Next, a bit about antigens (Ag`s)…
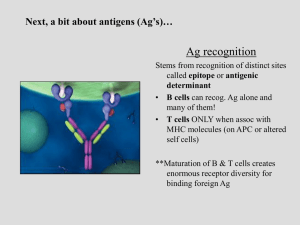
... Ag recognition Stems from recognition of distinct sites called epitope or antigenic determinant • B cells can recog. Ag alone and many of them! • T cells ONLY when assoc with MHC molecules (on APC or altered self cells) **Maturation of B & T cells creates enormous receptor diversity for binding fore ...
... Ag recognition Stems from recognition of distinct sites called epitope or antigenic determinant • B cells can recog. Ag alone and many of them! • T cells ONLY when assoc with MHC molecules (on APC or altered self cells) **Maturation of B & T cells creates enormous receptor diversity for binding fore ...
L18, Part 2: Immunune System, continued
... Signal 1: CD8 T cell recognizes antigen in MHC I on dendritic cell ...
... Signal 1: CD8 T cell recognizes antigen in MHC I on dendritic cell ...
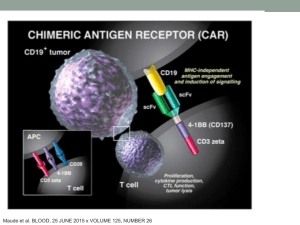
CAR T cell lecture 11.25
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
Boosting the immune system by giving T cells a push By
... Specifically CD4 T cells. And it turns out that the help has to come from a specialized type of CD4 T cell: a T follicular helper cell, Tfh. Since Tfh cells are required for most antibody responses, it is valuable to understand what triggers Tfh cell development. ...
... Specifically CD4 T cells. And it turns out that the help has to come from a specialized type of CD4 T cell: a T follicular helper cell, Tfh. Since Tfh cells are required for most antibody responses, it is valuable to understand what triggers Tfh cell development. ...
The Immune System - Holy Angels School
... • Immunity can also result from being infected with a disease or from being vaccinated. • Once a body has found a pathogen, the body produces memory cells. • Memory cells are T cells and B cells that remember specific pathogens. • A vaccination is a substance prepared from killed or weakened pathoge ...
... • Immunity can also result from being infected with a disease or from being vaccinated. • Once a body has found a pathogen, the body produces memory cells. • Memory cells are T cells and B cells that remember specific pathogens. • A vaccination is a substance prepared from killed or weakened pathoge ...
Immune system and allergies
... • Phagocytes (Fay-go-sites): white blood cells that surround, destroy, and digest invading organisms. ...
... • Phagocytes (Fay-go-sites): white blood cells that surround, destroy, and digest invading organisms. ...
... leads to immune response also in other compartments of MALT. • IgA is a predominant immunoglobulin secreted through the epitelial cells. • Oral administration of antigens frequently leads to induction of immune tolerance. • Intraepitelial lymphocytes - CD8+, restricted antigenic specificity. ...
Immune System
... Foreign antigens bind to antibodies on B-cells Antigen-antibody complex stimulation Stimulated B-cell will produce/release this specific antibody as free floating antibody 5. Free floating antibodies will bind to all other antigens of the same type 6. Macrophages recognize antibodies and phagocytosi ...
... Foreign antigens bind to antibodies on B-cells Antigen-antibody complex stimulation Stimulated B-cell will produce/release this specific antibody as free floating antibody 5. Free floating antibodies will bind to all other antigens of the same type 6. Macrophages recognize antibodies and phagocytosi ...
IN RESPONSE TO DAMAGE Innate, or nonspecific, immunity
... II MHC molecules, which then present the antigen to T helper cells. The T helper cells bind the presented antigen, which stimulates the T helper cells to divide and secrete stimulatory molecules called interleukins. The interleukins in turn activate any B lymphocytes that have also bound the antigen ...
... II MHC molecules, which then present the antigen to T helper cells. The T helper cells bind the presented antigen, which stimulates the T helper cells to divide and secrete stimulatory molecules called interleukins. The interleukins in turn activate any B lymphocytes that have also bound the antigen ...
Study guid Ch 15
... How are helper T cells activated? What kind of cell activates them and how does that cell present the antigenic peptide? What are the regions of the T cell receptor? What part of the receptor binds to and recognizes the antigen? Why do you think it’s important that this region is variable and unique ...
... How are helper T cells activated? What kind of cell activates them and how does that cell present the antigenic peptide? What are the regions of the T cell receptor? What part of the receptor binds to and recognizes the antigen? Why do you think it’s important that this region is variable and unique ...
immune practice test
... Organ taken from another animal species. Ex. transplanting a baboon heart into a human. ...
... Organ taken from another animal species. Ex. transplanting a baboon heart into a human. ...
Topic 19 - Roslyn Public Schools
... • (a) B-cell – produce antibodies that destroy invading microbes or pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, and parasite) – each pathogen triggers a different response – there are millions of different pathogens so there are millions of different B-cells in the blood • (b) T-cells – there are two ty ...
... • (a) B-cell – produce antibodies that destroy invading microbes or pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, and parasite) – each pathogen triggers a different response – there are millions of different pathogens so there are millions of different B-cells in the blood • (b) T-cells – there are two ty ...
The Immune System: Video Response Notes Part 1
... 9. What is a major role of dendritic cells in fighting the influenza-B virus? 10. Where are T-cells located? 11. What is the role of the T-cell in fighting infection? ...
... 9. What is a major role of dendritic cells in fighting the influenza-B virus? 10. Where are T-cells located? 11. What is the role of the T-cell in fighting infection? ...
Organism Physiology Immunity
... have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Campbell’s Biology 9th edition The Immune System Questions to Answer: 1. Why are defense systems needed in multi ...
... have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Campbell’s Biology 9th edition The Immune System Questions to Answer: 1. Why are defense systems needed in multi ...
Specific Immunity POGIL
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
BSC 361
... Mononuclear cells-includes lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages Immune response and disease: Many of the symptoms associated with microbial infection are caused by host immune response Fever, inflammation, change in blood pressure We are now beginning to examine if it is best to treat symptoms or ...
... Mononuclear cells-includes lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages Immune response and disease: Many of the symptoms associated with microbial infection are caused by host immune response Fever, inflammation, change in blood pressure We are now beginning to examine if it is best to treat symptoms or ...
B Cell - Biotechnology
... Each V, D and J is flanked by RSS (Recombination signal sequences) Mechanism is controlled by RAG-1 and RAG-2 proteins and an enzyme TdT If any of these proteins is defective no mature B cells can form; nor T cells ...
... Each V, D and J is flanked by RSS (Recombination signal sequences) Mechanism is controlled by RAG-1 and RAG-2 proteins and an enzyme TdT If any of these proteins is defective no mature B cells can form; nor T cells ...
Gene Therapy by calisa and carmen
... delivered using a carrier, called a vector. Commonly used as vectors are viruses because they can recognise certain cells and carry genetic material into the cells genes. ...
... delivered using a carrier, called a vector. Commonly used as vectors are viruses because they can recognise certain cells and carry genetic material into the cells genes. ...
Dental Microbiology #211 IMMUNOLOGY Lecture 1
... Antibodies are specific i.e. they react with, and bind to the antigen molecule that induced their production. Interaction between the antigen and antibody occurs both in vitro and in vivo ...
... Antibodies are specific i.e. they react with, and bind to the antigen molecule that induced their production. Interaction between the antigen and antibody occurs both in vitro and in vivo ...