Natural Defence - MedicalBooks.com
... system spring into action. Some of these defenses are effective against a variety of invaders, while others are tailor-made to fight a specific organism. White blood cells called phagocytes constantly travel through the bloodstream on the lookout for foreign objects. If they come upon a microorganis ...
... system spring into action. Some of these defenses are effective against a variety of invaders, while others are tailor-made to fight a specific organism. White blood cells called phagocytes constantly travel through the bloodstream on the lookout for foreign objects. If they come upon a microorganis ...
Abrams Presentation for 11/22 and 11/29
... • induced on target cells as a result of DNA damage, infection, etc., leading to downregulation of conventional MHC molecules • induction of stress-induced ligands in concert with the loss of MHC expression culminates in NK activation ...
... • induced on target cells as a result of DNA damage, infection, etc., leading to downregulation of conventional MHC molecules • induction of stress-induced ligands in concert with the loss of MHC expression culminates in NK activation ...
Chapter 15
... 1. Compete with pathogens or alter the environment 2. Members often produce compounds that are toxic to other microbes, thereby preventing their growth. • In hair follicles, normal flora break down lipids of body secretions releasing fatty acids that inhibit pathogen ...
... 1. Compete with pathogens or alter the environment 2. Members often produce compounds that are toxic to other microbes, thereby preventing their growth. • In hair follicles, normal flora break down lipids of body secretions releasing fatty acids that inhibit pathogen ...
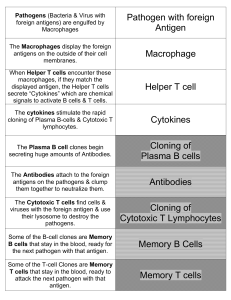
Pathogens (Bacteria with foreign antigens) are
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
part-3-and-4-immune-system-second-line-of
... o This binding either ____________ pathogen from ____________ a body cell or ____________ the pathogen for ________________ More B cells are produced to help with anti_________ production and attachment Some _______________ will remain in body to protect against further attack (___________) ________ ...
... o This binding either ____________ pathogen from ____________ a body cell or ____________ the pathogen for ________________ More B cells are produced to help with anti_________ production and attachment Some _______________ will remain in body to protect against further attack (___________) ________ ...
Immune System Period 1 - Mercer Island School District
... The main organs (or cell types) of this system and the function of each part At least one example of how this system helps to maintain homeostasis in the body Explanation of how the system works with other systems (some specified below) A description of at least 2 disorders/diseases that can affect ...
... The main organs (or cell types) of this system and the function of each part At least one example of how this system helps to maintain homeostasis in the body Explanation of how the system works with other systems (some specified below) A description of at least 2 disorders/diseases that can affect ...
nonspecific defense
... ex. infectious agents, foreign cells, even abnormal body cells (cancer). ...
... ex. infectious agents, foreign cells, even abnormal body cells (cancer). ...
Chapter 19
... • Binary fission: (asexual) DNA is replicated and the organism splits in half • Conjugation: (sexual) genetic info is exchanged across a “bridge” ...
... • Binary fission: (asexual) DNA is replicated and the organism splits in half • Conjugation: (sexual) genetic info is exchanged across a “bridge” ...
09.13.10 Lecture Cells and Size
... some cells have very long extensions ex. long ultra thin projections of nerve cells allow sending/receiving chemical signals from/to distant tissues ...
... some cells have very long extensions ex. long ultra thin projections of nerve cells allow sending/receiving chemical signals from/to distant tissues ...
Document
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
The Immune System
... These problems can arise from congenital factors in which blood cells are insufficient or inefective. › Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease Fail to develop mature T and B cells ...
... These problems can arise from congenital factors in which blood cells are insufficient or inefective. › Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease Fail to develop mature T and B cells ...
Innate immunity/ cont…II.Second line: 2.Phagocytosis:
... Phagocytosis: Phagocytes (eating cells) are body cells specialized for capture, ingestion and destruction of antigens (as bacteria and fungi), debris, and produce inflammatory molecules which regulate other components of the immune system. They express a wide range of surface receptors that allow th ...
... Phagocytosis: Phagocytes (eating cells) are body cells specialized for capture, ingestion and destruction of antigens (as bacteria and fungi), debris, and produce inflammatory molecules which regulate other components of the immune system. They express a wide range of surface receptors that allow th ...
Immunity in the gut
... and other glycoproteins that can interact with and trap bacteria in the mucus. In addition, antimicrobial peptides such as defensins are secreted by Paneth cells located at the bottom of the intestinal crypts. Epithelial cells also act as microbial sensors by secreting factors such as IL-8, MCP-1, R ...
... and other glycoproteins that can interact with and trap bacteria in the mucus. In addition, antimicrobial peptides such as defensins are secreted by Paneth cells located at the bottom of the intestinal crypts. Epithelial cells also act as microbial sensors by secreting factors such as IL-8, MCP-1, R ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... invading microorganisms by phagocytosis where lymphocytes are specific to one antigen Phagocytes are involved in innate and adaptive. Lymphocytes are only involved in adaptive ...
... invading microorganisms by phagocytosis where lymphocytes are specific to one antigen Phagocytes are involved in innate and adaptive. Lymphocytes are only involved in adaptive ...
Immune Worksheet Key Session 26
... 1) What are the specific responses or actions taken by the following immune cells? Natural Killer Cells: target cells without “self” cell-surface receptors Eosinophils: target allergens, parasites Basophils: release histamine, heparin (inflammation) Mast Cells: induce inflammation Dendritic Cells: a ...
... 1) What are the specific responses or actions taken by the following immune cells? Natural Killer Cells: target cells without “self” cell-surface receptors Eosinophils: target allergens, parasites Basophils: release histamine, heparin (inflammation) Mast Cells: induce inflammation Dendritic Cells: a ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑