Functional interaction between a novel protein phosphatase 2A
... inhibit PP2A, but not PP1 (Cohen et al., 1989; Honkanan et al., 1994). Figure 3c shows that the phosphatase activity in immunoprecipitates of the HAPR65 and the HA-PP2Ac-transfected cells could be inhibited by this concentration of okadaic acid, strongly suggesting that the phosphatase activity seen ...
... inhibit PP2A, but not PP1 (Cohen et al., 1989; Honkanan et al., 1994). Figure 3c shows that the phosphatase activity in immunoprecipitates of the HAPR65 and the HA-PP2Ac-transfected cells could be inhibited by this concentration of okadaic acid, strongly suggesting that the phosphatase activity seen ...
eXtra Botany - Journal of Experimental Botany
... 2009). Consequently, current data from genetic and biochemical approaches suggest a model in which development of specific plant cells and tissues is characterized by the expression of distinct tubulin genes and, consequently, by the use of distinct tubulin isotypes, which are post-translationally m ...
... 2009). Consequently, current data from genetic and biochemical approaches suggest a model in which development of specific plant cells and tissues is characterized by the expression of distinct tubulin genes and, consequently, by the use of distinct tubulin isotypes, which are post-translationally m ...
Structure and function of steroid receptor AF1 transactivation domains
... intracellular receptor proteins. These receptors function as ligandactivated transcription factors, switching on or off networks of genes in response to a specific hormone signal. The receptor proteins have a conserved domain organization, comprising a C-terminal LBD (ligand-binding domain), a hinge ...
... intracellular receptor proteins. These receptors function as ligandactivated transcription factors, switching on or off networks of genes in response to a specific hormone signal. The receptor proteins have a conserved domain organization, comprising a C-terminal LBD (ligand-binding domain), a hinge ...
Cell-cycle regulation
... The cdk-4 Cdk4/6 kinase and cyd-1 D-type cyclin genes are required for progression through G1 phase during larval development (Boxem and van den Heuvel, 2001; Park and Krause, 1999). CYD-1 and CDK-4 likely act in complex, as indicated by their direct interaction in vitro and close similarity in null ...
... The cdk-4 Cdk4/6 kinase and cyd-1 D-type cyclin genes are required for progression through G1 phase during larval development (Boxem and van den Heuvel, 2001; Park and Krause, 1999). CYD-1 and CDK-4 likely act in complex, as indicated by their direct interaction in vitro and close similarity in null ...
27_InstGuide_AR
... 4. Describe how prokaryotes carry out cellular respiration when they lack compartmentalized organelles such as mitochondria. 5. List the three domains of life. 6. Describe the structure, composition, and functions of prokaryotic cell walls. 7. Distinguish the structure and staining properties of gra ...
... 4. Describe how prokaryotes carry out cellular respiration when they lack compartmentalized organelles such as mitochondria. 5. List the three domains of life. 6. Describe the structure, composition, and functions of prokaryotic cell walls. 7. Distinguish the structure and staining properties of gra ...
Viral protein targeting to the cortical endoplasmic reticulum is
... various strategies to spread from one cell to another. Animal viruses commonly use vesicular transport machineries in the se cretory and endocytosis/exocytosis pathways for entry and exit (Pelkmans et al., 2001; Sieczkarski and Whittaker, 2002; Smith and Helenius, 2004; Greber and Way, 2006). Howev ...
... various strategies to spread from one cell to another. Animal viruses commonly use vesicular transport machineries in the se cretory and endocytosis/exocytosis pathways for entry and exit (Pelkmans et al., 2001; Sieczkarski and Whittaker, 2002; Smith and Helenius, 2004; Greber and Way, 2006). Howev ...
Plant nuclear proteomics inside the cell maestro
... Arabidopsis thaliana nuclear matrix by electron microscopy and MS. They observed a very similar structure to that described for the animal nuclear matrix. The other nucleic acid-containing structure is chromatin, which is arranged into chromosomes. They are organized in distinct areas [18] and occup ...
... Arabidopsis thaliana nuclear matrix by electron microscopy and MS. They observed a very similar structure to that described for the animal nuclear matrix. The other nucleic acid-containing structure is chromatin, which is arranged into chromosomes. They are organized in distinct areas [18] and occup ...
cytoplasm nucleus and the A specific subset of
... proteins accumulate in the nucleus at steady state, a subset of them shuttle continuously between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. We used techniques applied previously to the study of other shuttling proteins, such as hnRNP A1, as a positive control. This new activity of a distinct subset of SR prote ...
... proteins accumulate in the nucleus at steady state, a subset of them shuttle continuously between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. We used techniques applied previously to the study of other shuttling proteins, such as hnRNP A1, as a positive control. This new activity of a distinct subset of SR prote ...
Regulated trafficking of neurotransmitter transporters: common notes
... with several targets including subtypes of PKC and nonPKC targets (for a review see Kazanietz et al. 2000), it is possible intracellular and bath application results in interaction with, or activation of, different combinations of these targets. At present, it seems likely that the physiologically r ...
... with several targets including subtypes of PKC and nonPKC targets (for a review see Kazanietz et al. 2000), it is possible intracellular and bath application results in interaction with, or activation of, different combinations of these targets. At present, it seems likely that the physiologically r ...
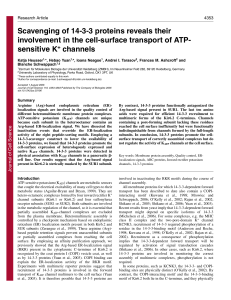
Scavenging of 14-3-3 proteins reveals their involvement in the cell
... the cell surface. Steric masking is a simple way of explaining this coupling in molecular terms: co-assembly might render the Arg-based signals present in Kir6.2 and SUR1 inaccessible to the COPI-vesicle coat. Unfortunately, currently available homology models of the assembled KATP channel do not pr ...
... the cell surface. Steric masking is a simple way of explaining this coupling in molecular terms: co-assembly might render the Arg-based signals present in Kir6.2 and SUR1 inaccessible to the COPI-vesicle coat. Unfortunately, currently available homology models of the assembled KATP channel do not pr ...
Hitching a ride on vesicles: Cauliflower mosaic virus movement
... (Supplemental Figure S1). Higher magnification images display co-localization of the ...
... (Supplemental Figure S1). Higher magnification images display co-localization of the ...
Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders
... Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders ...
... Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders ...
With-the-great-explosion-of-use-of
... fibrillation29,78-81. An important driving force for folding arises from the lower energetic cost of partitioning H-bonded peptide bonds compared to free peptide bonds 82-84. However, Miranker and coworkers have shown by NMR that mouse IAPP is capable of adopting a transient helical structure in so ...
... fibrillation29,78-81. An important driving force for folding arises from the lower energetic cost of partitioning H-bonded peptide bonds compared to free peptide bonds 82-84. However, Miranker and coworkers have shown by NMR that mouse IAPP is capable of adopting a transient helical structure in so ...
Pokeweed Antiviral Protein, a Ribosome Inactivating Protein: Activity
... (lac) promoter with an extremely low yield (0.13%–0.16% of the total bacterial protein) [82]. It was found that even the low level of gene expression slowed down bacterial growth significantly. Chen et al., also found that elimination of N-terminal signal peptide codons (22 amino acids) from the PAP ...
... (lac) promoter with an extremely low yield (0.13%–0.16% of the total bacterial protein) [82]. It was found that even the low level of gene expression slowed down bacterial growth significantly. Chen et al., also found that elimination of N-terminal signal peptide codons (22 amino acids) from the PAP ...
The Case of Protein Kinase CK2
... CK2β seems to interact directly with more than 40 different proteins, including other protein kinases such as A-Raf, Chk1, Chk2, PKC-ζ, Mos and p90rsk (Bibby & Lichfield, 2005; BolanosGarcia et al., 2006; Olsen & Guerra, 2008). It was shown that association of the human protein kinases Chk1, Mos, an ...
... CK2β seems to interact directly with more than 40 different proteins, including other protein kinases such as A-Raf, Chk1, Chk2, PKC-ζ, Mos and p90rsk (Bibby & Lichfield, 2005; BolanosGarcia et al., 2006; Olsen & Guerra, 2008). It was shown that association of the human protein kinases Chk1, Mos, an ...
Dual targeting of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases to the mitochondrion
... Accepted 18 September 2012 Journal of Cell Science 125, 6176–6184 ß 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi: 10.1242/jcs.116533 ...
... Accepted 18 September 2012 Journal of Cell Science 125, 6176–6184 ß 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi: 10.1242/jcs.116533 ...
Evidence for Amino Acid Snorkeling from a High
... Fis1p TA by up to three amino acids did not inhibit mitochondrial targeting, arguing against a model in which TA length directs insertion of TAs to distinct organelles. Most importantly, positively charged residues were more acceptable at several positions within the membrane-associated domain of th ...
... Fis1p TA by up to three amino acids did not inhibit mitochondrial targeting, arguing against a model in which TA length directs insertion of TAs to distinct organelles. Most importantly, positively charged residues were more acceptable at several positions within the membrane-associated domain of th ...
Interactions of Virus Proteins Within the Host Cell
... Bacteria and Archaea. Viruses usually specifically infect a determined cell type, largely defined by the receptors they recognise. Canine parvovirus is a small, non-enveloped animal virus that infects cells in dividing cells, especially in puppies. PRD1 is a bacteriophage infecting a wide range of G ...
... Bacteria and Archaea. Viruses usually specifically infect a determined cell type, largely defined by the receptors they recognise. Canine parvovirus is a small, non-enveloped animal virus that infects cells in dividing cells, especially in puppies. PRD1 is a bacteriophage infecting a wide range of G ...
Signaling
... e) Janus family of non-receptor TK s also bind some receptors receptors i) growth hormone receptors ii) prola ctin receptors iii) some cytokine receptors ...
... e) Janus family of non-receptor TK s also bind some receptors receptors i) growth hormone receptors ii) prola ctin receptors iii) some cytokine receptors ...
Protein quality control and elimination of protein waste: The role of
... denatured proteins to keep them in a folding-competent state. Further folding is finally exerted by the Hsp70 system [68,69]. The cytosol also possesses small heat shock proteins (sHsps) belonging to the class of ATP-independent chaperones. In yeast, the two most prominent members are Hsp42 and Hsp26 ...
... denatured proteins to keep them in a folding-competent state. Further folding is finally exerted by the Hsp70 system [68,69]. The cytosol also possesses small heat shock proteins (sHsps) belonging to the class of ATP-independent chaperones. In yeast, the two most prominent members are Hsp42 and Hsp26 ...
Palmitoylation of influenza virus proteins
... the enzymology of acylation of HA. Members of the DHHC family, polytopic membrane proteins containing a DHHC (Asp-His-His-Cys) motif within one of their cytoplasmic domains, were shown to palmitoylate cellular proteins [17], but a DHHC protein that acylates influenza HA (or other viral proteins) has ...
... the enzymology of acylation of HA. Members of the DHHC family, polytopic membrane proteins containing a DHHC (Asp-His-His-Cys) motif within one of their cytoplasmic domains, were shown to palmitoylate cellular proteins [17], but a DHHC protein that acylates influenza HA (or other viral proteins) has ...
The Plant Journal
... DNA-binding domain of LexA as the bait fusions. After transformation of plasmids containing the bait and prey fusions into yeast strain EGY48, we found that the SH3 domains of AtSH3P1 and AtSH3P2 did not interact with either CT1 or CT2 of ADL6 (results not shown). On the other hand, the SH3 domain o ...
... DNA-binding domain of LexA as the bait fusions. After transformation of plasmids containing the bait and prey fusions into yeast strain EGY48, we found that the SH3 domains of AtSH3P1 and AtSH3P2 did not interact with either CT1 or CT2 of ADL6 (results not shown). On the other hand, the SH3 domain o ...
HER2
... • Connects the αC helix with the A-loop, stabilizing the helix in the active site • Bond is conserved among ErbB family members: K851-E734 (EGFR), K856-E739 (ErbB4) ...
... • Connects the αC helix with the A-loop, stabilizing the helix in the active site • Bond is conserved among ErbB family members: K851-E734 (EGFR), K856-E739 (ErbB4) ...
Protein dynamics and proteolysis in plant vacuoles
... Plant cells cannot live without their vacuoles. The tissues and organs of a plant contain a wide variety of differentiated and specialized vacuoles—even a single plant cell can possess two or more types of vacuoles. Vacuolar proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and synthesized in the cytoplasm. The ...
... Plant cells cannot live without their vacuoles. The tissues and organs of a plant contain a wide variety of differentiated and specialized vacuoles—even a single plant cell can possess two or more types of vacuoles. Vacuolar proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and synthesized in the cytoplasm. The ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.