Document
... The Complement System • Serum proteins activated in a cascade • Activated via one of three pathways • Activated Complement proteins trigger 3 primary immune responses ...
... The Complement System • Serum proteins activated in a cascade • Activated via one of three pathways • Activated Complement proteins trigger 3 primary immune responses ...
546-547 Research Highlights WF SA.indd
... The authors took radio measurements at three-month intervals for a year and combined them with archival data. They reveal that the star–hole system, known as V404 Cygni, is just 2,390 parsecs from Earth — nearly half the distance previously thought. The group believes that the previous work underest ...
... The authors took radio measurements at three-month intervals for a year and combined them with archival data. They reveal that the star–hole system, known as V404 Cygni, is just 2,390 parsecs from Earth — nearly half the distance previously thought. The group believes that the previous work underest ...
Immunity
... • Non specific = first (skin) and second (inflammatory response) line of defenses; are effective against many different kinds of pathogens • Specific = third line (white blood cells) are effective against a specific pathogen ...
... • Non specific = first (skin) and second (inflammatory response) line of defenses; are effective against many different kinds of pathogens • Specific = third line (white blood cells) are effective against a specific pathogen ...
Riggs_Signal_Transduction-_PAMP_Presentation[1]
... INNATE IMMUNITY There are many types of pattern recognition receptors in different locations in tissues that respond to invading organisms Recognition molecules are expressed by: ...
... INNATE IMMUNITY There are many types of pattern recognition receptors in different locations in tissues that respond to invading organisms Recognition molecules are expressed by: ...
Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary
... Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary immune response begins when an antigen penetrates epithelial surfaces. It will eventually come into contact with macrophages or certain other classes of Antigen Presenting cells (APCs), which include B cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, La ...
... Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary immune response begins when an antigen penetrates epithelial surfaces. It will eventually come into contact with macrophages or certain other classes of Antigen Presenting cells (APCs), which include B cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, La ...
the-immune-system-part-4-teacher-notes
... Antihistamines: drugs for allergies that reduce symptoms Severe allergies may trigger anaphylactic shock o Swelling, breathing problems, potential death o Adrenaline injection reduces symptoms (“Epipen”) ...
... Antihistamines: drugs for allergies that reduce symptoms Severe allergies may trigger anaphylactic shock o Swelling, breathing problems, potential death o Adrenaline injection reduces symptoms (“Epipen”) ...
Adv
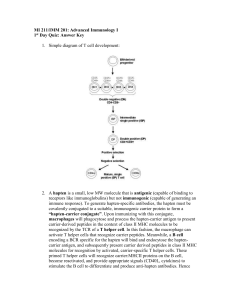
... 2. A hapten is a small, low MW molecule that is antigenic (capable of binding to receptors like immunoglobulins) but not immunogenic (capable of generating an immune response). To generate hapten-specific antibodies, the hapten must be covalently conjugated to a suitable, immunogenic carrier protein ...
... 2. A hapten is a small, low MW molecule that is antigenic (capable of binding to receptors like immunoglobulins) but not immunogenic (capable of generating an immune response). To generate hapten-specific antibodies, the hapten must be covalently conjugated to a suitable, immunogenic carrier protein ...
Chapter 13: Lymphatics
... 18. What do Cytotoxic CD8+ cells do? 19. What is the origin of “B” in the designation of B-cells? Which organs “educate” Bcells in humans? 20. What do B-cells secrete? 21. What is the special action of NK cells? What do they secrete? 22. What is apotosis? 23. Name the primary lymphatic organs in hu ...
... 18. What do Cytotoxic CD8+ cells do? 19. What is the origin of “B” in the designation of B-cells? Which organs “educate” Bcells in humans? 20. What do B-cells secrete? 21. What is the special action of NK cells? What do they secrete? 22. What is apotosis? 23. Name the primary lymphatic organs in hu ...
The immune system - Mount Mansfield Union High School
... into different types of blood cells Travel through both blood and lymphatic systems, pass from blood through lymph nodes, pass from lymphatic system through thoracic duct Two types ...
... into different types of blood cells Travel through both blood and lymphatic systems, pass from blood through lymph nodes, pass from lymphatic system through thoracic duct Two types ...
File - Westside High School Science Portal
... SC.912.L.14.52 Explain the basic functions of the human immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics. The human immune system has two levels of immunity: specific and nonspecific immunity. Through non-specific immunity, also called innate immunity, the human body protects itself against foreign materi ...
... SC.912.L.14.52 Explain the basic functions of the human immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics. The human immune system has two levels of immunity: specific and nonspecific immunity. Through non-specific immunity, also called innate immunity, the human body protects itself against foreign materi ...
Document
... complement system. Role in disease. Modulation by infections. 4. Immunoglobulins. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. Development and differentiation of B cells. Immunoglobulin diversity. Antibody deficiencies. 5. T lymphocytes –the immunological orchestra conductor. T cell receptors. Develop ...
... complement system. Role in disease. Modulation by infections. 4. Immunoglobulins. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. Development and differentiation of B cells. Immunoglobulin diversity. Antibody deficiencies. 5. T lymphocytes –the immunological orchestra conductor. T cell receptors. Develop ...
3.6 Immune System
... 6. Pus around a cut may look bad, but it is a good sign. Explain why. 7. Describe the difference between the first and second lines of defense. 8. What type of blood cells are involved in the acquired immune response? 9. What is the function of antibodies? ...
... 6. Pus around a cut may look bad, but it is a good sign. Explain why. 7. Describe the difference between the first and second lines of defense. 8. What type of blood cells are involved in the acquired immune response? 9. What is the function of antibodies? ...
Immune_System_2016_Z - Kenston Local Schools
... • Neutrophils "eat" pathogens and send off distress signals. • Monocytes are triggered to turn into pathogen-eating macrophages. • Eosinophils attack parasites • Basophils contain granules filled with histamine and other compounds related to allergies. • The second set of cells — the lymphocytes — ...
... • Neutrophils "eat" pathogens and send off distress signals. • Monocytes are triggered to turn into pathogen-eating macrophages. • Eosinophils attack parasites • Basophils contain granules filled with histamine and other compounds related to allergies. • The second set of cells — the lymphocytes — ...
1. dia - immunology.unideb.hu
... „yet it was with those who recovered from the disease that the sick and the dying found most compassion……. No fear for themselves; as no man was never attacked twice – never at least fatally” ...
... „yet it was with those who recovered from the disease that the sick and the dying found most compassion……. No fear for themselves; as no man was never attacked twice – never at least fatally” ...
Aankondiging_Immuno_7nov
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... T-helper cells – secrete CYTOKINES help B cells divide stimulate macrophages • Cytotoxic T cells (killer T cells) Kill body cells displaying antigen • Memory T cells remain in body ...
... T-helper cells – secrete CYTOKINES help B cells divide stimulate macrophages • Cytotoxic T cells (killer T cells) Kill body cells displaying antigen • Memory T cells remain in body ...
Langerhans` cells can take up antigen in the skin and migrate to
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
Immune Responses
... blood and lymph nodes. Lymphocytes recognize antigen molecules on the surface of pathogens, and coordinate the immune response against that pathogen. Collectively, lymphocytes can recognize millions of different antigens, due to the large variation of lymphocytes produced. ...
... blood and lymph nodes. Lymphocytes recognize antigen molecules on the surface of pathogens, and coordinate the immune response against that pathogen. Collectively, lymphocytes can recognize millions of different antigens, due to the large variation of lymphocytes produced. ...



![Riggs_Signal_Transduction-_PAMP_Presentation[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008651685_1-7a9da834997c5984d78c99bc734baadf-300x300.png)