1 - MSU Billings
... A. Maintenance of a stable environment within the body B. The transmission of traits from generation to generation C. The sum of chemical processes that take place in living cells D. Synthesis of macromolecules E. The process of gas exchange across cell membranes 70. What properties of cell membrane ...
... A. Maintenance of a stable environment within the body B. The transmission of traits from generation to generation C. The sum of chemical processes that take place in living cells D. Synthesis of macromolecules E. The process of gas exchange across cell membranes 70. What properties of cell membrane ...
Human Nutrition – Exam #1 1. Which of the following is a
... a) It is a food that contains significant amounts of all the essential amino acids b) It is a food hat contains significant amounts of every single amino acid. c) It is a food that is made completely of protein. d) It is a single protein that contains every single amino acid. 40. Which of the follow ...
... a) It is a food that contains significant amounts of all the essential amino acids b) It is a food hat contains significant amounts of every single amino acid. c) It is a food that is made completely of protein. d) It is a single protein that contains every single amino acid. 40. Which of the follow ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... Sulfur in soluble form is taken up by plant roots and incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine. It then travels through the food chain and is eventually released through decomposition SO2 and water vapor makes H2SO4 ( a weak sulfuric acid), which is then carried to Earth in the form of aci ...
... Sulfur in soluble form is taken up by plant roots and incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine. It then travels through the food chain and is eventually released through decomposition SO2 and water vapor makes H2SO4 ( a weak sulfuric acid), which is then carried to Earth in the form of aci ...
CARBOHYDRATE CHEMISTRY and MTABOLISM
... • Specific angle of rotation; considering the pH, concentration , temperature , and other dissolved materials in solution. • The angle of rotation value is preceded by the symbol (+) or (-) depending on the direction of rotation. The angle is measured by an instrument called Polarisoscope or Polarim ...
... • Specific angle of rotation; considering the pH, concentration , temperature , and other dissolved materials in solution. • The angle of rotation value is preceded by the symbol (+) or (-) depending on the direction of rotation. The angle is measured by an instrument called Polarisoscope or Polarim ...
Chapter 6 Slides
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
8.3 study guide answer key
... False-electron 5. ATP and NADPH are two types of protein carriers. 6. How does ATP synthase produce ATP? ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through the thylakoid membrane, rotating the enzyme. The rotation creates the energy needed to bind ADP to a phosphate and produces ATP. 7. When sunlight exci ...
... False-electron 5. ATP and NADPH are two types of protein carriers. 6. How does ATP synthase produce ATP? ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through the thylakoid membrane, rotating the enzyme. The rotation creates the energy needed to bind ADP to a phosphate and produces ATP. 7. When sunlight exci ...
Chemical Basis for Life
... and makes adenosine diphosphate (ADP). -This energy is used to do work in the cell. -Adding the phosphate back to make ATP requires that we add energy ...
... and makes adenosine diphosphate (ADP). -This energy is used to do work in the cell. -Adding the phosphate back to make ATP requires that we add energy ...
Hücrede Enerji Metabolizması
... •Conversion of 3phosphoglycerate to glucose is very similar to gluconeogenesis, but glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase uses NADPH not NADH. •Steps require consumption of ATP and NADPH. •3-phosphoglycerate could also be exported to cytsol and be used in normal gluconeogenesis. •Hexoses can then be used for ...
... •Conversion of 3phosphoglycerate to glucose is very similar to gluconeogenesis, but glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase uses NADPH not NADH. •Steps require consumption of ATP and NADPH. •3-phosphoglycerate could also be exported to cytsol and be used in normal gluconeogenesis. •Hexoses can then be used for ...
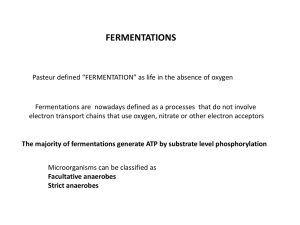
Energy Pathways and Anaerobic Metabolism
... your body comes to a fork in the road… Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate O2 absent ...
... your body comes to a fork in the road… Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate O2 absent ...
class title - Palomar College
... the role of chlorophyll-a and water; photosystem II and photosystem I; ATP production; the Calvin Cycle; the role of glucose; guard cells, stomata, and carbon dioxide; C4 and CAM plants. 12) Energetics, The Cellular Oxidation of Glucose A detailed look at glycolysis and cellular respiration. Aerobi ...
... the role of chlorophyll-a and water; photosystem II and photosystem I; ATP production; the Calvin Cycle; the role of glucose; guard cells, stomata, and carbon dioxide; C4 and CAM plants. 12) Energetics, The Cellular Oxidation of Glucose A detailed look at glycolysis and cellular respiration. Aerobi ...
Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... Over the years, ATP has been reported to contain various trace ionic impurities which affect enzyme ...
... Over the years, ATP has been reported to contain various trace ionic impurities which affect enzyme ...
Biochemistry Review Sheet Chemical Reactions and Properties of
... Explain the lock and key model of an enzyme. Be specific in its function. What is the function of a catalyst, such as an enzyme in a chemical reaction? There are two main things. 8. What are substrates usually made up of? 9. If the solution is too acidic or basic what happens to the enzyme? 10. What ...
... Explain the lock and key model of an enzyme. Be specific in its function. What is the function of a catalyst, such as an enzyme in a chemical reaction? There are two main things. 8. What are substrates usually made up of? 9. If the solution is too acidic or basic what happens to the enzyme? 10. What ...
Metabolism of ketonе bodies
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
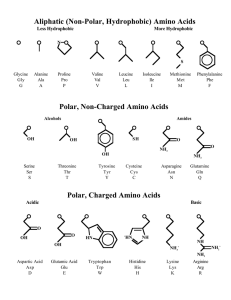
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
河北交通职业技术学院教案 Lesion 5 Alcoholic Beverages (1) 课题引
... and other cell reactions, are supplied by efficient anaplerotic reaction and other cell 三羧酸循环高效的补偿反应需要补充草酰乙酸盐,在柠檬酸合成酶的作用 下,进行缩合反应和其他的细胞反应。 ...
... and other cell reactions, are supplied by efficient anaplerotic reaction and other cell 三羧酸循环高效的补偿反应需要补充草酰乙酸盐,在柠檬酸合成酶的作用 下,进行缩合反应和其他的细胞反应。 ...
Acidaminococcus fermentans
... The strictly anaerobe Acidaminococcus fermentans is a non-pathogenic clostridial bacterium commonly ...
... The strictly anaerobe Acidaminococcus fermentans is a non-pathogenic clostridial bacterium commonly ...
Metabolism
... glucose 6-phosphate + ADP Reaction 3 Catalyzed by phosphofructokinase fructose 6-phosphate + ATP fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + ADP Reaction 10 Catalyzed by pyruvate kinase phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate+ ATP ...
... glucose 6-phosphate + ADP Reaction 3 Catalyzed by phosphofructokinase fructose 6-phosphate + ATP fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + ADP Reaction 10 Catalyzed by pyruvate kinase phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate+ ATP ...
Lecture 27 - Redox and PDH
... 3. The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex is a mitochondrial metabolic machine that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA in a favorable ...
... 3. The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex is a mitochondrial metabolic machine that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA in a favorable ...
CHAPTER 6
... The use of inhibitors to reveal the sequence of reactions in a metabolic pathway. (a) Control: Under normal conditions, the steady-state concentrations of a series of intermediates will be determined by the relative activities of the enzymes in the pathway. (b) Plus inhibitor: In the presence of an ...
... The use of inhibitors to reveal the sequence of reactions in a metabolic pathway. (a) Control: Under normal conditions, the steady-state concentrations of a series of intermediates will be determined by the relative activities of the enzymes in the pathway. (b) Plus inhibitor: In the presence of an ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.