* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune Response to HIV Infection
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
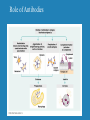
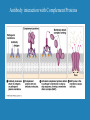
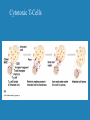
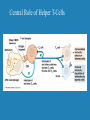
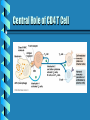
Immune Response to HIV Infection June 28, 2001 Ms. Jane Coyle-Morris Wyeth-Ayerst Research Immune Response to HIV Infection Immunology HIV Biology Immune Response to HIV Infection Role of Antibodies Antibody interaction with Complement Proteins Cytotoxic T-Cells Central Role of Helper T-Cells Macrophage Large, irregularly-shaped phagocytic cells that act as the body’s scavengers. Macrophages engulf and consume foreign material such as bacteria and viruses. T Cells Arise from stem cells in the bone marrow then migrate to the thymus gland where they develop the ability to recognize foreign antigens in a specific manner. Helper T Cells (TH) Detect infection and initiate both humoral and cell-mediated responses (CD4 cells) Cytotoxic T Cells (TC) Recruited by TH to lyse infected body cells (CD8 cells) Cell Marker Proteins CD4: cell marker found on the surface of TH and macrophages; acts as a receptor for HIV CD8: cell marker found on the surface of TC B Cells and Plasma Cells B Cells: precursors of plasma cells, specialized to recognize particular foreign antigens Plasma Cells: derived from B cells, they produce antibodies to specific antigens marking them for destruction Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Proteins markers found on the surface of the body’s cells to signal “self” from “nonself”. MHC-I can be found on every cell in the body while MHC-II is found only on B cells, T cells and macrophages. Cytokines Soluble proteins secreted by the cells of the immune system to signal activation and proliferation of the appropriate components of the immune response. IL-1 is released from macrophages and signals activation of T cells. Activated T cells produce IL-2 which signals proliferation of T cell clones and also helps B cells to start secreting antibodies. Cytokines The Immune Response Central Role of CD4 T Cell HIV Biology HIV in Action Natural Course of HIV Infection Overview Immune Response to HIV Infection Immunology: humoral vs. cell-mediated HIV biology: complex series of events leading to viral entry and course of infection; evasion of immune system Immune response to HIV: weak humoral response, strong cell-mediated response diminished over time by depletion of helper T-cells AIDS/HIV Internet Sites Www.ama-assn.org/special/hiv/hivhome.htm www.planetq.com/aidsvl/index.html www.thebody.com/cgi-bin/body.cgi www.cdc.gov/ www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/aids/ www.roche-hiv.com/default.htm