Graph an Inequality in Two Variables
... GRAPH AN INEQUALITY IN TWO VARIABLES • The graph of an inequality in two variables is the set of points that represent all solutions of the inequality. • There is a BOUNDARY LINE that divides the coordinate plane into two HALF-PLANES. Only one half-plane contains the points that represent the solut ...
... GRAPH AN INEQUALITY IN TWO VARIABLES • The graph of an inequality in two variables is the set of points that represent all solutions of the inequality. • There is a BOUNDARY LINE that divides the coordinate plane into two HALF-PLANES. Only one half-plane contains the points that represent the solut ...
UNIT 1
... • Perpendicular lines are lines that intersect at right angles. • Parallel lines are two lines in a plane that never intersect or cross. • A line that intersects two or more other lines is called a transversal. • If the two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then these special pairs of angles ...
... • Perpendicular lines are lines that intersect at right angles. • Parallel lines are two lines in a plane that never intersect or cross. • A line that intersects two or more other lines is called a transversal. • If the two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then these special pairs of angles ...
line - Brenda Womack
... A) The second line is steeper than the first line B) The graphs are perpendicular lines C) The second line is less steep than the first line D) The graphs are parallel lines ...
... A) The second line is steeper than the first line B) The graphs are perpendicular lines C) The second line is less steep than the first line D) The graphs are parallel lines ...
Graphs as matrices and PageRank
... Both the sums in the above expression are nonzero by assumption (in fact, positive). Also x is nonzero since v and w are linearly independent. Notice that n X ...
... Both the sums in the above expression are nonzero by assumption (in fact, positive). Also x is nonzero since v and w are linearly independent. Notice that n X ...
Lesson Plans 5/4
... model relationships between quantities? How do you decide which functional representation to choose when modeling a real world situation, and how would you explain your solution to the problem? How can we use univariate and bivariate data to analyze relationships and make predictions? How can we sho ...
... model relationships between quantities? How do you decide which functional representation to choose when modeling a real world situation, and how would you explain your solution to the problem? How can we use univariate and bivariate data to analyze relationships and make predictions? How can we sho ...
syllabus outline for grade 8 2013 2014
... Graph and analyze slope triangles. Graph a function using the x- and y-intercepts. Write an equation of a line. Solve systems of equations by graphing. Solve systems of equations algebraically. Solve real-world mathematical problems using two linear equations in two variables. Unit 3: Fu ...
... Graph and analyze slope triangles. Graph a function using the x- and y-intercepts. Write an equation of a line. Solve systems of equations by graphing. Solve systems of equations algebraically. Solve real-world mathematical problems using two linear equations in two variables. Unit 3: Fu ...
7th Grade Second Nine Weeks Review #8 Day 1
... told that there are 25 fluffs are at a party. If 7 are orange fluffs and 13 are blue fluffs, how many red fluffs are also at the party? Be careful because the answer is not five! ...
... told that there are 25 fluffs are at a party. If 7 are orange fluffs and 13 are blue fluffs, how many red fluffs are also at the party? Be careful because the answer is not five! ...
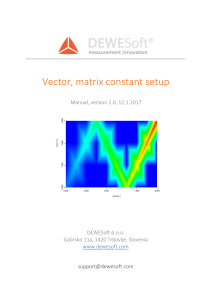
Vector, matrix constant
... Our arrays can be presented on the 2D graph (vectors) and on the 3D graph (matrices). If we output only one element in an array, the number can be displayed on a digital meter. ...
... Our arrays can be presented on the 2D graph (vectors) and on the 3D graph (matrices). If we output only one element in an array, the number can be displayed on a digital meter. ...
Learning Outcomes
... (a) Understand the relationships of different number systems. (b) Recognize and use properties of real numbers. (c) Use the definition of absolute value. (d) Simplify algebraic, exponential and radical expressions. (e) Understand and use the terminology associated with the rectangular coordinate sys ...
... (a) Understand the relationships of different number systems. (b) Recognize and use properties of real numbers. (c) Use the definition of absolute value. (d) Simplify algebraic, exponential and radical expressions. (e) Understand and use the terminology associated with the rectangular coordinate sys ...
Glossary of Mathematical Terms – Grade 7
... *Circle- a closed curve within a plane where all the points on the curve are the same distance from a point called the center Circumference-the distance around a circle Circle Graph (Pie Graph; Pie Chart)- a graph using a circle to show how the whole is divided into parts *Closest *Combination- an a ...
... *Circle- a closed curve within a plane where all the points on the curve are the same distance from a point called the center Circumference-the distance around a circle Circle Graph (Pie Graph; Pie Chart)- a graph using a circle to show how the whole is divided into parts *Closest *Combination- an a ...
2-2-guided-notes
... Objective 1: I can graph a linear equation in slope-intercept or standard form. A function whose graph is a line is a ____________________. You can represent a linear function with a ____________________, such as __________. A solution of a linear equation is any __________________ (x, y) that makes ...
... Objective 1: I can graph a linear equation in slope-intercept or standard form. A function whose graph is a line is a ____________________. You can represent a linear function with a ____________________, such as __________. A solution of a linear equation is any __________________ (x, y) that makes ...
Additional Mathematics Paper 1 2006 June (IGCSE) - Star
... If you have been given an Answer Booklet, follow the instructions on the front cover of the Booklet. Write your Centre number, candidate number and name on all the work you hand in. Write in dark blue or black pen on both sides of the paper. You may use a soft pencil for any diagrams or graphs. Do n ...
... If you have been given an Answer Booklet, follow the instructions on the front cover of the Booklet. Write your Centre number, candidate number and name on all the work you hand in. Write in dark blue or black pen on both sides of the paper. You may use a soft pencil for any diagrams or graphs. Do n ...