Long noncoding RNA found to quell inflammation
... 14 July 2016, by Jim Fessenden A long non-coding RNA (lincRNA) - called lincRNA- this brake, and the pro-inflammatory response is EPS - responsible for regulating innate immunity initiated. Mice that were lacking lincRNA-EPS has been identified by a team of scientists at the exhibited increased leve ...
... 14 July 2016, by Jim Fessenden A long non-coding RNA (lincRNA) - called lincRNA- this brake, and the pro-inflammatory response is EPS - responsible for regulating innate immunity initiated. Mice that were lacking lincRNA-EPS has been identified by a team of scientists at the exhibited increased leve ...
Immune System
... • Helper T cells activate antibody production in B cells and activates cytotoxic T cells • Cytotoxic T cells destroy pathogens and release chemicals ...
... • Helper T cells activate antibody production in B cells and activates cytotoxic T cells • Cytotoxic T cells destroy pathogens and release chemicals ...
Immune Response
... These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
... These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
adaptive immunity
... Circulating B cells which have not been exposed to the antigen naive B cells When BCR binds to the antigen, the antigen is internalised by the B cell and presented to the T cells ...
... Circulating B cells which have not been exposed to the antigen naive B cells When BCR binds to the antigen, the antigen is internalised by the B cell and presented to the T cells ...
Immunity Student Outline
... 2.28 The student is able to use representations or models to analyze quantitatively and qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. 2.30 The students can create representat ...
... 2.28 The student is able to use representations or models to analyze quantitatively and qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. 2.30 The students can create representat ...
Immunity Questions
... 7. Describe the differences between the antigens that B cell receptors and antibodies recognize, and the antigens that T cell receptors on cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells recognize. 8. Describe the differences between the humoral immune response and the cell-mediate immune response. 9. Describe ...
... 7. Describe the differences between the antigens that B cell receptors and antibodies recognize, and the antigens that T cell receptors on cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells recognize. 8. Describe the differences between the humoral immune response and the cell-mediate immune response. 9. Describe ...
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy: New Insights and
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
AnS 214 SI Session 5 Sunday, September 13, 8pm A) Antigens and
... 3) What are the three organelles necessary for the extreme rates of protein synthesis found in plasma cells? 4) Write in the names of the antibody killing mechanism corresponding to the description. _________________ Antibody binds to multiple enemy cells, immobilizing them. _________________ Antibo ...
... 3) What are the three organelles necessary for the extreme rates of protein synthesis found in plasma cells? 4) Write in the names of the antibody killing mechanism corresponding to the description. _________________ Antibody binds to multiple enemy cells, immobilizing them. _________________ Antibo ...
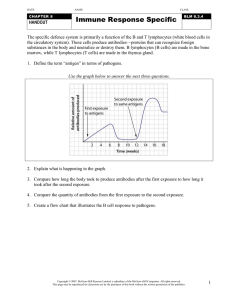
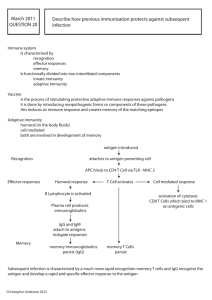
March 2011 QUESTION 20 Describe how previous
... Describe how previous immunisation protects against subsequent infection ...
... Describe how previous immunisation protects against subsequent infection ...
Chapter 21 - Fundamentals of Microbiology
... c. Distinguish between humoral and cell mediate immunity. d. Identify the types of T- and B-cell receptors, and assess their importance to antigen recognition. e. Explain how the clonal selection activates only those B and T cells that recognize “nonself” antigens or epitopes. f. Discuss the cellula ...
... c. Distinguish between humoral and cell mediate immunity. d. Identify the types of T- and B-cell receptors, and assess their importance to antigen recognition. e. Explain how the clonal selection activates only those B and T cells that recognize “nonself” antigens or epitopes. f. Discuss the cellula ...
the original file
... 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phagocytoses a gram-negative bacteria. Which PAMP(s) may be detected? Which innate immune receptor will be detecting the PAMP(s) ...
... 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phagocytoses a gram-negative bacteria. Which PAMP(s) may be detected? Which innate immune receptor will be detecting the PAMP(s) ...
Cell Signalling and communication between cells.
... • Pathogens carry an antigen on its cell surface, they act as markers, they enable it to be detected by our body cells, as a ‘foreign cell’. Our own cells also carry antigens, but they are recognised as ‘self’. In order to avoid destroying any ‘self’ cells, the immune system will contain no cells w ...
... • Pathogens carry an antigen on its cell surface, they act as markers, they enable it to be detected by our body cells, as a ‘foreign cell’. Our own cells also carry antigens, but they are recognised as ‘self’. In order to avoid destroying any ‘self’ cells, the immune system will contain no cells w ...
Unit #11: Animal Anatomy and Physiology- Immune
... 3. What are the non-specific defenses (1st line of defense) used in the immune system? ...
... 3. What are the non-specific defenses (1st line of defense) used in the immune system? ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 6. The second line of defense makes use of many different cell types. Name two cell types involved in the innate defenses. Name two other non-cellular defenses in the innate immune system. ...
... 6. The second line of defense makes use of many different cell types. Name two cell types involved in the innate defenses. Name two other non-cellular defenses in the innate immune system. ...
Immune System
... non-antibody-producing lymphocytes which are also produced in the bone marrow but sensitized in the thymus and constitute the basis of cell-mediated immunity. ...
... non-antibody-producing lymphocytes which are also produced in the bone marrow but sensitized in the thymus and constitute the basis of cell-mediated immunity. ...