Chapter 16
... glycogen phosphorylysis (bond cleavage by the substitution of a phosphate group) and yields glucose-1phosphate (G1P) 2. Glycogen debranching enzyme removes glycogen’s branches, allowing glycogen phosphorylase to complete it’s reactions. 92% of glycogen’s glucose residues are converted to G1P and 8% ...
... glycogen phosphorylysis (bond cleavage by the substitution of a phosphate group) and yields glucose-1phosphate (G1P) 2. Glycogen debranching enzyme removes glycogen’s branches, allowing glycogen phosphorylase to complete it’s reactions. 92% of glycogen’s glucose residues are converted to G1P and 8% ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
... Print your name: _____________________________________________ ...
... Print your name: _____________________________________________ ...
Mechanistic and Computational Studies of Ferroin, Simple Organic
... Belousov, then in his late fifties, was attempting to simulate the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, our primary means of liberating electrons for use in the mitochondrial respiratory chain where their motion provides energy to pump protons against a voltage/concentration gradient as the electrons are ...
... Belousov, then in his late fifties, was attempting to simulate the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, our primary means of liberating electrons for use in the mitochondrial respiratory chain where their motion provides energy to pump protons against a voltage/concentration gradient as the electrons are ...
Research Associate, Dept
... coccidia, C. parvum appears to lack a functional mannitol cycle. In addition, a relict mitochondrion, to which both chaperonin Hsp60 and Hsp70 can be localized, was described. Although the C. parvum mitochondrion is incapable of generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation (Krebs cycle and respirator ...
... coccidia, C. parvum appears to lack a functional mannitol cycle. In addition, a relict mitochondrion, to which both chaperonin Hsp60 and Hsp70 can be localized, was described. Although the C. parvum mitochondrion is incapable of generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation (Krebs cycle and respirator ...
- Wiley Online Library
... YADH-1 has been crystallized, but only preliminary crystallographic studies have been reported [56]. The threedimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase in several binary and ternary complexes with coenzymes, substrates and inhibitors has been solved at high resolution [47]. The tert ...
... YADH-1 has been crystallized, but only preliminary crystallographic studies have been reported [56]. The threedimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase in several binary and ternary complexes with coenzymes, substrates and inhibitors has been solved at high resolution [47]. The tert ...
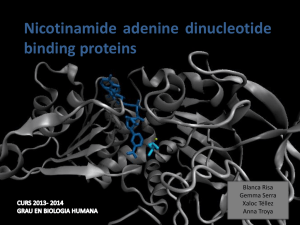
NAD - SBI
... Enzymes that bind nucleotides • Some enzymes require non-protein molecules called cofactors for activity • Nucleotides play a central role in cellular metabolism • Nucleotides can be involved in two different energy transfer processes: • High-energy phosphate bonds in triphosphates: - ATP - GTP • Ox ...
... Enzymes that bind nucleotides • Some enzymes require non-protein molecules called cofactors for activity • Nucleotides play a central role in cellular metabolism • Nucleotides can be involved in two different energy transfer processes: • High-energy phosphate bonds in triphosphates: - ATP - GTP • Ox ...
Module 2. Drug substances of aromatic structure
... D. Phenolphthalein E. *Solution of starch 81. The chemical name of xeroform: A. Oxybenzene B. Dihydroxybenzene C. 3-Methyl-5-methylphenol D. 5-Methyl-2-(methylethyl)phenol E. *Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide 82. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance: A. ...
... D. Phenolphthalein E. *Solution of starch 81. The chemical name of xeroform: A. Oxybenzene B. Dihydroxybenzene C. 3-Methyl-5-methylphenol D. 5-Methyl-2-(methylethyl)phenol E. *Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide 82. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance: A. ...
PRODUCTION OF PYRUVATE AND LACTATE BY
... atom (position 1) on either molecule is an acid or carboxyl group; at the other terminal carbon atom (position 3) is a methyl group. The only difference between the two compounds is that the central carbon atom of pyruvic acid is a keto group while the central carbon atom of lactic acid is a hydroxy ...
... atom (position 1) on either molecule is an acid or carboxyl group; at the other terminal carbon atom (position 3) is a methyl group. The only difference between the two compounds is that the central carbon atom of pyruvic acid is a keto group while the central carbon atom of lactic acid is a hydroxy ...
Fermentation for Liquid-type Yogurt with Lactobacillus casei 911LC
... 2 ml/min and two mobile phases were used: solvent A was 0.05 M sodium acetate (pH 6.3), and solvent B, methanol: Changes in pH and titratable acidity THF (90:10, v/v). The linear gradient of solvent B was Changes in pH during the 72 h fermentation of yogurt programmed at 5 levels as follows: initial ...
... 2 ml/min and two mobile phases were used: solvent A was 0.05 M sodium acetate (pH 6.3), and solvent B, methanol: Changes in pH and titratable acidity THF (90:10, v/v). The linear gradient of solvent B was Changes in pH during the 72 h fermentation of yogurt programmed at 5 levels as follows: initial ...
IEMs Emergency Management
... – violent flexor spasms of limbs and neck muscles. elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
... – violent flexor spasms of limbs and neck muscles. elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
Studies Into the Allosteric Regulation of ADP
... values close to 1, the reaction is essentially irreversible in the forward direction, via Le Chatelier's Principle, in vivo. This is due to the presence of inorganic pyrophosphatases in the cell which breaks down PPi into two component Pi. The reaction is further driven to the ADP-Glc synthesis dire ...
... values close to 1, the reaction is essentially irreversible in the forward direction, via Le Chatelier's Principle, in vivo. This is due to the presence of inorganic pyrophosphatases in the cell which breaks down PPi into two component Pi. The reaction is further driven to the ADP-Glc synthesis dire ...
here - Solve ME/CFS Initiative
... Oxidative stress (both, more in sepsis) Mitochondrial dysfunction at oxidative phosphorylation site (both) Low blood volume (both) Hypometabolism (starvation) Hyperglycemia (starvation) Mitochondria use lipids and amino acids for ATP production Collagen breakdown - POTS, hypermobility, slow gastric ...
... Oxidative stress (both, more in sepsis) Mitochondrial dysfunction at oxidative phosphorylation site (both) Low blood volume (both) Hypometabolism (starvation) Hyperglycemia (starvation) Mitochondria use lipids and amino acids for ATP production Collagen breakdown - POTS, hypermobility, slow gastric ...
A Study of the Effects of Exercise on the Urinary Metabolome
... increased in habitually active male subjects following exhaustive exercise. Allantoin can only be formed non-enzymatically in humans, and it was concluded that uric acid was acting as an antioxidant against reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during exercise. Hence, this could be a useful tool i ...
... increased in habitually active male subjects following exhaustive exercise. Allantoin can only be formed non-enzymatically in humans, and it was concluded that uric acid was acting as an antioxidant against reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during exercise. Hence, this could be a useful tool i ...
- Wiley Online Library
... blocks PEP and pyruvate. Recently, a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was detected which is unique as it functions under strictly anaerobic conditions and has to compete with the overwhelming pyruvate decarboxylase activity while showing similar affinity to pyruvate [39]. A complete TCA cycle is absen ...
... blocks PEP and pyruvate. Recently, a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was detected which is unique as it functions under strictly anaerobic conditions and has to compete with the overwhelming pyruvate decarboxylase activity while showing similar affinity to pyruvate [39]. A complete TCA cycle is absen ...
phospholipids
... Glycolipid synthesis • Synthesis of glycosphingolipids takes place in the ER and Golgi by the sequential addition of sugars by specific glycosyltransferases • The sugars are activated: UDP-Glu, UDP-Gal, CMPNANA ...
... Glycolipid synthesis • Synthesis of glycosphingolipids takes place in the ER and Golgi by the sequential addition of sugars by specific glycosyltransferases • The sugars are activated: UDP-Glu, UDP-Gal, CMPNANA ...
VITAMINS
... Intestinal bacteria and also found in animals. Vitamin K3 (menadione) is synthetic form. All the three vitamin (k1,k2,k3) are naphthoquinone derivatives. Isoprenoid side chain is present in vitamins K1 and k2. The three vitamins are stable to heat. Their activity is, however, lost by oxidizing age ...
... Intestinal bacteria and also found in animals. Vitamin K3 (menadione) is synthetic form. All the three vitamin (k1,k2,k3) are naphthoquinone derivatives. Isoprenoid side chain is present in vitamins K1 and k2. The three vitamins are stable to heat. Their activity is, however, lost by oxidizing age ...
Protein Structure, Neighbor Effect, and a New Index of Amino Acid
... The genetic variation of protein-coding genes represents a major component in genetic biodiversity, and much effort has been spent in understanding how proteins evolve and diversify by amino acid substitutions. Two approaches have been taken to study the pattern of amino acid substitutions. The firs ...
... The genetic variation of protein-coding genes represents a major component in genetic biodiversity, and much effort has been spent in understanding how proteins evolve and diversify by amino acid substitutions. Two approaches have been taken to study the pattern of amino acid substitutions. The firs ...
APPLICATION OF LACTIC ACID BACTERIA TO CONTROL
... inhibit S. Typhimurium effectively. It seemed that the inhibitory activity of LAB against S. Typhimurium was not only due to the organic acids production, but there was also a possibility influence due to a combination effect with H2O2 (Nousianen et al, 2003). 3.3. Antimicrobial-Hydrogen Peroxide Ac ...
... inhibit S. Typhimurium effectively. It seemed that the inhibitory activity of LAB against S. Typhimurium was not only due to the organic acids production, but there was also a possibility influence due to a combination effect with H2O2 (Nousianen et al, 2003). 3.3. Antimicrobial-Hydrogen Peroxide Ac ...
Acetate formation in the photoheterotrophic bacterium Chloroflexus
... involve the classical EM pathway, as concluded from enzyme measurements and genome information (Kondratieva et al., 1992; Tang et al., 2011). However, the enzymes involved in acetate formation have not been analyzed. Here we report that in cell extracts of glucosegrown C. aurantiacus, activities of ...
... involve the classical EM pathway, as concluded from enzyme measurements and genome information (Kondratieva et al., 1992; Tang et al., 2011). However, the enzymes involved in acetate formation have not been analyzed. Here we report that in cell extracts of glucosegrown C. aurantiacus, activities of ...
Protein synthesis 2 - Pima Community College : Directories
... 10.8 The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life – Characteristics of the genetic code – Triplet: Three nucleotides specify one amino acid – 61 codons correspond to amino acids – AUG codes for methionine and signals the start of transcription – 3 “stop” codons signal the end of translation ...
... 10.8 The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life – Characteristics of the genetic code – Triplet: Three nucleotides specify one amino acid – 61 codons correspond to amino acids – AUG codes for methionine and signals the start of transcription – 3 “stop” codons signal the end of translation ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTION
... Calomel, long use in medicine, has the formula Hg2Cl2. What are the oxidation numbers on the atoms in this compound? The rule for assigning oxidation number: No. 4 & 6 4. The oxidation number of any nonmetal in its binary compounds with metals equals the charge of the monatomic anion 6. The sum of t ...
... Calomel, long use in medicine, has the formula Hg2Cl2. What are the oxidation numbers on the atoms in this compound? The rule for assigning oxidation number: No. 4 & 6 4. The oxidation number of any nonmetal in its binary compounds with metals equals the charge of the monatomic anion 6. The sum of t ...
Anaerobic Respiration Using a Complete Oxidative TCA Cycle
... catabolism is the oxidative and nonoxidative PPP, during which NADPH and sugars, such as ribose-5-phosphate, G3P, and fructose-6-phosphate, are interconverted, respectively. Distinct swarming phenotypes were also observed for the PPP (class III); mutations within gnd of the oxidative PPP and talB of ...
... catabolism is the oxidative and nonoxidative PPP, during which NADPH and sugars, such as ribose-5-phosphate, G3P, and fructose-6-phosphate, are interconverted, respectively. Distinct swarming phenotypes were also observed for the PPP (class III); mutations within gnd of the oxidative PPP and talB of ...
Prevention of Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage as a
... membrane potential and a smaller pH gradient, is used by the ATP synthase to make ATP, which is then mostly exported to the cytoplasm to carry out work. Protons can also reenter the mitochondrial matrix through nonspecific leak pathways and via proteins such as uncoupling proteins (UCPs), which may ...
... membrane potential and a smaller pH gradient, is used by the ATP synthase to make ATP, which is then mostly exported to the cytoplasm to carry out work. Protons can also reenter the mitochondrial matrix through nonspecific leak pathways and via proteins such as uncoupling proteins (UCPs), which may ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.