The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases
... 1st Defense is the Skin and Mucus 2nd Defense occurs when injured cells release chemicals that increase blood flow to an area (cut or scrape). The blood brings Macrophage: a white blood cell that engulfs and kills pathogens • 3rd Defense macrophages along with T cells and B cells attach and kill inf ...
... 1st Defense is the Skin and Mucus 2nd Defense occurs when injured cells release chemicals that increase blood flow to an area (cut or scrape). The blood brings Macrophage: a white blood cell that engulfs and kills pathogens • 3rd Defense macrophages along with T cells and B cells attach and kill inf ...
Immune System Crossword PARA3002
... spaces and initiate local inflammatory responses against them; typically found clustered deep to an epithelium or along blood vessels. 12. Protective cell type common in connective tissue, lymphoid tissue, and many body organs; phagocytizes tissue cells, bacteria, and other foreign debris; presents ...
... spaces and initiate local inflammatory responses against them; typically found clustered deep to an epithelium or along blood vessels. 12. Protective cell type common in connective tissue, lymphoid tissue, and many body organs; phagocytizes tissue cells, bacteria, and other foreign debris; presents ...
Innate Immunity Chapter Study Questions
... Describe and understand the functions of the soluble mediators and the membrane-associated receptors a. Table 3-2 b. Acute phase response c. Pattern recognition molecules d. TLRs Name and describe the functions of the various cell types involved in innate immunity. Discuss the ubiquity of innate imm ...
... Describe and understand the functions of the soluble mediators and the membrane-associated receptors a. Table 3-2 b. Acute phase response c. Pattern recognition molecules d. TLRs Name and describe the functions of the various cell types involved in innate immunity. Discuss the ubiquity of innate imm ...
43 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 3. Contrast the roles of the nonspecific cellular defenses. [2 points] a. Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens b. NK cells punch virus-infected and cancerous cells 4. Rationalize the four cardinal signs of an acute inflammatory response. a. Histamine and kinins released b. Increased blood flow ca ...
... 3. Contrast the roles of the nonspecific cellular defenses. [2 points] a. Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens b. NK cells punch virus-infected and cancerous cells 4. Rationalize the four cardinal signs of an acute inflammatory response. a. Histamine and kinins released b. Increased blood flow ca ...
Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Tropical Medicine
... initiation of CD8+ T cell response in the gut • Is NK-DC interaction critical for induction of robust CD8+ T cell immunity • Can long term central memory CD8+ T cell response be generated • What is the role of cytokines like IL-7 and IL-15 in the generation and maintenance of CD8+ T cell immunity in ...
... initiation of CD8+ T cell response in the gut • Is NK-DC interaction critical for induction of robust CD8+ T cell immunity • Can long term central memory CD8+ T cell response be generated • What is the role of cytokines like IL-7 and IL-15 in the generation and maintenance of CD8+ T cell immunity in ...
Chapter 21 - Fundamentals of Microbiology
... Chapter 21 continues to look at the immune system. Then the immune system is discussed as the center of specific resistance. A major section is devoted to the antigen–antibody reaction because it is fundamental to immunology. On completing the chapter, you should be able to answer the following essa ...
... Chapter 21 continues to look at the immune system. Then the immune system is discussed as the center of specific resistance. A major section is devoted to the antigen–antibody reaction because it is fundamental to immunology. On completing the chapter, you should be able to answer the following essa ...
Immune_System_2016_Z - Kenston Local Schools
... First lines of defense saliva antibacterial enzymes skin prevents entry stomach acid low pH kills harmful microbes ...
... First lines of defense saliva antibacterial enzymes skin prevents entry stomach acid low pH kills harmful microbes ...
"ISG15 regulates peritoneal macrophage functionality against viral
... upregulation of IFN stimulated genes (ISGs) generate an antiviral state with an important role in the activation of innate and adaptive host immune responses. The ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) ISG15 is a critical IFN-induced antiviral molecule that protects against several viral infections, but the m ...
... upregulation of IFN stimulated genes (ISGs) generate an antiviral state with an important role in the activation of innate and adaptive host immune responses. The ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) ISG15 is a critical IFN-induced antiviral molecule that protects against several viral infections, but the m ...
Lecture Notes: Immune System (Part I)
... 9. Infection granulomas are tumorlike growths containing macrophages infected by pathogens “hiding” within it surrounded by uninfected macrophages and an outer fibrous capsule. 10. Antimicrobial proteins i. attack microorganisms directly or inhibit their ability to reproduce ii. interferon a. differ ...
... 9. Infection granulomas are tumorlike growths containing macrophages infected by pathogens “hiding” within it surrounded by uninfected macrophages and an outer fibrous capsule. 10. Antimicrobial proteins i. attack microorganisms directly or inhibit their ability to reproduce ii. interferon a. differ ...
Reading Guide-InnateImmune (CH15)
... digestive tract, are coated with secretions to continually wash the microbes from the surface. There are additional structures to help remove bacteria, the cilia in the respiratory tract, and peristalsis in the digestive tract. Many of the secretions found in these areas also have antimicrobial subs ...
... digestive tract, are coated with secretions to continually wash the microbes from the surface. There are additional structures to help remove bacteria, the cilia in the respiratory tract, and peristalsis in the digestive tract. Many of the secretions found in these areas also have antimicrobial subs ...
Chapter 18 Answers to Even Numbered Study Questions
... The normal flora is commonly considered a mutualistic symbiosis, that benefits the host by protecting it from colonization by other, less benign, microbes. However, members of the normal flora can cause disease if they get into the wrong place, or if the local ecology is disturbed. ...
... The normal flora is commonly considered a mutualistic symbiosis, that benefits the host by protecting it from colonization by other, less benign, microbes. However, members of the normal flora can cause disease if they get into the wrong place, or if the local ecology is disturbed. ...
Unit Question: What is life and how does it maintain balance? Notes
... 3. Antibodies have receptors on their cell membranes that recognize and bind to the antigens. ...
... 3. Antibodies have receptors on their cell membranes that recognize and bind to the antigens. ...
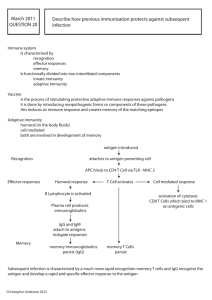
ANTIBODY PRODUCTION
... Antigens from the ruined pathogen are displayed on the surface of the phagocyte (or B-cell), bound to a membrane called MHC protein. This combination of antigen and MHC attracts the help of a mature, matching Helper T Cell. ...
... Antigens from the ruined pathogen are displayed on the surface of the phagocyte (or B-cell), bound to a membrane called MHC protein. This combination of antigen and MHC attracts the help of a mature, matching Helper T Cell. ...
Lines of Defense - Trinity Christian School
... Monocytes follow the neutrophils into the area 3. Within 8-12 hours the monocytes develop into ...
... Monocytes follow the neutrophils into the area 3. Within 8-12 hours the monocytes develop into ...
Immune Response
... called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
... called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
The Immune System : (page 382) Recognizes and destroys
... system. Immunity is the ability to resist disease once exposed to it in the past. Body defences can be divided into 2 groups Non-specific defences : guard against a wide range of “pathogens” (disease causing agents), do not need earlier exposure. First line of defence - the skin ( outer dry layers r ...
... system. Immunity is the ability to resist disease once exposed to it in the past. Body defences can be divided into 2 groups Non-specific defences : guard against a wide range of “pathogens” (disease causing agents), do not need earlier exposure. First line of defence - the skin ( outer dry layers r ...
Media Release Unravelling the mysteries of the Natural Killer within
... Unravelling the mysteries of the Natural Killer within us Scientists have discovered more about the intricacies of the immune system in a breakthrough that may help combat viral infections such as HIV. Co-led by Professor Jamie Rossjohn of Monash University and Associate Professor Andrew Brooks from ...
... Unravelling the mysteries of the Natural Killer within us Scientists have discovered more about the intricacies of the immune system in a breakthrough that may help combat viral infections such as HIV. Co-led by Professor Jamie Rossjohn of Monash University and Associate Professor Andrew Brooks from ...
Matching – Each question is worth 0.5 pt
... They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. They consist of polypeptides with variable and constant regions. They are associated with signal transduction molecules at the cell surface. They can interact wi ...
... They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. They consist of polypeptides with variable and constant regions. They are associated with signal transduction molecules at the cell surface. They can interact wi ...
MICROBIO320 Short Answers – These should be typically 1
... The antigen binding specificity of an antibody is due to: (0.5 pt) A. the constant regions of the light chains B. the variable framework regions of the heavy & light chains C. the variable regions of the heavy chains D. the hypervariable regions of both heavy & light chains E. All of the above The f ...
... The antigen binding specificity of an antibody is due to: (0.5 pt) A. the constant regions of the light chains B. the variable framework regions of the heavy & light chains C. the variable regions of the heavy chains D. the hypervariable regions of both heavy & light chains E. All of the above The f ...
Unit 8 Communicable Diseases
... It’s a network of cells, tissues, organs, and chemicals that fight off pathogens. ...
... It’s a network of cells, tissues, organs, and chemicals that fight off pathogens. ...
How does my immune system react when I puncture my skin on
... Then, the MHCII/antigen complex moves to the cell surface and presents to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds ...
... Then, the MHCII/antigen complex moves to the cell surface and presents to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds ...
File
... -Example 2: Tears and saliva contain the enzyme Lysozyme which digests the cell walls of bacteria and destroys them -Example 3: Mucous membranes secrete sticky mucus which traps microbes -Example 4: The epithelial lining of the stomach secretes acid which destroys microbes ...
... -Example 2: Tears and saliva contain the enzyme Lysozyme which digests the cell walls of bacteria and destroys them -Example 3: Mucous membranes secrete sticky mucus which traps microbes -Example 4: The epithelial lining of the stomach secretes acid which destroys microbes ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑