* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 2. Drug substances of aromatic structure
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hydroxide wikipedia , lookup
Hyaluronic acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sulfuric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nitric acid wikipedia , lookup
Acid throwing wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Nitrocellulose wikipedia , lookup
Sodium bicarbonate wikipedia , lookup
Thermometric titration wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hypochlorite wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrochloric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Module 2. Analysis of the quality of drug substances of aromatic structure, which are used as
components of pharmaceuticals.
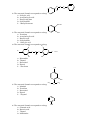
COONa
1. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sodium salicylate
B. Benzoic acid
C. Salicylic acid
D. Sodium acetate
E. *Sodium benzoate
O
C
OH
2. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Acetic acid
B. Salicylic acid
C. Resorcinol
D. Phenol
E. *Benzoic acid
OH
OH
3. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Methanol
B. Xeroform
C. Salicylic acid
D. Phenol
E. *Resorcinol
O
C
ONa
4. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Benzoic acid
B. Salicylic acid
C. Sodium benzoate
D. Sodium acetate
E. *Sodium salicylate
OH
O
OH
NH
C
CH3
5. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Procaine
B. Acetylsalicylic acid
C. Phenyl salicylate
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Paracetamol
O
C
HN
6. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
OH
ÎÍ
B.
C.
D.
E.
Salicylamide
Phenyl salicylate
Salicylanilide
*Oxaphenamide
O
C
HN
7. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Salicylamide
C. Acetylsalicylic acid
D. Phenyl salicylate
E. *Salicylanilide
OH
O
C
NH2
8. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Acetylsalicylic acid
C. Phenyl salicylate
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Salicylamide
OH
O
C
OH
O
9. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Benzyl benzoate
C. Phenyl salicylate
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Acetylsalicylic acid
Ñ
СН3
O
O
C
O
10. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Benzyl benzoate
C. Acetylsalicylic acid
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Phenyl salicylate
C6H5
OH
O
C
O
11. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Acetylsalicylic acid
C. Phenyl salicylate
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Methylsalicylate
OH
CH3
Ñ
O
O
12. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Salicylic acid
B. Acetylsalicylic acid
C. Phenyl salicylate
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Benzyl benzoate
ÑOOH
OH
13. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Xeroform
B. Acetylsalicylic acid
C. Benzoic acid
D. Salicylanilide
E. *Salicylic acid
14. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
Br
Br
Br
O
Bi
Br . Bi2O3
O
OH
Br
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Br
Bismuthite
Thymol
Resorcinol
Phenol
*Xeroform
CH3
OH
15. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Menthol
B. Xeroform
C. Resorcinol
D. Phenol
E. *Thymol
16. The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Glutamic acid
B. Benzoic acid
C. Thymol
D. Methionine
CH3
C
H
OH
CH3
C
H2
E. *Phenol
17. For identification of acetylsalicylic acid chemist used dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. After
boiling and next cooling he added dilute sulphuric acid R. What product of reaction is formed?
A. Smoke
B. Opalescense
C. Green precipitate
D. Brown gas
E. *White precipitate
18. The pharmacopoeial method of assay for benzyl benzoate is back acid-base titration of alkaline
hydrolysis products.What is titrant in this method?
A. Silver nitrate
B. Sodium hydroxyde
C. Potassium hydroxyde
D. Perchloric acid
E. *Chloride acid
19. The physical method, which is used for the analysis of paracetamol, according to Pharmacopoeia, is:
A. Polarimetry
B. Refractometry
C. Tin layer chromatography
D. Gas chromatography
E. *Melting point
20. The method of assay for salicylamide is:
A. Iodometry, direct titration
B. Cerymetry, back titration
C. Permanganatometry
D. Argentometry, back titration
E. *Modified Keldal method
21. Salicylanilide use as agent:
A. Purgative
B. Anaestetic
C. Keratolytic
D. Analgesic and antipyretic
E. *Antibacterial
22. The molar weight of equivalent (Em) at assay of acetylsalicylic acid by means of acidimetry after
saponification alcoholic solution (back titration) equals:
A. М m.
B. М m./4
C. 2М. M.
D. М m./3
E. *М m./2
23. The chemical name of benzyl benzoate is:
A. 2-(Acetoxy)benzoic acid
B. o-Hydroxybenzamide
C. Phenylsalicylamide
D. p-Oxyphenylsalicylamide
E. *Phenylmethyl benzoate
24. The initial substance for synthesis oxaphenamide is:
A. Pyrogalol
B. Toluene
C. Resorcinol
D. Phenol
E. *Phenyl salicylate
25. Phenolic hydroxyl in paracetamol molecule it is possible to identify by means reactions with:
A. FeCl3, CuSO4
B. AgNO3, HNO3
C. FeCl2, KCl
D. HCl, NaNO3
E. *FeCl3, diazonium salts
26. What titrant can be used for assay of paracetamol by means of nitritometry (direct titration)?
A. Nitric acid
B. Sodium nitrite in the alkaline medium
C. Chloride acid
D. Sodium chloride
E. *Sodium nitrite in the acid medium
27. The Pharmacopoeial method of assay for definition methyl salicylate is:
A. Nitritometry
B. Permanganatometry
C. Iodometry
D. Alkalimetry after alkaline hydrolysis
E. *Acidimetry after preliminary alkaline hydrolysis
28. Methyl salicylate can be synthesed by means of boiling in the presence of sulphatic acid:
A. Sodium benzoate with ethane
B. Sodium salicylate with methane
C. Resorcinil with ethanol
D. Benzoic acids with methanol
E. *Salicylic acid with methanol
29. What can be observed the chemist-analyst at addition to alcoholic solution of phenyl salicylate
solution iron (ІІІ) chloride FeCl3?
A. White smoke
B. Green solution
C. White precipitate
D. Allocation of poisoning gas
E. *Violet colouring of solution
30. Under the description salicylanilide represents:
A. White, crystalline powder or small, colourless crystals or shiny flakes
B. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
C. White, crystalline powder or white or colourless, acicular crystals
D. White, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, odourless or with a very slight
characteristic odour
E. *White or yellowish crystal powder, baking taste.
31. What functional groups are available in a molecule salicylamide?
A. Keto-group, amide group
B. Integrally connected chlorine
C. Alcoholic hydroxyl, amino group
D. Amino group, benzene cycle
E. *Amide group, phenolic hydroxyl
32. Assay of acetylsalicylic acid, according to Pharmacopoeia, makes by means of such method:
A. Alkalimetry, back titration
B. Argentometry
C. Acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration
D. Alkalimetry in alcoholic solution, direct titration
E. *Acidimetry, after saponification alcoholic solution, back titration
33. The initial substances for synthesis benzyl benzoate is:
A. Pyrogalol
B. Toluene
C. Resorcinol
D. Phenol
E. *Sodium benzoate
34. Paracetamol in medical practice apply as means:
A. Purgative
B. Antimicrobial preservative
C. Keratolytic
D. Expectorant
E. *Analgesic and antipyretic.
35. The chemical name of oxaphenamide:
A. Phenylmethyl benzoate
B. Phenyl ester 2-oxybenzoic acid
C. Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate
D. p-Acetaminophenol
E. *p-Oxyphenylsalicylamide
36. In the medical practice the benzoic acid use as agent:
A. Purgative
B. Anti-inflammatory; analgesic
C. Keratolytic
D. Expectorant
E. *Antimicrobial preservative
37. What indicator must be used, according to Pharmacopoeia, for assay of sodium benzoate in the
method of acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration?
A. Any
B. Methyl orange
C. Phenolphthalein
D. Phenol red solution
E. *Naphtholbenzein solution
38. What pharmacopoeial method of assay for salicylic acid?
A. Acidimetry, non-aqueous back titration
B. Argentometry
C. Acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration
D. Alkalimetry, back titration
E. *Alkalimetry in alcoholic solution, direct titration
39. For identification of sodium benzoate the chemist-analyst makes sublimation of dug (some crystals
of the crushed drug moisten with sulphatic acid R, cautiously heat up a test tube bottom). What
he observed?
A. Smoke
B. Opalescense
C. Green precipitate
D. Brown gas
E. *White scurf
40. At decarboxylation of salicylic acid (heating with concentrated sulphatic acid) chemist-analyst
observed allocation of gas bubles. What gas allocated?
A. Hydrogen
B. Sulphur dioxide
C. Carbon oxide
D. Oxygen
E. *Carbon dioxide
41. For identification of benzoic acid the chemist-analyst, according to Pharmacopoeia, uses reaction
with:
A. Perchloric acid
B. Potassium hydroxyde
C. Nitric acid
D. Wine acid
E. *Iron (ІІІ) chloride
42. For identification of ions of Sodium in sodium benzoate the chemist-analyst can use reaction with:
A. Iron (ІІІ) chloride
B. Potassium hydroxyde
C. Wine acid
D. Silver nitrate
E. *Methoxyphenylacetic acid reagent
43. Under the description sodium salicylate is:
A. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
B. Black crystalline powder, acicular crystals
C. Green crystalline or granular powder or flakes
D. Colourless crystals, odourless or with a very slight characteristic odour
E. *White, crystalline powder or small, colourless crystals or shiny flakes
44. The initial substance for synthesis of sodium benzoate is:
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Toluene
C. Salicylic acid
D. Phenol
E. *Benzoic acid
45. The chemical name of salicylic acid:
A. Oxybenzene
B. Sodium benzenecarboxylate
C. Benzenecarboxylic acid
D. 2-Methyloxybenzenecarboxylic acid
E. *2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid
46. In the medical practice sodium benzoate use as means:
A. Purgative
B. Anti-inflammatory; analgesic
C. Keratolytic
D. Antimicrobial preservative
E. *Expectorant
47. The equivalent weight (Em) at assay of salicylic acid by means of alkalimetry in alcoholic solution
is:
М m./2
М m./3
М m./4
2М. M.
*М m.
48. Pharmacopoeial method of assay for sodium benzoate is acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration.
What titrant in this method?
A. Silver nitrate
B. Sodium thiosulphate
C. Potassium bromate
D. Chloride acid
E. *Perchloric acid
49. What formed at interaction sodium salicylate with chloride acid?
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Phenol
C. Benzoic acid
D. Toluene
E. *Salicylic acid
50. For identification of benzoic acid the chemist-analyst can uses reaction with:
A. Potassium hydroxyde
B. Wine acid
C. Sodium carbonate
D. Perchloric acid
E. *Silver nitrate
51. For identification of salicylic acid the chemist-analyst can uses reaction with:
A. Perchloric acid
B. Potassium hydroxyde
C. Wine acid
D. Sodium carbonate
E. *Iron (ІІІ) chloride
52. For identification of Sodium ions in sodium benzoate the chemist-analyst used pyrochemical
reaction. What colour of flame he observed?
A. White
B. Green
C. Yellow
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
D. Violet
E. *Brown
53. Under the description salicylic acid represents:
A. White, crystalline powder or small, colourless crystals or shiny flakes
B. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
C. White, crystalline or granular powder or flakes
D. White, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, odourless or with a very slight
characteristic odour
E. *White, crystalline powder or white or colourless, acicular crystals
54. The initial substance for synthesis of benzoic acid is:
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Benzoic acid
C. Salicylic acid
D. Phenol
E. *Toluene
55. The chemical name of sodium salicylate:
A. Sodium benzenecarboxylate
B. Benzenecarboxylic acid
C. 2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid
D. Oxybenzene
E. *2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylate
56. In the medical practice salicylic acid use as means:
A. Purgative
B. Anti-inflammatory; analgesic
C. Expectorant
D. Antimicrobial preservative
E. *Keratolytic
57. What indicator must be used, according to Pharmacopoeia, for assay of sodium benzoate in the
method of acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration?
A. Methyl orange
B. Phenolphthalein
C. Naphtholbenzein solution
D. Phenol red solution
E. *Determining the end-point potentiometrically
58. What pharmacopoeial method of assay for sodium benzoate?
A. Alkalimetry, back titration
B. Acidimetry, non-aqueous back titration
C. Argentometry
D. Alkalimetry in alcoholic solution, direct titration
E. *Acidimetry, non-aqueous direct titration
59. For identification of salicylic acid the chemist-analyst makes reaction formation of aurin dye. He
must used such reagents:
A. Potassium hydroxide and silver nitrate
B. Iron (ІІІ) chloride and bromine water
C. Solution of sodium carbonate and chloride acid
D. Perchloric acid and nitric acid
E. *Solution of formaldehyde in sulphatic acid concentrated
60. At decarboxylation of salicylic acid (heating above 160°C with sodium carbonate) is formed:
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Toluene
C. Benzoic acid
D. Sodium salicylate
E. *Phenol
61. For identification of sodium benzoate acid the chemist-analyst can uses reaction with:
A. Wine acid
B. Potassium hydroxyde
C. Sodium carbonate
D. Perchloric acid
E. *Iron (ІІІ) chloride
62. For identification of ions of Sodium in sodium benzoate the chemist-analyst can use reaction with:
A. Potassium hydroxyde
B. Iron (ІІІ) chloride
C. Silver nitrate
D. Wine acid
E. *Potassium hexahydroxostibat
63. Under the description the benzoic acid is:
A. Colourless liquid
B. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
C. Colourless crystalline powder, acicular crystals
D. White, crystalline or granular powder or flakes
E. *White, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, odourless or with a very slight
characteristic odour
64. The initial substance for synthesis of sodium salicylate is:
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Toluene
C. Benzoic acid
D. Phenol
E. *Salicylic acid
65. The chemical name of sodium benzoate is:
A. Oxybenzene
B. 2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylate
C. Benzenecarboxylic acid
D. 2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid
E. *Sodium benzenecarboxylate
66. In the medical practice sodium salicylate use as means:
A. Purgative
B. Keratolytic
C. Expectorant
D. Antimicrobial preservative
E. *Anti-inflammatory; analgesic
67. The molar weight of equivalent (Em) at assay of benzoic acid by means of alkalimetry in alcoholic
solution equals:
A. М m./3
B. М m./4
C. 2М. M.
D. М m./2
E. *М m.
68. The pharmacopoeial method of assay for sodium salicylate is acidimetry, non-aqueous direct
titration. What titrant in this method?
A. Silver nitrate
B. Sodium thiosulphate
C. Potassium bromate
D. Chloride acid
E. *Perchloric acid
69. For identification of benzoic acid the chemist-analyst used solution of silver nitrate. What colour of
formed precipitate he observed?
A. Brown
B. Green
C. Yellow
D. Violet
E. *White
70. What formed at interaction of sodium benzoate with chloride acid:
A. Pyrocatechol
B. Toluene
C. Sodium salicylate
D. Phenol
E. *Benzoic acid
71. For identification of sodium salicylate acid the chemist-analyst can uses reaction with:
A. Potassium hydroxyde
B. Wine acid
C. Sodium carbonate
D. Perchloric acid
E. *Iron (ІІІ) chloride
72. For identification of ions of Sodium in sodium salicylate the chemist-analyst can use reaction with:
A. Iron (ІІІ) chloride
B. Potassium hydroxyde
C. Silver nitrate
D. Wine acid
E. *Methoxyphenylacetic acid reagent
73. Under the description sodium benzoate represents:
A. Grey crystalline powder
B. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
C. Red crystalline powder, acicular crystals
D. Blue crystalline powder, odourless or with a very slight characteristic odour
E. *White, crystalline or granular powder or flakes
74. The initial substance for synthesis of salicylic acid is:
A. Pyrogalol
B. Toluene
C. Benzoic acid
D. Resorcinol
E. *Phenol
75. The chemical name of benzoic acid:
A. Oxybenzene
B. 2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylate
C. 2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid
D. Sodium benzenecarboxylate
E. *Benzenecarboxylic acid
76. For identification of xeroform the chemist-analyst can use reaction with:
A. Barium sulphate
B. Tartaric acid
C. Silver nitrate
D. Chloroform in the alkaline medium
E. *Solution of sodium sulphide in chloride-acid medium
77. The molar weight of equivalent (Em) at assay of thymol (by means of bromatometry, direct titration)
equals:
A. М m.
B. М m./3
C. 2М. M.
D. М m./2
E. *М m./4
78. In medical to practice phenol use as means:
A. Antiseptic, disinfectant and vermicidal agent
B. Keratolytic.
C. Astringent, drying and antiseptic
D. Antiseptic, drying, expectorant
E. *Antiseptic; antimicrobial preservative; antipruritic
79. For identification of resorcinol, according to Pharmacopoeia, expert of Quality Department of the
pharmaceutical enterprise uses reaction with solution:
A. Calcium chloride
B. Copper sulphate in the alkaline medium
C. Sulphate barium
D. Silver nitrate in the acid medium
E. *Potassium hydrogen phthalate in the alkaline medium
80. For assay of phenol the chemist-analyst uses a method of bromatometry, back titration with
iodometric finishing. What indicator he used:
A. Methyl orange
B. Tropeolin 00
C. Methyl red
D. Phenolphthalein
E. *Solution of starch
81. The chemical name of xeroform:
A. Oxybenzene
B. Dihydroxybenzene
C. 3-Methyl-5-methylphenol
D. 5-Methyl-2-(methylethyl)phenol
E. *Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide
82. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance:
A. Phenylsalicylate
B. Phthalic acid
C. Benzol
D. Phenol
E. *3-Metylphenol (m-cresol)
83. For assay of resorcinol, according to Pharmacopoeia, use method:
A. Cerymetry, direct titration
B. Iodometry, direct titration
C. Chelatometry, back titration
D. Bromatometry, direct titration
E. *Bromathometry, back titration with iodometric finishing
84. According to Pharmacopoeia, the resorcinol is:
A. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
B. Colourless crystals
C. Colourless or faintly pink or faintly yellowish crystals or crystalline masses
D. Crystalline powder of yellow colour
E. *Colourless or slightly pinkish-grey, crystalline powder or crystals, turning red on exposure
to light and air
85. What titrant you must use for assay of xeroform in the chelatometry, direct titration?
A. Sodium thiosulphate
B. Potassium bromate
C. Chloride acid
D. Silver nitrate
E. *Sodium EDTA
86. Pharmacopoeial method of assay for phenol is bromathometry, back titration with iodometric
finishing. What titrant you must add in buret?
A. Potassium bromide
B. Potassium bromate
C. Silver nitrate
D. Chloride acid
E. *Sodium thiosulphate
87. For identification of resorcinol the chemist-analyst can use reaction with:
A. Copper chloride
B. Barium sulphate
C. Tartaric acid
D. Silver nitrate
E. *Chloroform in the alkaline medium
88. Under the description phenol represents:
A. Colourless crystals
B. Amorphous substance of yellow colour with specific smell
C. Colourless or slightly pinkish-grey, crystalline powder or crystals, turning red on exposure
to light and air
D. Crystalline powder of yellow colour
E. *Colourless or faintly pink or faintly yellowish crystals or crystalline masses
89. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance:
A. Phenylsalicylate
B. Phthalic acid
C. Benzol
D. Phenol
E. *m-Cresol
90. The molar weight of equivalent (Em) at assay (chelatometry) of xeroform equals:
A. М m.
B. М m./3
C. М m./4
D. 2М. M.
E. *М m./2
91. In the medical to practice xeroformium use as means:
A. Antiseptic, disinfectant and vermicidal agent
B. Keratolytic
C. Antiseptic; antimicrobial preservative; antipruritic
D. Antiseptic, drying, expectorant
E. *Astringent, drying and antiseptic
92. The chemical name of thymol:
A. Oxybenzene
B. m-Dihydroxybenzene
C. Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide
D. 3-Methyl-5-methylphenol
E. *5-Methyl-2-(methylethyl)phenol
93. For identification of phenolic hydroxyl, as chemical component structure of many drugs, can be used
reaction with:
A. Phenylhydrazine
B. Chloride acid
C. Ninhydrin
D. Nitric acid
E. *Lime chloride or bromine water in the presence of ammonia
94. The bromatometric definition of the phenols derivatives (phenol, resorcinol, etc.) is based on
reaction:
A. Reduction
B. Elimination
C. Addition
D. Oxydation
E. *Substitution
95. In the control-analytical laboratory makes limit tests for pyrocatechol in the resorcinol. To solution S
(water solution of resorcinol) add solution of (NH4)2MoO4 and shake up. What analytical effect
of reaction?
A. Green
B. Red
C. Blue
D. White
E. *Yellow
Ag
H 2N
96.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfadimethoxine
B. Sulfathiazole
C. Salazodimethoxine
D. *Silver sulfadiazine
SO
2
N
N
N
E. Sulfacetamide sodium
Í
H2N
97.
N
N
N
SO2
OCH3
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. Salazodimethoxine
D. Phthalylsulfathiazole
E. *Sulfapyridazine
Na N
SO2N
H2N
98.
S
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfadimethoxine
B. Sulfathiazole
C. Sulfacetamide sodium
D. Salazodimethoxine
E. *Sulfathiazole sodium
OH
HOOC
OCH3
H
N
N
99.
SO2
N
N
N
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfadimethoxine
C. *Salazodimethoxine
D. Sulfadimethoxine
E. Phthalylsulfathiazole
OCH3
H
O
C
HN
N
N
SO2
S
100.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfadimezine
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. Sulfadimethoxine
D. Sulfanilamidopyrimidine
E. *Phthalylsulfathiazole
COOH
OCH3
H
H2N
101.
102.
SO2
N
N
N
OCH3
The structural formulacorresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfaguanidine
B. *Sulfadimethoxine
C. Sulfanilamidopyrimidine
D. Sulfathiazole
E. Sulfacetamide sodium
Pyridine cycle in a molecule of nikethamide it is possible to identify by means of such reagents:
A. *2,4-dinitrochlorbenzole, ethanol, sodium hydroxide solution
B. Silver nitrate, nitric acid
C. Ethylacetic ether, benzene
D. Methoxiphenylacetatic acid, tetramethylammonium hidroxyde
E. Zinc chloride, sulphatic acid
H
H2N
103.
SO2
N
N
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfadimethoxine
C. *Sulfanilamidopyrimidine
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Sulfacarbamide
N
N
H2N
104.
105.
SO2
N
H
S
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. *Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. Streptocide
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Sulfacarbamide
The structural formulacorresponds to a
O
H2N
SO2
NH
C
NH2
.
H 2O
drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. Streptocide
D. Sulfadimezine
E. *Sulfacarbamide
NH
H2N
106.
SO2
N
H
NH2 .
C
The structural formulacorresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. *Sulfaguanidine
C. Streptocide
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Phthalazole
O
H2N
107.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. *Streptocide soluble
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Phthalazole
N
Na
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. *Sulfacetamide sodium
C. Streptocide soluble
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Phthalazole
NaO3S
108.
SO2
C
H2
N
H
C
.
CH3
SO2NH2
H 2O
H 2O
H2N
109.
110.
SO2NH2
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaguanidine
C. *Streptocide
D. Sulfadimezine
E. Phthalazole
The structural formula corresponds to a
Cl
O
C
O
H
N
H2
C
H2
C
S
O
H
N
H
N
C
O
OCH
drug:
A. Chloramine
B. Carbutamide
C. *Glibenclamide
D. Chlorpropamide
E. Tolbutamide
In the medical practice phthivazid use as agent:
A. Anaesthetic
B. Helminthicide
C. Purgative
D. Expectorant
E. *Antituberculous
3
111.
H
H3C
112.
SO2 NH
O
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Chloramine
B. Chloralhydrate
C. Pantosept
D. Chlorpropamide
E. *Tolbutamide
Cl
113.
SO2
NH
C
O
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Chloramine
B. Chloralhydrate
C. Pantosept
D. *Chlorpropamide
E. Tolbutamide
O
Cl
C
114.
C
The structural formula corresponds to a drug: HO
A. Chloramine
B. Chloralhydrate
C. *Pantosept
D. Ibuprofen
E. Toluene
SO2
N
Cl
N
C4H9
NH
C3H7
O
ONa
S
NCl
. 3H2O
115.
CH3
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. *Chloramine
B. Chloralhydrate
C. Pantosept
D. Ibuprofen
E. Toluene
O
H2
C
C
ONa
Cl
HN
116.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. *Diclofenac sodium
B. Anthranilic acid
C. Mefenamic acid
D. Sodium salicylate
E. Sodium benzoate
Cl
O
C
OH
N
H
117.
H3C
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Anthranilic acid
B. *Mefenamic acid
C. 2-Amonobenzoic acid
D. Lidocaine
E. Benzocaine
CH3
H3C
O
CH
118.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Diclofenac sodium
B. Mefenamic acid
C. o-Amonobenzoic acid
D. *Ibuprofen
E. Articaine hydrochloride
H
C
C
H2
H3C
CH3
H3C
N
H
O
CH3
C
C
H
O
S
119.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
C
C
O
CH3
N
H
OH
C3H7 . HCl
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Procainamide hydrochloride
*Articaine hydrochloride
Tetracaine hydrochloride
Benzocaine
Procaine hydrochloride
CH3
H3C
CH3
HN
120.
C
C
H2
N
C2H5
O
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Lidocaine hydrochloride
B. Articaine hydrochloride
C. Tetracaine hydrochloride
D. *Trimecaine hydrochloride
E. Procaine hydrochloride
C2H5
. HCl
CH3
O
N
H
121.
122.
H2N
C
C
C
H2
N
.
HCl
C2H5
CH3
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. *Lidocaine hydrochloride
B. Articaine hydrochloride
C. Tetracaine hydrochloride
D. Benzocaine
E. Procaine hydrochloride
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
O
C2H5
C2H5
N
H
C
H2
C
H2
HCl
.
N
C2H5
*Procainamide hydrochloride
Articaine hydrochloride
Tetracaine hydrochloride
Benzocaine
Procaine hydrochloride
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
123.
O
C4H9
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
N
H
C
CH3
O
C
H2
C
H2
.
N
HCl
CH3
Procainamide hydrochloride
Articaine hydrochloride
*Tetracaine hydrochloride
Benzocaine
Procaine hydrochloride
O
H2N
C
O
124.
The structural formulacorresponds to a drug:
A. Procainamide hydrochloride
B. Articaine hydrochloride
C. Tetracaine hydrochloride
H2
C
H2
C
C2H5
N
*HCl
C2H5
D. Benzocaine
E. *Procaine hydrochloride
O
H2N
C
O
C2H5
125.
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Mefenamic acid
B. Ibuprofen
C. Trimecaine hydrochloride
D. *Benzocaine
E. Procaine hydrochloride
126.
What reaction can be used for identification aromatic cycle in the molecule structure of
phthalylsulfathiazole?
A. Acetylation
B. Hydration
C. *Halogenation
D. Reduction
E. Oxidation
What external indicator can be used for assay of sulfadimezine by means of nitritometry?
A. Starch solution
B. Lead paper
C. *Potassium iodide test paper
D. Universal litmus paper
E. Litmus paper
What method of assay can be used for sulfathiazole sodium?
A. Chelatometry
B. Cerimetry
C. *Alkalimetry in the presence of alcohol
D. Acidimetry in the presence of alcohol
E. Iodometry
For identification of a primary aromatic amino group, as chemical compound structure of
Sulfametoxazolum (part of Biseptolum), the chemist can used reaction with:
A. Solution of sodium nitrate, chloride acid
B. Chloride acid concentrated.
C. *Solution of sodium nitrite, chloride acid, naphthol alkaline solution
D. Reagent Zoneshtein
E. Chloramine or lime chlorine in the presence of ammonia
The pharmacist-analyst makes assay for Trimethoprimum (the part of Biseptolum) by means of
Keldal method. The molecular weight of equivalent (Em) of preparation is:
A. M. m./3
B. *M. m./4
C. M.m.
D. M.m./2
E. M. m./6
The products of acid hydrolysis for sulfacetamide sodium is:
A. p-Aminotoluene, urea, sodium carbonate
B. p-Aminobenzene, sulfanilic acid, sodium
C. Toluene, sulphatic acid, sodium acetate
D. Benzene, ammonia, sodium hydroxide
E. *p-Aminobenzenesulphamide, sodium hydrosulphate
The specific impurity in the preparation of streptocide soluble is:
A. Potassium sulphate
B. *Sodium sulphite
C. Hlorides
D. Sulfate ashes
E. Heavy metals
127.
128.
129.
130.
131.
132.
133.
134.
135.
136.
Presence of Sulfur in the sulfamide group of salazodimethoxine define after its previous:
A. Decomposition
B. Esterification
C. Alkalis hydrolysis
D. Acid hydrolysis
E. *Melting with КNO3
Action and use of sulfadimethoxine is:
A. Antibacterial incontinuous action
B. *Antibacterial with long action
C. Anaesthetic
D. Antypiretic
E. Antiseptic
The pharmacist-analyst makes identification of substance salazodimethoxine by means of such
reagents:
A. Bromine water
B. Sodium hydroxide solution, sulphatic acid
C. Chloramine solution, chloroform
D. Solution of sodium nitroprusside, sodium hydroxide
E. *Solution of nitrite sodium, chloride acid, naphthol alkaline solution after preparation
hydrolysis
The pharmacological action sulfadimidine is in the:
A. The big molecular weight
B. *The theory of competitive antagonism
C. Substance transition in other condition
D. Principle “phenacetinum”
E. Principle “salol”
O
C
NH
N
CH
.
OH H2O
OCH3
137.
138.
139.
140.
141.
N
The structural formulacorresponds to a drug:
A. Flurinizidum
B. Nicodine
C. Isoniasid
D. *Phthivazid
E. Nikethamide
The pharmacist-analyst used for assay of sulfadimezine iodochlorometry. Molar weight of
equivalent (Em) of a preparation is:
A. M. m./3
B. M. m.
C. M.m./2
D. M. m./6
E. *M. m./4
Sulfathiazole sodium it is possible to distinguish from sulfathiazole by means of reactions for:
A. Sulphate-ions
B. Benzene ring
C. Thiazole cycle
D. Primary aromatic amino group
E. *Sodium-ions
Sulfathiazole sodium do not use in the form:
A. Powder
B. Injection solutions
C. Inhalypt
D. Ophthalmic drops
E. *Pills
The chemical name of a preparation Sulfathiazole is:
Sodium 2 (p-aminobenzolsulfamide)-thiazole
2 (p-Aminobenzolsulfamide)-pyrimidine
*2 (p-Aminobenzolsulfamide)-thiazole
p-Aminobenzene sulfonamide
Sodium p-aminobenzolsulphonylacetamide hydrate
For assay of trimethoprimum (part of Biseptolum) it is possible to use such method:
A. Iodochlorometry
B. *Keldal
C. Iodometry
D. Gravimetry
E. Alkalimetry
The chemical name of salazodimethoxine is:
A. 3-Diethylaminomethylamide p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
B. *5 {p - [(2,4-dimethoxypyrimidinyl-6)-sulfamide]-phenylazo}-salicylic acid
C. Ethyl ester p-aminobenzoic acid
D. 5 (p - [N - (3-Methoxypyridazinil-6)-sulfamido] phenylazo)-salicylic acid
E. Diethylamino-2,4,6-trimethylacetanilide hydrochloride
For identification of a primary aromatic amino group, which is included into structure
Sulfametoxazolum (a component of Biseptolum), can be used reaction with such reagent:
A. Solution of nitrite sodium, chloride acid
B. Chloride acid
C. Chloramine in the presence of ammonia
D. Zonenshtein reagent
E. *Solution of p-aminobenzaldehyde
The pharmacist-analyst makes assay of salazodimethoxine by means of bromatometry. The
molecular weight of equivalent (Em) of preparation is:
A. M. m./3
B. *M. m./4
C. M.m./2
D. M.m.
E. M. m./6
The chemical name of salazodimethoxine is:
A. 6-( p-Aminobenzenesulfamide)-1,4- dimethoxypyrimidine
B. 6-( p-Aminobenzenesulfamide)-2,5- dimethoxypyrimidine
C. 5-(p-Aminobenzenesulfamide)-2,4-dimethoxypyrimidine
D. 6-(Benzenesulfamide)-2,4-dimethoxy-pyrimidine
E. *6-(p-Aminobenzenesulfamide)-2,4-dime-thoxypyrimidine
What functional group is not presence in molecule of sulfadimethoxine?
A. Pyrimidine cycle
B. Sulfamide group
C. Methoxy-radical
D. Primary aromatic amino group
E. *Alcohol hydroxyl
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
142.
143.
144.
145.
146.
147.
O
HN
C 2H 5
N
C 2H 5
O
148.
149.
H
O
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Phenobarbital
B. Hexenal
C. Thiopental sodium
D. *Barbital
E. Barbamyl
The one of initial substances for sulfadimezine synthesis is:
A. Guanidine
Acetic acid
*N-Carbomethoxyaniline
Toluene
Resorcinol
For identification of the phthalic acid rest in the molecule of phthalylsulfathiazole it is possible
to use reagents:
A. NaNO2, KCl and naphthol solution
B. Chloramine or lime chlorine, ammonia solution
C. NaNO2, HCl and naphthol solution
D. *Resorcinol, concentrated H2SO4, NaOH
E. NaNO2, HCl
What method of assay for sulfathiazole sodium is not possible?
A. Nitritometry
B. Keldal
C. Gravimetry
D. Acidimetry
E. *Alkalimetry
The chemical name 4-amino-N-(thiazol-2-yl)benzenesulphonamide is for such sulfanilamide:
A. Salazodimethoxine
B. Phthalylsulfathiazole
C. Sulfadimezine
D. *Sulfathiazole
E. Sulfanilamide
The specific impurities are in such preparation:
A. Sulfathiazole
B. Sulfaquanidine
C. Sulfadimethoxine
D. Sulfanilamide
E. *Phthalylsulfathiazole
Unlike sulfathiazole, sulfathiazole sodium:
A. Insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol
B. Soluble in alkalis
C. Soluble in acids and alkalis
D. Slightly soluble in water and alcohol
E. *Freely soluble in water
For identification of thiazole cycle in the sulfathiazole the pharmacist-analyst used reaction with
such solution:
A. Sodim nitrite in the medium of HCl
B. Silver nitrate in the medium of HNO3
C. Silver nitrate in the medium of HNO3 after a preparation mineralization
D. *Barium chloride in the medium of HCl after a preparation mineralization
E. Barium chloride in the medium of HCl
For revealing of Sulphur in the sulfaguanidine molecule is necessary oxidizes preparation by
means of concentrated HNO3. What reagent use for identification of this element?
A. Copper chloride
B. *Barium chloride
C. Sodium hydroxide
D. Lead acetate
E. Silver nitrate
Sulfacarbamide is soluble in alkalis because in its molecule is:
A. Organo-fixed Sulphur
B. Benzene cycle
C. *Sulfamide group
D. Aromatic amino group
E. The urea rest
What reagent is necessary to distinguish sulfacarbamide from others sulfanilamides:
A. Sulphatic acid
B.
C.
D.
E.
150.
151.
152.
153.
154.
155.
156.
157.
158.
Ammonia solution
*5 % Sodium nitrite solution
Chloride acid
Alkaline solution of naphthol
Sulfaquanidine in medical practice used for treatment:
A. Tuberculosis
B. *Intestinal infections
C. Sharp respiratory diseases
D. Meningitis
E. Syphilis
For assay of sulfacetamide sodium can be used such method:
A. Mercurimetry
B. Permanganatometry
C. Alkalimetry
D. Complexometry
B.
C.
D.
E.
159.
160.
E. *Acidimetry
161.
162.
163.
164.
165.
166.
167.
The chemical name of sulfacarbamide is:
A. 2-(p-Aminobenzenesulfamide)-thiazole
B. p-Aminobenzenesulamide
C. p-Aminobenzenesulfonilacetamide
D. *p-Aminobenzenesulfonilcarbamide
E. p-Aminobenzenesulfonilguanidine
The method of assay for barbital is:
A. Coppermetry
B. Permanganatometry
C. Ceriumetry
D. *Alkalimetry, non-aqueous titration
E. Chelatometry
The chemical name sodium p-sulfamidobenzolamino methylenesulphonate is for preparation:
A. Sulfanilamide
B. Sulfathiazole
C. *Streptocide soluble
D. Phthalylsulfathiazole
E. Sulfacetamide sodium
Sulfanilamide freely soluble in the:
A. *Boiling water
B. Diluted HCl
C. Alkali
D. Acetone
E. Water
What of sulfanilamides has the chemical name - sodium derivative of N-[(4aminophenyl)sulphonyl]acetamide?
A. Sulfacarbamide
B. Sulfathiazole
C. Sulfanilamide
D. Phthalylsulfathiazole
E. *Sulfacetamide sodium
The chemist has spent heating of streptocide soluble with the concentrated sulfuric acid in the
presence of salicylic acid. What colour the solution will turn out?
A. Violet
B. Blue
C. *Crimson
D. Green
E. Colourless
The most rational and economical method of synthesis all amides of sulfanilic acid are synthesis
from:
*N-carbomethoxyaniline
Urea
Ammonia
Methane
Anthraquinone
The chemist-laboratorian makes pyrochemical reaction for sulfacetamide sodium. What colour
of flame he observes?
A. Green
B. Pink
C. Dark blue
D. Violet
E. *Yellow
The initial substance for synthesis all amides of sulfanilic acid is:
A. N-Carbomethoxyaniline
B. Urea
C. *Sulfanilic acid
D. p-Sulfamidebenzeneaminemethane
E. Antrahinon
The pharmacist-analyst for assay of sulfacarbamide used nitritometry. Molar weight of
equivalent (Em) of preparation is:
A. M.m./3
B. M.m./4
C. *M.m.
D. M.m./2
E. M.m./6
At alkaline hydrolysis sulfaguanidine it is allocated:
A. *Ammonia
B. Sulphurous gas
C. Hydrogen sulphide
D. Carbon dioxide
E. Aniline
(4-Aminophenylsulphonyl)guanidine is the chemical name of such preparation:
A. Biseptolum
B. *Sulfaquanidine
C. Sulfathiazole
D. Sulfanilamide
E. Sulfacarbamide
The urea rest in sulfacarbamide molecule can be defined by means of allocation after pyrolysis:
A. CO
B. *NH3
C. NO2
D. CO2
E. H2S
The molar weight of an equivalent (Em) of hexenal at assay by means of acidimetry is equal:
A. 3M.m.
B. M. m./3
C. M. m./4
D. *M.m.
E. M. m./6
The chemist-laboratorian has added to solution of sulfacetamide sodium copper sulphate
solution. What analytical effect of reaction he will see?
A. Red gelatinous precipitate
B. White precipitate
C. Brown gas
D. *Precipitate of blue-green colour
E. White smoke
For assay of sulfanilamide, agrees the AND, can be used such method:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
168.
169.
170.
171.
172.
173.
174.
175.
176.
*Nitritometry
Alkalimetry
Cerimetry
Permanganatometry
Gravimetry
The characters of sulfanilamide is:
A. Yellow crystalline powder, soluble in water
B. *White or yellowish-white crystals or fine powder, slightly soluble in water
C. White amorphous powder, soluble in alkalis
D. White amorphous powder, soluble in acetone
E. White amorphous powder, soluble in ether
What of drugs is not used as antidiabetic agent:
A. Glibenclamide
B. *Pantosept
C. Chlorpropamide
D. Tolbutamide
E. Carbutamide
In the drugstore for realisation go on sale maninil. What chemical compound is the main
component this drug?
A. *Glibenclamide
B. Pantosept
C. Carbutamide
D. Chloranine B
E. Tolbutamide
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
177.
178.
179.
O
HN
C2H5
N
C6H5
O
O
180.
181.
182.
183.
C
O
C6H5
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Barbital
B. Phenobarbital
C. Thiopental sodium
D. Hexenal
E. *Benzonal
The chemical name of chlorpropamide is:
A. (2RS)-2 [4-methylprophyl) phenyl]-propanoic acid
B. N-(p-methylbenzene-sulphonyl)-N '-butylurea
C. Sodium N-chlor-4-methylbenzene-sulphoneimide trihydrate
D. *1-[(4-chlorophenyl)sulphonyl]-3-propylurea
E. Diethylamino-2,4,6-trimethylacetanilide hydrochloride
The initial substance for synthesis of tolbutamide is:
A. Benzoic acid
B. Dimethyaminoethylamine
C. *Toluene
D. Benzene
E. Aniline
The pharmacist-analyst spends assay of tolbutamide by means of alkalimetry in the presence of
alcohol. The molecular weight of equivalent (Em) of preparation is equal:
A. *M m.
B. M. M./2
C. M. m./4
D. M.m./6
E. M. m./3
184.
185.
186.
187.
188.
189.
190.
191.
192.
What reagents use for identification of chloride-ions after mineralization of pantosept?
A. Reagent of methoxyphenylacetic acid
B. Ba(NO3)2 solution
C. BaCl2 solution
D. *Solutions of K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, diphenylcarbazide
E. K[Sb(OH)6] solution
For assay of pantosept can be used method:
A. *Iodometry
B. Argentometry
C. Nitritometry
D. Gravimetry
E. Mercurimetry
For identification of chloramine, the pharmacist-analyst has dipped a red litmus paper into a
water solution of substance. What thus he observed?
A. The first red colouring of paper, which then vanished
B. Orange colouring of paper, which passed in red colour
C. Yellow colouring of paper, which passed in violet colour
D. Red colouring of paper, which passed in violet colour
E. *The first dark blue colouring of paper, which then vanished
Under the description chloramine is:
A. White liquid
B. *A crystal powder of white or white colour with a yellowish shade
C. Grey weight
D. Yellow amorphous powder
E. Colourless crystals
Action and use of carbutamide?
A. Hypnagogue
B. Antiseptic
C. *Antidiabetic (hypoglycemic)
D. Antipyretic
E. Local anesthetic
Synonymic (other) name of glibenclamide is:
A. Butamide
B. *Maninil
C. Procainamide hydrochloride
D. Procaine hydrochloride
E. Benzocaine
For identification of tolbutamide can be used alkaline hydrolysis of substance. What analytical
effect this reaction?
A. Precipitation of p-toluene sulphonamide
B. Formation of yellow precipitate
C. Allocation of carbonic gas
D. *Fat drops on liquid surface and liberation of gas with a characteristic smell
E. Precipitate of benzene sulphonic acid
Action and use of tolbutamide?
A. Antipyretic
B. *Hypoglycaemic
C. Expectorant
D. Antiseptic
E. Anaesthetic
The pharmacist-analyst spends of assay of chlorpropamide by means of alkalimetry in the
presence of alcohol. The molecular weight of equivalent (Em) for chlorpropamide is equal:
A. M.m./3
B. M. m./2
C. M. m./4
D. M.m./6
E. *M m.
193.
194.
195.
196.
197.
198.
199.
200.
201.
For Chlorine-ions identification in chlorpropamide molecule it is necessary:
A. Precipitate of acid hydrolysis product
B. Makes alkaline hydrolysis of preparation
C. *Makes mineralization of substance by meams of method of burning with a mix for sintering
D. Makes dry pyrolysis of substance
E. Add AgNO3 solution and HNO3
The chemist-analyst made pantosept mineralization. What method of assay can be used?
A. Permanganatometry
B. Acidimetry
C. Mercurimetry
D. Morh
E. *Keldal
Under the description pantosept is:
A. White liquid
B. *White powder with a weak smell of chlorine
C. Grey weight
D. Yellow amorphous powder
E. Colourless crystals
The pharmacist-analyst spends assay of chloramine by means of iodometry. As indicator he use:
A. *Starch solution
B. Iron-amoniachnye alum
C. Methyl orange
D. Phenolphthalein
E. Methylene dark blue and tropeolin 00
The initial substance for synthesis of chloramine is:
A. Benzoic acid
B. Dimethylaminoethylamine
C. p-Aminobenzoyl chloride
D. *Benzene
E. Anhydride p-nitrobenzoic acid
What characters of thiopental sodium?
A. A red solution, without a smell, soluble in water, difficultly soluble in 95 % alcohol,
practically insoluble in ether
B. Black crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol,
practically insoluble in methylene chloride
C. An oily liquid or a crystalline mass, colourless or slightly yellowish, miscible with water and
with alcohol
D. A blue crystalline powder or colourless crystals, slightly soluble in water, soluble in boiling
water and in alcohol
E. *A yellowish-white powder, hygroscopic, freely soluble in water, partly soluble in ethanol
For assay of trimecaine hydrochloride use argentometry (Volhard method), back titration. As
indicator use:
A. Methyl red
B. Bromothymol blue
C. Potassium chromate
D. Phenolphthalein
E. *Iron(III) ammonium sulphate
For assay of trimecaine hydrochloride use acidimetry, direct titration. What solvent use for
dissolution shot of trimecaine hydrochloride?
A. Chloroform
B. *Anhydrous acetic acid
C. Methanol
D. Ether
E. Water
For assay of lidocaine use mercurimetry, direct titration. As titrant use:
A. Hg2Cl2
B. HgCl2
C. Hg(CH3COO)2
D. Hg
E. *Hg(NO3)2
202.
203.
204.
205.
206.
In the nitritometry is not necessary to adhere to such condition:
A. Slow of titration
B. *Temperature rise
C. Catalyst presence
D. Temperature fall
E. Internal or the external indicator
What analytical functional group can be identified by means of solutions AgNO3, HNO3,
NH4OH?
A. Ester group
B. Methyl group
C. Sodium-ions
D. *Chloride-ions
E. Primary aromatic amino group
By means of lignin test it is possible to identify presence in the structure of molecule such
functional group:
A. *Primary aromatic amino group
B. Carboxylic group
C. Amide group
D. Benzene cycle
E. Ester group
What is the gravimetric form at assay of sodium salt of mefenamic acid?
A. Mefenamic acid and its salt
B. Sodium cations
C. *Mefenamic acid
D. Anthranilic acid
E. Sodium salt of mefenamic acid
The methods of assay for phthivazid is acidimetry, non-aqueous titration. The molecular weight
of equivalent (Em) is:
A. М m./3
B. *М m.
C. 3M.m.
D. М. m./4
E. 2М. m.
O
HN
C 2 H5
HN
C 6 H5
O
207.
208.
209.
O
The structural formula corresponds to a drug:
A. Barbital
B. Barbamyl
C. Thiopental sodium
D. Hexenal
E. *Phenobarbital
What physical and chemical method of identification use for ibuprofen, according to
Pharmacopoeia?
A. Polarimetry
B. Refractometry
C. *IR-spectroscopy
D. Liquit chromatography
E. Potentiometry
The chemical name of ibuprofen, according to Pharmacopoeia, is:
A. 3-Dimethylaminoethyl ester p-buthylaminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
Ethyl ester p-aminobenzoic acid
3-Diethylaminoethyl ester p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
Diethylamino-2,4,6-trimethylacetanilide hydrochloride
*(2RS)-2-[4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid
The initial substance for trimecaine hydrochloride synthesis is:
A. Benzoic acid
B. 2-Dimethylaminoethylamine
C. p-Aminobenzoic acid chloride
D. *2,4,6-Trimethylaniline
E. Anhydride p-nitrobenzoic acid
In the medical practice trimecaine hydrochloride use as agent:
A. *Local anesthetic
B. Antidiabetic
C. Antipyretic
D. Expectorant
E. Antiseptic
What titrant is used for assay of lidocaine by means of Fajans method?
A. HCl
B. NaOH
C. *AgNO3
D. NH4Fe (SO4) 2
E. NH4SCN
The pharmacist-analyst makes assay for lidocaine by means of alkalimetry. What indicator he
must use?
A. *Phenolphthalein
B. Sodium thyosulphate
C. Methylene dark blue
D. Tropeolin 00
E. Starch
For identification of Sodium cations in the diclofenac sodium the chemist add
methoxyphenylacetic acid reagent. This reagent consist of such reagents:
A. Acetic acid and methoxyphenol
B. Methoxyphenylacetic acid and water
C. *Methoxyphenylacetic acid and tetramethylammonium hydroxide
D. Methanol and acetic acid
E. Methoxyphenylacetic acid
For assay of trimecaine hydrochloride use argentometry (Fajans method), direct titration. As
indicator use:
A. Methyl red
B. Iron(III)-ammonium sulphate
C. Potassium chromate
D. Phenolphthalein
E. *Bromothymol blue
Barbamyl is derivative of:
A. Benzoic acid
B. *Barbituric acid
C. Salicylic acid
D. Salicylic acid
E. Nicotinic acid
What titrant is used for assay of lidocaine by means of Volhard method?
A. HCl
B. *NH4SCN
C. AgNO3
D. NH4Fe (SO4) 2
E. NaOH
The pharmacist-analyst makes assay for ibuprofen by means of alkalimetry, direct titration at
presence:
B.
C.
D.
E.
210.
211.
212.
213.
214.
215.
216.
217.
218.
Hexane
Acetone
Chloroform
Anhydrous acetic acid
*Methanol
What reagents the pharmacist-analyst used for identification primary aromatic amino group in
the lidocaine, after alkaline hydrolysis?
A. Mix of acids and naphthol
B. Alkaline solution of naphthol
C. *NaNO2, HCl, naphthol alkaline solution
D. KNO2, HCl, naphthol acid solution
E. NaNO3, HCl, naphthol neutral solution
What reaction use for identification ester group in the structure of molecule?
A. *Formation of salts hydroxamic acids
B. Decarboxylation
C. Neutralization
D. Complex formation
E. Formation of Schiff base
For identification of cations in the molecule of sodium diclofenac, according to Pharmacopoeia,
is necessary to use reaction with:
A. Glyoxalhydroxyanil
B. Feling reagent
C. Barium sulphate in the medium of H2SO4
D. *Potassium hexahydroxostibat
E. Silver nitrate in the medium of HNO3
Mefenamic acid use in medical practice as agent:
A. Antiarrhytmic, resolvent
B. Disinfectant, anaesthetic
C. *Analgesic, resolvent
D. Antituberculosis, antiseptic
E. Antidiabetic, antipyretic
Assay of sodium diclofenac makes by means of method:
A. *Acidimetry, non-aqueous titration
B. Argentometry, direct titration
C. Gravimetry
D. Alkalimetry in non-aqueous titration
E. Alkalimetry in the water medium
What is equivalent weight (Em) of ibuprofen at quantitative definition by means of alkalimetry
its methanol solution?
A. М m./16
B. М m./8
C. М m./5
D. 2 М m
E. *М m.
The physical and chemical method for identification of ibuprofen is:
A. Polarimetry
B. Refractometry
C. *UV-spectroscopy
D. Solution chromatography
E. Potentiometry
Presence in the molecule structure of trimecaine hydrochloride amide group can be defined by
means of such reaction:
A. Acid or alkaline hydrolysis with the subsequent identification of hydrolysis products
B. Esterification
C. Polymerisation
D. Combination reaction
E. *Acid hydrolysis
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
219.
220.
221.
222.
223.
224.
225.
226.
227.
228.
229.
230.
231.
232.
233.
234.
235.
The chemical name of trimecaine hydrochloride is:
A. Diethylaminomethylamide p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
B. Dimethylaminoethyl ester of p-buthylaminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
C. Ethyl ester p-aminobenzoic acids
D. Diethylaminoethyl ester of p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride
E. *Diethylamino-2,4,6-trimethylacetanilide hydrochloride
What drug is used as local anesthetic:
A. Resorcinol
B. *Lidocaine
C. Sodium benzoate
D. Phenyl salicylate
E. Acetylsalicylic acid
The method of assay for lidocaine is nitritometry after the previous hydrolysis. What external
indicator can be used?
A. Iodide paper
B. Phenolphthalein paper
C. Starch paper
D. Litmus paper
E. *Potassium iodide test paper
For identification of ester group as chemical component of structure of preparation, can be used
such reaction:
A. Indophenol test
B. Decolouration of bromine water
C. Diazotization
D. *Alkaline hydrolysis at heating
E. Lignin test
For distinguishing tetracaine hydrochloride from benzocaine it is possible to use reaction with:
A. Alkaline solution of naphthole
B. Bromic water
C. Alkali at presence hydroxylamine
D. Sodium nitrite in the presence of HCl
E. *Silver nitrate in the medium of HNO3
The pharmacist-analyst spends assay of procainamide hydrochloride by means of argentometry
(Volhard method). As indicator he used:
A. Methylene dark blue and tropeolin 00
B. *Ammonium iron alum
C. Methyl orange
D. Phenolphthaleine
E. Potassium iodide test paper
For identification of a primary aromatic amino group in procainamide hydrochloride, the chemist
has spent reaction with:
A. Ketones
B. Carboxylic acids
C. Aliphatic aldehydes
D. *Aromatic aldehydes
E. Aromatic acids
Hexenal use in medical practice as agent:
A. Picoline
B. Sedative of short term action
C. *Purgative
D. For an inhalation narcosis
E. Sedative of long action
For assay of procaine hydrochloride can be used nitritometry. As indicator use:
A. *Mix of tropeolin 00 and methylene dark blue
B. Phenolphthaleine
C. Bromphenol dark blue
D. Litmus paper
E. Methyl orange
236.
237.
238.
239.
240.
241.
242.
243.
244.
Procaine hydrochloride do not use in the such medicinal form:
A. Ointment
B. *Aerosol
C. Injection solution
D. Suppositories
E. Tablets
What reagents for identification Chloride-ions in the articaine hydrochloride?
A. MgSO4, BaCl2
B. 8-Oxyquinoline, (NH4)2C2O4
C. m-Dinitrobenzene, Feling reagent
D. *AgNO3, HNO3, NH4OH
E. NaNO2, HCl, naphthol
The chemical name of drug is 2-diethylaminoethyl-4-aminobenzoate hydrochloride. What this
drug?
A. Articaine hydrochloride
B. Benzocaine
C. Procainamide hydrochloride
D. Tetracaine hydrochloride
E. *Procaine hydrochloride
Procaine hydrochloride is the competitor of streptocide, because in an organism its hydrolysed
with formation:
A. Sulfanilic acid
B. Ethanol
C. Diethylaminoethanole
D. o-Aminobenzoic acid
E. *p-Aminobenzoic acid
The characteristic reaction for benzene cycle is interaction with:
A. Sodium hydroxyde at heating
B. *Bromic water
C. Sodium nitrite in the acid medium
D. Potassium dichromate
E. Sodium hydroxyde and hydroxylamine
The pharmacist-analyst makes assay of procainamide hydrochloride by means of nitritometry.
The molecular weight of equivalent (Em) of preparation is:
A. M.m./3
B. M.m./4
C. M.m./2
D. *M.m.
E. M.m./6
The pharmacist-analyst makes identification of procainamide hydrochloride. Thus he can used
such reagents:
A. Solution of potassium chromate, diphenylcarbazone
B. Solution of sodium hydroxyde, sulphatic acid
C. Solution of nitrate sodium, nitric acid
D. Solution of sodium hydroxyde, chloroform
E. *Solution of nitrite sodium, chloride acid, naphthol alkaline solution
Under the description tetracaine hydrochloride is:
A. Colourless liquid with a pungent smell
B. White amorphous powder with a characteristic smell
C. Oily liquid without a smell
D. Yellow crystal powder with a characteristic smell
E. *White crystal powder without a smell
Presence ester group in structure of tetracaine hydrochloride molecule can be confirmed by
means of reaction:
A. *Formation of hydroxamic acids salts
B. Decarboxylation
C. Neutralization
D. Complex formation
E. Formation of Schiff base
245.
246.
247.
248.
Procaine hydrochloride use as agent:
A. Resolvent
B. Helminthicide
C. Expectorant
D. Antiallergenic
E. *Local anesthetic, the competitor of streptocide
For assay of procaine hydrochloride it is possible to use argentometry (Morh method). The
essence of this method is:
A. Titration with AgNO3 in the presence of NH3
B. *Direct titration with solution AgNO3 in the presence of indicator K2CrO4 to occurrence of
orange-red precipitate
C. Back titration with solution AgNO3
D. Direct titration with solution NH4SCN at presence ammonium iron alum
E. Titration of excess AgNO3 by means of standard solution NH4SCN at presence ammonium
iron alum
The initial substance for benzocaine synthesis is:
A. Benzene
B. Phenol
C. *Toluene
D. Benzocaine
E. Novocaine
As local anesthetic use:
A. Vanillin
B. Salicylic acid
C. Thymol
D. *Articaine hydrochloride
E. Resorcinol