* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA and Amino Acid Comparisons
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
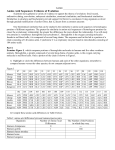
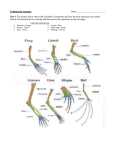
NAME: ________________________________________ Period: ______________Date:_______ DNA and Amino Acid Comparisons Introduction: Mutation provides all initial change. A mutation occurs when the DNA does not replicate perfectly. When a mutation occurs, a new allele is created. These mutations are random (can occur at any location along the DNA). The rate of these mutations is relatively constant within a given species. If the mutation occurs in a critical location the result is usually disastrous. Other areas will accept change with no immediate consequence. Once made, the mutation is maintained in offspring and variability within the gene pool of the species is increased. Mutations add variability to the gene pool!!!! Examine the amino acid sequences below which compare corresponding portions of hemoglobin molecules in humans and five other vertebrate animals. The sequence shown is only a small portion of the chain of 146 amino acids. The numbered columns indicate the position of each amino acid within the whole chain. Procedure: 1. Look at each numbered column and CIRCLE the amino acids in each column that are DIFFERENT from the human amino acid for that column. 2. PUT an X in the blank under each numbered column in which all of the organisms have the same amino acid listed in that column. 3. In the blanks on the right hand side of each row, identify how many amino acids were circles (different from the human amino acids). Table A: Comparing hemoglobin of a human to other vertebrates Human Chimp Gorilla Rhesus Monkey Horse Kangaroo 87 THR THR THR GLU 88 LEU LEU LEU LEU 89 SER SER SER SER 90 GLU GLU GLU GLU 91 LEU LEU LEU LEU 92 HIS HIS HIS HIS 93 CYS CYS CYS CYS 94 ASP ASP ASP ASP 95 LYS LYS LYS LYS 96 LEU LEU LEU LEU 97 HIS HIS HIS HIS 98 VAL VAL VAL VAL 99 ASP ASP ASP ASP 100 PRO PRO PRO PRO 101 GLU GLU GLU GLU ALA LYS LEU LEU SER SER GLU GLU LEU LEU HIS CYS HIS CYS ASP ASP LYS LYS LEU LEU HIS HIS VAL VAL ASP ASP PRO GLU PRO GLU Human Chimp Gorilla Rhesus Monkey Horse Kangaroo 102 ASN ASN ASN ASN 103 PHE PHE PHE PHE 104 ARG ARG LYS LYS 105 LEU LEU LEU LEU 106 LEU LEU LEU LEU 107 GLY GLY GLY GLY 108 ASN ASN ASN ASN 109 VAL VAL VAL VAL 110 LEU LEU LEU LEU 111 VAL VAL VAL VAL 112 CYS CYS CYS CYS 113 VAL VAL VAL VAL 114 LEU LEU LEU LEU 115 ALA ALA ALA ALA 116 HIS HIS HIS HIS ASN ASN PHE PHE ARG LYS LEU LEU LEU LEU GLY GLY ASN ASN VAL ILE LEU ILE ALA VAL LEU ILE VAL CYS VAL LEU ALA ALA ARG GLU Questions: 1. Identify in the chart below how many total differences of amino acids each organism had when compared to the human amino acid sequence. Table B Organism # of differences from human Chimpanzee Gorilla Rhesus monkey Horse Kangaroo 2. How many columns from Table A were the amino acids that same for each organism? 3. Based on the information in Table B above, which organism is the most closely related to humans? Explain how you know this. 4. Based on the information in Table B above, which organism is the least closely related to humans? Explain how you know this. 5. There is a difference of only one amino acid in one chain of hemoglobin between humans and gorillas. What might have caused this difference? 6. If the amino acid sequences in the proteins of two organisms are similar, why will their DNA also be similar? (NOTE: What is the relationship between amino acid sequences and DNA?) Many biologists believe that the number of differences between the amino acid sequences (proteins) of different species indicate how long ago the species diverged from a common ancestor. Molecular Clock Geologic Time Scale (million years ago) 450 350 270 70 0 _______________________________________________ 79 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Hemoglobin Amino Acid Differences 7. Why do these biologists believe that humans and gorillas diverged from a common ancestor only a few million years ago? 8. There are 79 differences in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin when you compare humans to sharks. How long ago do you think humans and sharks diverged from a common ancestor? 9. There are 35 differences in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin when you compare humans to birds. How long ago do you think humans and birds diverged from a common ancestor? (just estimate) Table C: Comparing cytochrome C of a human to other organisms Organism # of Differences Chimpanzee 0 Fruit Fly 29 Horse 6 Gorilla 1 Rattlesnake 14 Red Bread Mold 28 Rhesus Monkey 1 Screwworm Fly 27 Snapping Turtle 15 Tuna Fish 21 Wheat 43 Pigeon 12 10. Based on the information in Table C above, which organism is the most closely related to humans? Explain how you know this. 11. Based on the information in Table C above, which organism is the least closely related to humans? Explain how you know this. 12. Other proteins can be used to establish degrees of evolutionary relatedness between organisms. Would you expect to find roughly the same number of differences in the amino acid sequence when comparing organisms? Explain your answer.