
SBI-4U1 Exam Review
... Water – Electron transport chain (light rxns) – Water is split by Z protein to replenish electron deficit in photosystem I. Also Calvin. Light energy – Photoexcitation in the ETC – photosystems I and II b. Where is each of the products produced? Oxygen – Electron transport chain. Produced when water ...
... Water – Electron transport chain (light rxns) – Water is split by Z protein to replenish electron deficit in photosystem I. Also Calvin. Light energy – Photoexcitation in the ETC – photosystems I and II b. Where is each of the products produced? Oxygen – Electron transport chain. Produced when water ...
1. Amino Acids,Peptides, Proteins
... 16. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism Ch. 20. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway & Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism - without the metabolism of aminosugars 17. Overview of Glucose Metabolism. Control of the Blood Glucose Ch. 19. Gluconeogenesis & the Control of Bloo ...
... 16. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism Ch. 20. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway & Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism - without the metabolism of aminosugars 17. Overview of Glucose Metabolism. Control of the Blood Glucose Ch. 19. Gluconeogenesis & the Control of Bloo ...
Amino Acid Metabolism - Breakdown Other metabolic
... Other metabolic pathways Urea Cycle - regulation 1. By flux of nitrogen through cycle - depends on diet lots protein in diet = carbon skeletons used for fuel, lots of urea starvation = breakdown muscle protein for energy, lots of urea All enzymes (CPS-I and 4 in cycle) synthesized at higher rates i ...
... Other metabolic pathways Urea Cycle - regulation 1. By flux of nitrogen through cycle - depends on diet lots protein in diet = carbon skeletons used for fuel, lots of urea starvation = breakdown muscle protein for energy, lots of urea All enzymes (CPS-I and 4 in cycle) synthesized at higher rates i ...
AP Biology
... 1. Define the two catabolic pathways: a. Fermentation b. Cellular respiration 2. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent and oxidizing agent. 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? 4. In cellular respi ...
... 1. Define the two catabolic pathways: a. Fermentation b. Cellular respiration 2. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent and oxidizing agent. 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? 4. In cellular respi ...
Concentration of solutes and solvent in a solution
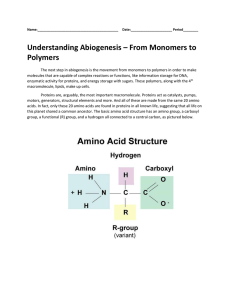
... Organic vs. Inorganic – be able to identify examples Be able to recognize structures/formulas of monomers, dimers and polymers of carbs, proteins and nucleic acids What elements are found in each category of organic compounds Identify examples of food sources for each category of organic com ...
... Organic vs. Inorganic – be able to identify examples Be able to recognize structures/formulas of monomers, dimers and polymers of carbs, proteins and nucleic acids What elements are found in each category of organic compounds Identify examples of food sources for each category of organic com ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... • Monomer (most): Fatty Acid – hydrophilic head (carboxyl end), hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) >Saturated – means all Carbons have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. >Unsaturated – means that some Carbons have double bonds (less H atoms) ...
... • Monomer (most): Fatty Acid – hydrophilic head (carboxyl end), hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) >Saturated – means all Carbons have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. >Unsaturated – means that some Carbons have double bonds (less H atoms) ...
Exam III answer key - Chemistry Courses: About
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
Reactions
... • 4: Several enzymes of the Calvin Cycle are activated by the breaking of disulphide bridges of enzymes involved in the working of the cycle. – the activity of the light reactions is communicated to the dark reactions by an enzyme intermediate ...
... • 4: Several enzymes of the Calvin Cycle are activated by the breaking of disulphide bridges of enzymes involved in the working of the cycle. – the activity of the light reactions is communicated to the dark reactions by an enzyme intermediate ...
Chem464 Abrol Spring2017 FlippedReview4
... out on a yeast extract maintained under strictly anaerobic conditions to produce ethanol. The experiment consists of incubating a small amount of 14C-labeled substrate (the pulse) with the yeast extract just long enough for each intermediate in the fermentation pathway to become labeled. The label i ...
... out on a yeast extract maintained under strictly anaerobic conditions to produce ethanol. The experiment consists of incubating a small amount of 14C-labeled substrate (the pulse) with the yeast extract just long enough for each intermediate in the fermentation pathway to become labeled. The label i ...
SBI-4U1 Exam Review
... Water – Electron transport chain (light rxns) – Water is split by Z protein to replenish electron deficit in photosystem I. Also Calvin. Light energy – Photoexcitation in the ETC – photosystems I and II b. Where is each of the products produced? Oxygen – Electron transport chain. Produced when water ...
... Water – Electron transport chain (light rxns) – Water is split by Z protein to replenish electron deficit in photosystem I. Also Calvin. Light energy – Photoexcitation in the ETC – photosystems I and II b. Where is each of the products produced? Oxygen – Electron transport chain. Produced when water ...
- Circle of Docs
... when glucose enter a cell, it is trapped by addition of a phosphate glucokinase (found only in liver) and hexokinase (found in all other tissues) catalyze glucose-6P kinase at end of an enzyme – adds phosphate groups Vmax = maximum velocity at which the enzyme will work 3. Which of the following is ...
... when glucose enter a cell, it is trapped by addition of a phosphate glucokinase (found only in liver) and hexokinase (found in all other tissues) catalyze glucose-6P kinase at end of an enzyme – adds phosphate groups Vmax = maximum velocity at which the enzyme will work 3. Which of the following is ...
Bioenergetics Test Study Guide - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... Keep in mind that while not all organisms perform photosynthesis, ALL organisms perform cellular respiration, including plants (ALL ORGANISMS) One last thing to note is that while eukaryotes perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria, bacterial cells do not contain mitochondria! So how do th ...
... Keep in mind that while not all organisms perform photosynthesis, ALL organisms perform cellular respiration, including plants (ALL ORGANISMS) One last thing to note is that while eukaryotes perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria, bacterial cells do not contain mitochondria! So how do th ...
Mechanisms of hormonal regulation and pathologies of protein
... acids are transformed into metabolic intermediates that can be converted into glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies or oxidized by the citric acid cycle. ...
... acids are transformed into metabolic intermediates that can be converted into glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies or oxidized by the citric acid cycle. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 11. Which of the following best describes the process that occurs during the citric acid cycle? a. Pyruvate is processed to release one molecule of carbon dioxide, and the remaining carbons are used to form acetyl CoA. b. One molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate, ATP is produ ...
... 11. Which of the following best describes the process that occurs during the citric acid cycle? a. Pyruvate is processed to release one molecule of carbon dioxide, and the remaining carbons are used to form acetyl CoA. b. One molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate, ATP is produ ...
Semester 1 AP Biology Exam Review Guide Directions: Use this as
... 16. Why is this process called chemiosmosis or oxidative phosphorylation? 17. What do the NADH and the FADH2 do for this process? 18. Describe the ETC in five steps. Be sure to include NADH, FADH2, cytochrome carrier proteins, H+ ions, concentration gradient, pump, ATP synthase, ADP, ATP, oxygen as ...
... 16. Why is this process called chemiosmosis or oxidative phosphorylation? 17. What do the NADH and the FADH2 do for this process? 18. Describe the ETC in five steps. Be sure to include NADH, FADH2, cytochrome carrier proteins, H+ ions, concentration gradient, pump, ATP synthase, ADP, ATP, oxygen as ...
Bioenergetics
... • Recall: If oxygen is present in sufficient quantities, the end product of glycolysis, Pyruvate, is not converted to lactate but is transported to the mitochondria, where it is taken up and enters the Krebs cycle ...
... • Recall: If oxygen is present in sufficient quantities, the end product of glycolysis, Pyruvate, is not converted to lactate but is transported to the mitochondria, where it is taken up and enters the Krebs cycle ...
Macromolecules 9-3
... c. Four Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary 1. Sequence of amino acids in the protein a. Determined by the structure of the DNA sequence in the nucleus! b. Every three letters in DNA codes for an amino acid c. These amino acids form chains to make proteins ii. Secondary 1. The folding and/or coil ...
... c. Four Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary 1. Sequence of amino acids in the protein a. Determined by the structure of the DNA sequence in the nucleus! b. Every three letters in DNA codes for an amino acid c. These amino acids form chains to make proteins ii. Secondary 1. The folding and/or coil ...
Exam 2 Key
... ___Cytochrome b6f complex 7. (2 pts) In which part of the chloroplast do the 'light reactions' take place? ...
... ___Cytochrome b6f complex 7. (2 pts) In which part of the chloroplast do the 'light reactions' take place? ...
- Circle of Docs
... at a pH of five at a pH of seven in a buffer system in an acid solution at their isoelectric point ...
... at a pH of five at a pH of seven in a buffer system in an acid solution at their isoelectric point ...
[j26]Chapter 5#
... perform routine functions. These include such vital functions as the transport of materials across cell membranes; generating membrane potentials (chapter 6) and transmitting these electrical impulses (chapters 7-10); the synthesis and secretion of hormones (chapter 11); and muscle contraction (chap ...
... perform routine functions. These include such vital functions as the transport of materials across cell membranes; generating membrane potentials (chapter 6) and transmitting these electrical impulses (chapters 7-10); the synthesis and secretion of hormones (chapter 11); and muscle contraction (chap ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
... Ribonucleic acid (______) - plays many key roles in building of proteins and can act as enzymes. ...
... Ribonucleic acid (______) - plays many key roles in building of proteins and can act as enzymes. ...
Advanced Biology
... d) Come up with an analogy to describe ATP’s role in cells. How does this illustrate the importance of coupled reactions? 3. Take a look at the “Metabolic Pathways” poster in the science lab. It shows most of the typical metabolic reactions that happen in cells. a) There will be a quiz on this poste ...
... d) Come up with an analogy to describe ATP’s role in cells. How does this illustrate the importance of coupled reactions? 3. Take a look at the “Metabolic Pathways” poster in the science lab. It shows most of the typical metabolic reactions that happen in cells. a) There will be a quiz on this poste ...
22. pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
... other pathway, except perhaps glycolysis. The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that bring about the complete oxidation of acetyl-CoA to CO2 and liberate hydrogen equivalents which ultimately form water. This cyclic sequence of reactions provides electrons to the transport s ...
... other pathway, except perhaps glycolysis. The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that bring about the complete oxidation of acetyl-CoA to CO2 and liberate hydrogen equivalents which ultimately form water. This cyclic sequence of reactions provides electrons to the transport s ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.


















![[j26]Chapter 5#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013325615_1-93c4a55e793afe312f3604738fdd639e-300x300.png)


