Chapter 14: Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity
... • Serum is the fluid part of blood, containing: • minerals • salts • proteins, etc. • Plasma is serum that contains clotting agents • Leukocytes (white blood cells) are produced in the bone marrow • Neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes [PMNs]) are phagocytes • Eosinophils contain toxic compound ...
... • Serum is the fluid part of blood, containing: • minerals • salts • proteins, etc. • Plasma is serum that contains clotting agents • Leukocytes (white blood cells) are produced in the bone marrow • Neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes [PMNs]) are phagocytes • Eosinophils contain toxic compound ...
Q9 Describe how the body defends against infection
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
Immunology 3 – Innate Immunity
... Phagocyte deficiency is associated with infections due to extracellular bacteria and fungi. Macrophages - when blood monocytes enter tissues they become tissue macrophages. ...
... Phagocyte deficiency is associated with infections due to extracellular bacteria and fungi. Macrophages - when blood monocytes enter tissues they become tissue macrophages. ...
Lecture #23 - Suraj @ LUMS
... membranes. • The skin is a passive barrier to infectious agents such as bacteria and viruses. • Tears and saliva secrete enzymes that breakdown bacterial cell walls. Skin glands secrete chemicals that retard the growth of bacteria. • Mucus membranes lining the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and re ...
... membranes. • The skin is a passive barrier to infectious agents such as bacteria and viruses. • Tears and saliva secrete enzymes that breakdown bacterial cell walls. Skin glands secrete chemicals that retard the growth of bacteria. • Mucus membranes lining the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and re ...
An immune system is a collection of mechanisms within an organism
... pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess enzyme systems that protect against viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants, fish, reptiles, and insects. These mechanisms include antimi ...
... pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess enzyme systems that protect against viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants, fish, reptiles, and insects. These mechanisms include antimi ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
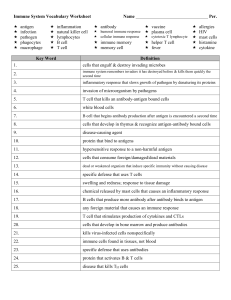
Immune System Review Worksheet
... B cells that produce more antibody after antibody binds to antigen ...
... B cells that produce more antibody after antibody binds to antigen ...
Chapter 40 review notes
... -diseases are spread either by person to person contact, contaminated water or food, or infected animals -STD’s dangerous pathogens spread by sexual contact -antibiotics kill bacteria without harming the cells of humans or animals 40-2 The Immune System -The body first line of defense is to keep pat ...
... -diseases are spread either by person to person contact, contaminated water or food, or infected animals -STD’s dangerous pathogens spread by sexual contact -antibiotics kill bacteria without harming the cells of humans or animals 40-2 The Immune System -The body first line of defense is to keep pat ...
Section Assignment 1.3 Part C: Defence Systems
... Cells that attack and destroy bacteria and viruses Ability of the body to protect itself from invaders and disease-causing agents Foreign objects, living or non-living, found on or in the body Once antibodies have been produced for a certain antigen or pathogen, the body keeps some extras to guard a ...
... Cells that attack and destroy bacteria and viruses Ability of the body to protect itself from invaders and disease-causing agents Foreign objects, living or non-living, found on or in the body Once antibodies have been produced for a certain antigen or pathogen, the body keeps some extras to guard a ...
Nonspecific Defenses
... Macrophages and Cytokines • Macrophages: in tissues, that devour many pathogens and survive • Have receptors that allow them to recognize the presence of pathogens • Release cytokines • Cytokines: chemical signals that stimulate other white cells such as neutrophils and monocytes, that then mature ...
... Macrophages and Cytokines • Macrophages: in tissues, that devour many pathogens and survive • Have receptors that allow them to recognize the presence of pathogens • Release cytokines • Cytokines: chemical signals that stimulate other white cells such as neutrophils and monocytes, that then mature ...
Foundation Block Lecture Two Natural defense mechanism
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
Cell Signalling and communication between cells.
... • Cell signalling is vital in the immune system, it helps to activate all the different types of white blood cells that are needed. Communication is achieved through cell surface molecules, and through the release of hormonelike chemicals called ‘cytokines’. To be able to detect these molecules the ...
... • Cell signalling is vital in the immune system, it helps to activate all the different types of white blood cells that are needed. Communication is achieved through cell surface molecules, and through the release of hormonelike chemicals called ‘cytokines’. To be able to detect these molecules the ...
Reading Worksheet KEY 6.4, pg 250 6.4_rw_key
... 1. What is the body’s largest organ? The skin 2. Define pathogen: any disease causing micro organisms 3. Name 5 “natural doors” into the body. Mouth, nose, ears, eyes, genitals 4. What is the first line of defense in the immune system? Saliva, tears, sweat, mucus 5. What does a plant do to protect i ...
... 1. What is the body’s largest organ? The skin 2. Define pathogen: any disease causing micro organisms 3. Name 5 “natural doors” into the body. Mouth, nose, ears, eyes, genitals 4. What is the first line of defense in the immune system? Saliva, tears, sweat, mucus 5. What does a plant do to protect i ...
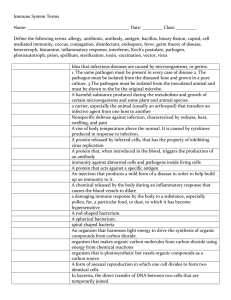
Immunity Questions
... The Immune System 1. Identify and describe three external defenses of the human body. 2. How do the words innate and acquired relate to when these types of immunity develop in a human body? 3. Describe the function of the following cells and chemicals of the innate immune system: macrophages, natura ...
... The Immune System 1. Identify and describe three external defenses of the human body. 2. How do the words innate and acquired relate to when these types of immunity develop in a human body? 3. Describe the function of the following cells and chemicals of the innate immune system: macrophages, natura ...
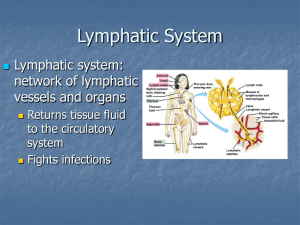
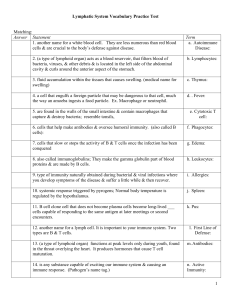
Lymphatic Review Sheet
... -4 cardinal signs are: _________________________________________ 3. 3rd line of defense is specific/nonspecific and is called the ___________________________. -Special about the immune system is that it acts slower/faster. -Makes two types of lymphocytes: __________________ and ____________________ ...
... -4 cardinal signs are: _________________________________________ 3. 3rd line of defense is specific/nonspecific and is called the ___________________________. -Special about the immune system is that it acts slower/faster. -Makes two types of lymphocytes: __________________ and ____________________ ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑