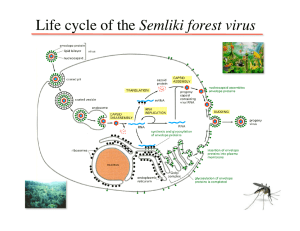
Lymphatic System Notes- Chapter 12
... *Most become _______________ that secrete _____________________ and last _____ * Some become __________________ and cause a _____________ response the 2nd time -T cells become immunocompetent in ________________________ *Cytotoxic T cells- specialized in _______________________________ *____________ ...
... *Most become _______________ that secrete _____________________ and last _____ * Some become __________________ and cause a _____________ response the 2nd time -T cells become immunocompetent in ________________________ *Cytotoxic T cells- specialized in _______________________________ *____________ ...
chapter 22 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
T cell-mediated immune response
... • Recognition of antigen by specific Ig, bound i cell membrane of naive B lymphocyte • The binding of antigen cross-links Ig receptors of specific B cells and then biochemical signal is delivered to the inside B cell; a breakdown product of the complement protein C3 provides ...
... • Recognition of antigen by specific Ig, bound i cell membrane of naive B lymphocyte • The binding of antigen cross-links Ig receptors of specific B cells and then biochemical signal is delivered to the inside B cell; a breakdown product of the complement protein C3 provides ...
Immunity
... because they can present antigens of other cells on their own cell-surface membrane. This type of response is called cell-mediated immunity ...
... because they can present antigens of other cells on their own cell-surface membrane. This type of response is called cell-mediated immunity ...
11.2
... 7. T Cells divide into two separate populations - memory cytotoxic T cells - (killer) effector cytotoxic T cells ...
... 7. T Cells divide into two separate populations - memory cytotoxic T cells - (killer) effector cytotoxic T cells ...
BIOLOGY 212 SI!
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
Document
... • 1st line of specific defense • Help recruit other immune cells & tell them to attack ...
... • 1st line of specific defense • Help recruit other immune cells & tell them to attack ...
Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System
... patches of the gut, and appendix. The secondary lymphoid organs are where mature T and B cells have the opportunity to bind antigen and undergo further antigen dependent differentiation. The active immune response both cell mediated and humoral immunity begins. All of the secondary lymphoid organs a ...
... patches of the gut, and appendix. The secondary lymphoid organs are where mature T and B cells have the opportunity to bind antigen and undergo further antigen dependent differentiation. The active immune response both cell mediated and humoral immunity begins. All of the secondary lymphoid organs a ...
Medical Immunology
... increased expression of class II MHC and costimulatory B7. Antigen–BCR complexes are internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis and degraded to peptides, which are bound by class II MHC and presented as peptide–MHC complexes. Th cell recognizes Ag–class II MHC and B7-CD28 co-stimulation on Bcell ...
... increased expression of class II MHC and costimulatory B7. Antigen–BCR complexes are internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis and degraded to peptides, which are bound by class II MHC and presented as peptide–MHC complexes. Th cell recognizes Ag–class II MHC and B7-CD28 co-stimulation on Bcell ...
Cell Signaling
... • Amplifies the signal and provides numerous opportunities for cellular control, coordination, and regulation • Diversity of organisms with such similar pathways suggests that signal transduction pathways evolved from a common ancestor millions of ...
... • Amplifies the signal and provides numerous opportunities for cellular control, coordination, and regulation • Diversity of organisms with such similar pathways suggests that signal transduction pathways evolved from a common ancestor millions of ...
The Immune System - Mercer Island School District
... Types and Purposes of White Blood Cells Types: Neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. Neutrophils fight off bacterial or fungal infections, acting as the first responders. Basophils are responsible for allergic and antigen response by releasing a chemical hist ...
... Types and Purposes of White Blood Cells Types: Neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. Neutrophils fight off bacterial or fungal infections, acting as the first responders. Basophils are responsible for allergic and antigen response by releasing a chemical hist ...
1. Describe the first non-specific line of defense the
... B memory cells which bear receptors specific for that antigen for a long time - called “cloning selection” ...
... B memory cells which bear receptors specific for that antigen for a long time - called “cloning selection” ...
Transplants
... Purine analogs: These are relatives of the purines used in DNA synthesis. Because they interfere with DNA synthesis, they interfere with the rapid cell proliferation needed for immune responses. Unfortunately, these drugs also interfere with the many other tissues that depend on rapid cell division ...
... Purine analogs: These are relatives of the purines used in DNA synthesis. Because they interfere with DNA synthesis, they interfere with the rapid cell proliferation needed for immune responses. Unfortunately, these drugs also interfere with the many other tissues that depend on rapid cell division ...
What is Mathematical Biology and How Useful is It?
... Increasing susceptibility to many infectious diseases is highly associated with the loss or delay in the generation of antigen specific CD4+ T cells mediated immunity. For tuberculosis, where antigen specific CD4+ T cell derived IFN-g is essential, such a loss is associated with aging, and it can le ...
... Increasing susceptibility to many infectious diseases is highly associated with the loss or delay in the generation of antigen specific CD4+ T cells mediated immunity. For tuberculosis, where antigen specific CD4+ T cell derived IFN-g is essential, such a loss is associated with aging, and it can le ...
File
... An allergy is an __________________________________________ or reaction to substances that are generally ________________________. _________________________ are molecules involved in local, innate immune responses. These simple molecules trigger an _____________________________response to pathogen e ...
... An allergy is an __________________________________________ or reaction to substances that are generally ________________________. _________________________ are molecules involved in local, innate immune responses. These simple molecules trigger an _____________________________response to pathogen e ...
The Immune System and Disease Chapter 40 Page 1030
... When pathogens are detected, the immune system produces millions of white blood cells which fight the infection. Blood vessels near the wound expand, and white blood cells move from the vessels to enter the infected tissues. The infected tissue may become swollen and painful. The immune system ...
... When pathogens are detected, the immune system produces millions of white blood cells which fight the infection. Blood vessels near the wound expand, and white blood cells move from the vessels to enter the infected tissues. The infected tissue may become swollen and painful. The immune system ...
Physiology of the Blood III. White Blood Cells and the Immune
... 2. STRANGER CELLS and MOLECULES (transplantation, allergic reactions) 3. SELF CELLS (autoimmunity, tumor cells) 4. DANGER SIGNALS (e.g., after tissue injury) Enemy in general – e.g., differentiation of bacteria from self cells Enemy specifically – recognition of one particular bacterium or its subty ...
... 2. STRANGER CELLS and MOLECULES (transplantation, allergic reactions) 3. SELF CELLS (autoimmunity, tumor cells) 4. DANGER SIGNALS (e.g., after tissue injury) Enemy in general – e.g., differentiation of bacteria from self cells Enemy specifically – recognition of one particular bacterium or its subty ...
Stochastic Stage-structured Modeling of the Adaptive
... Immune response (studies of the immune response of organisms) ...
... Immune response (studies of the immune response of organisms) ...
Immune Response to HIV Infection
... Plasma Cells: derived from B cells, they produce antibodies to specific antigens marking them for destruction ...
... Plasma Cells: derived from B cells, they produce antibodies to specific antigens marking them for destruction ...
Adaptive Immune Response (Part II) (Antibody
... 1. To describe B-cells as the mediators of humoral immunity, (antibody-mediated immunity) 2. To describe activation of B-cells which involve: -Antigen recognition -T-dependent & T-independent antigens - Requirement for T-helper cells 3. To explain clonal selection, clonal expansion & generation of p ...
... 1. To describe B-cells as the mediators of humoral immunity, (antibody-mediated immunity) 2. To describe activation of B-cells which involve: -Antigen recognition -T-dependent & T-independent antigens - Requirement for T-helper cells 3. To explain clonal selection, clonal expansion & generation of p ...
factors
... Can be life threatening, so individuals should be aware • Skin tests – injection – see wheal and flare • Lab tests for circulating IgE ...
... Can be life threatening, so individuals should be aware • Skin tests – injection – see wheal and flare • Lab tests for circulating IgE ...