol Taylor for her understanding, assistance, and help in molding a biologist into an organic chemist. I would also like to thank my other committee members, Dr. Aaron Smith and Dr. David Donze ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.