Assembly of AO and DHAS - Journal of Cell Science
... the AO and DHAS from the pellet (Fig. 1C) and no the only species that crosses the peroxisomal membrane. peroxisomal membrane (Fig. 1D). In summary, there is little Having shown that AO is imported as a monomer and DHAS cross contamination between cytosol (in the SUP), matrix and as a dimer, we next ...
... the AO and DHAS from the pellet (Fig. 1C) and no the only species that crosses the peroxisomal membrane. peroxisomal membrane (Fig. 1D). In summary, there is little Having shown that AO is imported as a monomer and DHAS cross contamination between cytosol (in the SUP), matrix and as a dimer, we next ...
Functional recognition of fragmented operator sites
... Arc and Ant synthesis results. Arc represses transcription from Pant by binding to an overlapping operator site, Oarc . Although Arc also represses its own expression through binding Oarc , transcription of mnt from Pmnt is stimulated, leading to the synthesis of Mnt protein. Mnt binds to Omnt to pr ...
... Arc and Ant synthesis results. Arc represses transcription from Pant by binding to an overlapping operator site, Oarc . Although Arc also represses its own expression through binding Oarc , transcription of mnt from Pmnt is stimulated, leading to the synthesis of Mnt protein. Mnt binds to Omnt to pr ...
Analysis of p75NTR-dependent apoptotic
... apoptosis is associated with an increase in Rac and Jun kinase (JNK) activity, and recent work from our laboratory has shown that the p75NTR interactor, NRAGE, activates a mitochondrial death pathway involving JNK-dependent cytochrome C release and activation of Caspase-9, Caspase-7 and Caspase-3. D ...
... apoptosis is associated with an increase in Rac and Jun kinase (JNK) activity, and recent work from our laboratory has shown that the p75NTR interactor, NRAGE, activates a mitochondrial death pathway involving JNK-dependent cytochrome C release and activation of Caspase-9, Caspase-7 and Caspase-3. D ...
View Full Page PDF
... terminus and the extreme NH2 terminus (Fig. 1). A number of invariant residues coordinate two metals, presumably Fe2⫹ and Zn2⫹, near the front edge of the -sandwich, and these metals are thought to contribute to catalysis by enhancing the nucleophilicity of metal-bound water and the electrophilicit ...
... terminus and the extreme NH2 terminus (Fig. 1). A number of invariant residues coordinate two metals, presumably Fe2⫹ and Zn2⫹, near the front edge of the -sandwich, and these metals are thought to contribute to catalysis by enhancing the nucleophilicity of metal-bound water and the electrophilicit ...
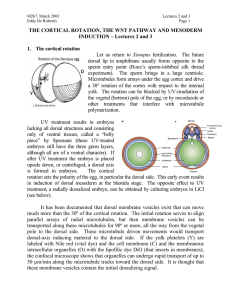
the cortical rotation, the wnt pathway
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
INFERRING PROPERTY SELECTION PRESSURE FROM
... uniformly distant from the amino acids in every other cluster. Consequently, even the properties that are used for clustering are modeled at only a very coarse level. More sophisticated approaches use mutation-based substitution matrices to quantify the physical-chemical similarity between amino aci ...
... uniformly distant from the amino acids in every other cluster. Consequently, even the properties that are used for clustering are modeled at only a very coarse level. More sophisticated approaches use mutation-based substitution matrices to quantify the physical-chemical similarity between amino aci ...
The role of lipids in the biogenesis of integral membrane
... (Bowie 2005). The energy for translocation is derived from GTP hydrolysis and translocation requires an electrochemical gradient across the membrane. The topology of the newborn protein generally follows the positive-inside rule to position lysine and arginine residues flanking the transmembrane dom ...
... (Bowie 2005). The energy for translocation is derived from GTP hydrolysis and translocation requires an electrochemical gradient across the membrane. The topology of the newborn protein generally follows the positive-inside rule to position lysine and arginine residues flanking the transmembrane dom ...
The mRNA-bound proteome of the early fly embryo
... a high-confidence set of 476 putative RBPs and confirmed RNA-binding activities for most of 24 tested candidates. Most proteins in the interactome are known RBPs or harbor canonical RBP features, but 99 exhibited previously uncharacterized RNA-binding activity. mRNA-bound RBPs and TFs exhibit distin ...
... a high-confidence set of 476 putative RBPs and confirmed RNA-binding activities for most of 24 tested candidates. Most proteins in the interactome are known RBPs or harbor canonical RBP features, but 99 exhibited previously uncharacterized RNA-binding activity. mRNA-bound RBPs and TFs exhibit distin ...
Functional Characterization of the 180
... A combination of strategies was used to isolate and assemble a full-length clone encoding RRp. A 3.7-kb clone, representing the 3' end of the m R N A , was isolated from an M D C K cell c D N A expression library using a rabbit antiRRp antiserum (Savitz and Meyer, 1990). The primary structure deduce ...
... A combination of strategies was used to isolate and assemble a full-length clone encoding RRp. A 3.7-kb clone, representing the 3' end of the m R N A , was isolated from an M D C K cell c D N A expression library using a rabbit antiRRp antiserum (Savitz and Meyer, 1990). The primary structure deduce ...
Mitochondrial Proton Leak and the Uncoupling Proteins
... Locke, 1984; see Lowell, 1998 for recent review). Fleury et al (1997) and Gimeno et al (1997) independently discovered and described an “uncoupling protein 2” (UCP2), a protein with a notably high (59%) amino acid identity to UCP1. An important feature of UCP2 was that it appeared to be expressed in ...
... Locke, 1984; see Lowell, 1998 for recent review). Fleury et al (1997) and Gimeno et al (1997) independently discovered and described an “uncoupling protein 2” (UCP2), a protein with a notably high (59%) amino acid identity to UCP1. An important feature of UCP2 was that it appeared to be expressed in ...
SMN, the Product of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Gene, Binds
... SMN can discriminate between the RG domains from different proteins (Friesen and Dreyfuss, 2000), and arginine methylation now emerges as a new mechanism for enhancing SMN substrate selection. Our view that protein arginine methylation is a general mechanism by which high-affinity Sm protein substra ...
... SMN can discriminate between the RG domains from different proteins (Friesen and Dreyfuss, 2000), and arginine methylation now emerges as a new mechanism for enhancing SMN substrate selection. Our view that protein arginine methylation is a general mechanism by which high-affinity Sm protein substra ...
Metabolic homeostasis of the heart
... Pi, calculated ADP, and creatine were essentially constant during physiological changes in workload. However, as maximum workloads were approached (Katz et al., 1989; Zhang et al., 1995; Lamb et al., 1997) or the tissue was metabolically compromised by ischemia, demand ischemia, different disease st ...
... Pi, calculated ADP, and creatine were essentially constant during physiological changes in workload. However, as maximum workloads were approached (Katz et al., 1989; Zhang et al., 1995; Lamb et al., 1997) or the tissue was metabolically compromised by ischemia, demand ischemia, different disease st ...
Selective protein degradation: a rheostat to
... Fig. 2. Progression through G1 to S phase. The transition from G1 towards the S phase requires a decreased level of CKI proteins (green curve) in order to release CDK activity (red curve), resulting in interconnected regulation. (A) In mammals, two ubiquitin E3 ligases, at least, trigger the degrad ...
... Fig. 2. Progression through G1 to S phase. The transition from G1 towards the S phase requires a decreased level of CKI proteins (green curve) in order to release CDK activity (red curve), resulting in interconnected regulation. (A) In mammals, two ubiquitin E3 ligases, at least, trigger the degrad ...
Identification of a Second Collagen-Like
... BclA⫺ mutants contains much lower levels of these carbohydrates. This clearly demonstrates that BclA is the major spore glycoprotein. However, it is entirely possible that another minor glycoprotein may have not been detected in these studies. Mutants that have BclA genes coding for BclA with shorte ...
... BclA⫺ mutants contains much lower levels of these carbohydrates. This clearly demonstrates that BclA is the major spore glycoprotein. However, it is entirely possible that another minor glycoprotein may have not been detected in these studies. Mutants that have BclA genes coding for BclA with shorte ...
The role of AMPK and CREB-1 in the regulation of mitochondrial
... promoter as a representative promoter since cytochrome c levels correlate well with respiratory chain complexes. We chose the AMP activated kinase (AMPK) and cyclic AMP-response element binding protein 1 (CREB-1) as promising candidates, which could control the process of mitochondrial proliferation ...
... promoter as a representative promoter since cytochrome c levels correlate well with respiratory chain complexes. We chose the AMP activated kinase (AMPK) and cyclic AMP-response element binding protein 1 (CREB-1) as promising candidates, which could control the process of mitochondrial proliferation ...
161021 NGF revised Manuscript with figs
... infusion or subcutaneous injection. A long circulating half-life in vivo, therefore, is highly desirable to ...
... infusion or subcutaneous injection. A long circulating half-life in vivo, therefore, is highly desirable to ...
Journal of Applied Microbiology
... USA) and Omp48 (48 kDa protein) was identified by SDSPAGE. Preparation of polyclonal antiserum and Western blot Polyclonal anti-Omp48 antiserum was raised in rabbits by immunization with Omp48 from Aer. veronii strain A186 according to Harlow and Lane (1988). Briefly, electro-eluted Omp48 was electr ...
... USA) and Omp48 (48 kDa protein) was identified by SDSPAGE. Preparation of polyclonal antiserum and Western blot Polyclonal anti-Omp48 antiserum was raised in rabbits by immunization with Omp48 from Aer. veronii strain A186 according to Harlow and Lane (1988). Briefly, electro-eluted Omp48 was electr ...
Dynamin and the Actin Cytoskeleton Cooperatively Regulate
... These observations prompted us to carry out a more systematic comparison between BAR domain- and FCH domain-containing proteins. Sequence comparisons and structural predictions suggested that the FCH domain, together with the CC region that typically follows this domain, define a protein module simi ...
... These observations prompted us to carry out a more systematic comparison between BAR domain- and FCH domain-containing proteins. Sequence comparisons and structural predictions suggested that the FCH domain, together with the CC region that typically follows this domain, define a protein module simi ...
Transport of Storage Proteins to Protein Storage Vacuoles Is
... some vesicles also contained small vesicle-like structures. Immunocytochemical analysis revealed numerous electrondense aggregates of storage proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. It is likely that these aggregates develop into the electron-dense cores of the PAC vesicles and then leave the end ...
... some vesicles also contained small vesicle-like structures. Immunocytochemical analysis revealed numerous electrondense aggregates of storage proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. It is likely that these aggregates develop into the electron-dense cores of the PAC vesicles and then leave the end ...
ATP-binding-cassette (ABC) transport systems: Functional and
... hydrolysis of ATP to the translocation of solutes across a biological membrane. Recognized by their common modular organization and two sequence motifs that constitute a nucleotide binding fold, ABC transporters are widespread among all living organisms. They accomplish not only the uptake of nutrie ...
... hydrolysis of ATP to the translocation of solutes across a biological membrane. Recognized by their common modular organization and two sequence motifs that constitute a nucleotide binding fold, ABC transporters are widespread among all living organisms. They accomplish not only the uptake of nutrie ...
Molecular mechanisms of Salmonella invasion
... homology with the β-subunit of F0F1 ATPases [20]. This homology suggests that InvC may play a role in energizing the secretion system. In biochemical studies, it was demonstrated that InvC has an ATPase activity. This activity was abolished by the change of a single residue in the predicted nucleoti ...
... homology with the β-subunit of F0F1 ATPases [20]. This homology suggests that InvC may play a role in energizing the secretion system. In biochemical studies, it was demonstrated that InvC has an ATPase activity. This activity was abolished by the change of a single residue in the predicted nucleoti ...
Chemotaxis in Bacteria
... for obtaining motility and chemotaxisin defined media(8-11) and to find objective, quantitative methods for demonstrating chemotaxis. (a) Plate method: For positive chemotaxis, a petri dish containing metabolizable attractant, salts needed for growth, and soft agar (a low enough concentration so tha ...
... for obtaining motility and chemotaxisin defined media(8-11) and to find objective, quantitative methods for demonstrating chemotaxis. (a) Plate method: For positive chemotaxis, a petri dish containing metabolizable attractant, salts needed for growth, and soft agar (a low enough concentration so tha ...
Light-dependent Dl Protein Synthesis and Translocation Is
... complexes were resolved in the first dimension by nondenaturing polyacrylamide (6% w/v) gel electrophoresis in the presence of the zwitterionic detergent Deriphat-160 (17, 18). Gel strips were excised and incubated for 15 min at 70 “C in SDS sample buffer to denature the complexes. The strips were e ...
... complexes were resolved in the first dimension by nondenaturing polyacrylamide (6% w/v) gel electrophoresis in the presence of the zwitterionic detergent Deriphat-160 (17, 18). Gel strips were excised and incubated for 15 min at 70 “C in SDS sample buffer to denature the complexes. The strips were e ...
Integrin cytoplasmic domain-binding proteins
... and β3 but not β2 tails was also reported recently (Reddy et al., 1998). Skelemin has an unique N-terminal region followed by Ig superfamily C2 and fibronectin (FN) type II motifs. Reddy et al., localized the skelemin-binding site to the membrane proximal ten residues of β1. Under some conditions, s ...
... and β3 but not β2 tails was also reported recently (Reddy et al., 1998). Skelemin has an unique N-terminal region followed by Ig superfamily C2 and fibronectin (FN) type II motifs. Reddy et al., localized the skelemin-binding site to the membrane proximal ten residues of β1. Under some conditions, s ...
pdf-Dokument - Universität Bonn
... related to the yeast ARFGAPs (Age2p, Gcs1p and Glo3p) which perform their function at the TGN (Trans-Golgi Network). Mutagenesis experiments in yeast cells that have a suppressed GAP activity for Glo3p and Gsc1p showed an impaired retrograde protein transport from ER to Golgi apparatus. In animal ce ...
... related to the yeast ARFGAPs (Age2p, Gcs1p and Glo3p) which perform their function at the TGN (Trans-Golgi Network). Mutagenesis experiments in yeast cells that have a suppressed GAP activity for Glo3p and Gsc1p showed an impaired retrograde protein transport from ER to Golgi apparatus. In animal ce ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.