Ship Observations of the Tropical Pacific Ocean along the Coast of
... in sensible heat flux from the air to the ocean. The air temperature is considerably cooler than the SST (3.58C) in the warm pool north of 38S, because advection from the south has a cooling effect of approximately 108C day21 on the surface air. The largest sea–air temperature difference of 4.258C w ...
... in sensible heat flux from the air to the ocean. The air temperature is considerably cooler than the SST (3.58C) in the warm pool north of 38S, because advection from the south has a cooling effect of approximately 108C day21 on the surface air. The largest sea–air temperature difference of 4.258C w ...
Which Gets Hotter, Land or Water?
... This is a laboratory to be used when studying weather. The uneven heating of the Earth’s surface causes weather. When you have differences in air temperature, the hot air will rise and the cold air will sink. These movements create wind (which also is affected by the rotation of the Earth). Hotter a ...
... This is a laboratory to be used when studying weather. The uneven heating of the Earth’s surface causes weather. When you have differences in air temperature, the hot air will rise and the cold air will sink. These movements create wind (which also is affected by the rotation of the Earth). Hotter a ...
water cycle – The continuous movement of water on
... 24. wind vane: Also referred to as a weather vane. It is an instrument for showing the direction of the wind 25. wind direction: is reported by the direction from which it originates (comes from). For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. 26. wind speed: how fast the wind is m ...
... 24. wind vane: Also referred to as a weather vane. It is an instrument for showing the direction of the wind 25. wind direction: is reported by the direction from which it originates (comes from). For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. 26. wind speed: how fast the wind is m ...
Practice_Exam_2A
... 7. A test charge of +5x10-6C experiences forces from two other nearby charges: a force of 10N due east and a force of 7N due west. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the location of the test charge in N/C? A) 6 x 105 B) 15 x 10-6 C) 4 x 10-5 D) 3 x 103 E) 34 x 105 8. A 60kg person is tra ...
... 7. A test charge of +5x10-6C experiences forces from two other nearby charges: a force of 10N due east and a force of 7N due west. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the location of the test charge in N/C? A) 6 x 105 B) 15 x 10-6 C) 4 x 10-5 D) 3 x 103 E) 34 x 105 8. A 60kg person is tra ...
Meteorology Powerpoint
... comes from the fact that many used mercury as the liquid in the barometer Air pressure pushes on liquid and squeezes it up a certain height (giving pressure) ...
... comes from the fact that many used mercury as the liquid in the barometer Air pressure pushes on liquid and squeezes it up a certain height (giving pressure) ...
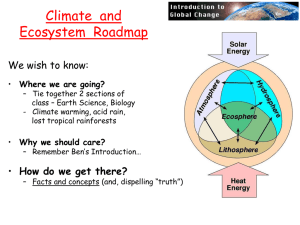
Climate and the Environment
... parcel of air as specific humidity and expressed it as kilograms of water vapor per kilogram of air (kg/kg). By definition, specific humidity can only change be adding or removing water vapor molecules, either through evaporation and sublimation (which increases the specific humidity) or condensatio ...
... parcel of air as specific humidity and expressed it as kilograms of water vapor per kilogram of air (kg/kg). By definition, specific humidity can only change be adding or removing water vapor molecules, either through evaporation and sublimation (which increases the specific humidity) or condensatio ...
WPF-Weather101
... portion of this heat energy from reaching the Earth’s surface, thereby reducing the day temperature. • Cloudy nights are generally warmer than clear nights because cloud cover reduces the loss of terrestrial radiation to space. ...
... portion of this heat energy from reaching the Earth’s surface, thereby reducing the day temperature. • Cloudy nights are generally warmer than clear nights because cloud cover reduces the loss of terrestrial radiation to space. ...
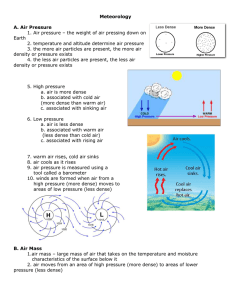
Meteorology A. Air Pressure 1. Air pressure – the
... b. if you increased the temperature of a room without adding more moisture, the relative humidity of the room would decrease ...
... b. if you increased the temperature of a room without adding more moisture, the relative humidity of the room would decrease ...
Solution Tutorial 4 - Aerospace Engineering, IIT Madras
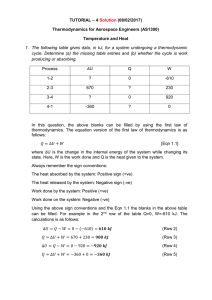
... atmosphere. The piston weighs 50 kg and has a face area of 0.01 m2. The air initially occupies a volume of 0.005 m3 . The air now undergoes a process wherein its volume deceases to 0.0025 m3 and 1.41 kJ of heat is lost to the surroundings. Determine the change in specific internal energy of the air. ...
... atmosphere. The piston weighs 50 kg and has a face area of 0.01 m2. The air initially occupies a volume of 0.005 m3 . The air now undergoes a process wherein its volume deceases to 0.0025 m3 and 1.41 kJ of heat is lost to the surroundings. Determine the change in specific internal energy of the air. ...
43 Weather
... Air pressure is the force on any given area by the weight of the air above it. Air temperature affects air pressure. When air is warmer, air particles have more energy. The particles move around more and spread apart. The air's density, or mass per unit volume, decreases. The warm air rises above ai ...
... Air pressure is the force on any given area by the weight of the air above it. Air temperature affects air pressure. When air is warmer, air particles have more energy. The particles move around more and spread apart. The air's density, or mass per unit volume, decreases. The warm air rises above ai ...
A virtual ambient wet-bulb temperature sensor for performance
... Ambient wet-bulb temperature measurement is critical in the water-cooled chiller plant system to enhance the holistic energy efficiency through advanced control strategies, such as the cooling tower temperature relief, condenser water supply temperature reset, and so on. The outside air (OA) wet-bul ...
... Ambient wet-bulb temperature measurement is critical in the water-cooled chiller plant system to enhance the holistic energy efficiency through advanced control strategies, such as the cooling tower temperature relief, condenser water supply temperature reset, and so on. The outside air (OA) wet-bul ...
J.T. Reddick Middle School 6th Grade Earth Science Course
... Course: Unit 5 “Weather and Climate” Textbook: Prentice Hall Science Explorer – Georgia Earth Science (pages 392, 398-402, 404, 414-424, 432-464, and 472-479) Unit Overview: Meteorology is the study of the atmospheric conditions and weather in an area and how to forecast it. In this unit, students w ...
... Course: Unit 5 “Weather and Climate” Textbook: Prentice Hall Science Explorer – Georgia Earth Science (pages 392, 398-402, 404, 414-424, 432-464, and 472-479) Unit Overview: Meteorology is the study of the atmospheric conditions and weather in an area and how to forecast it. In this unit, students w ...
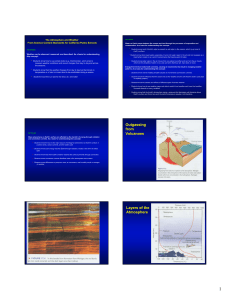
Magma Supply Vs Magma Plumbing
... • Modern Ice Averages 18OSMOW = -25‰ but it depends on location • During Ice Ages it was colder and therefore ice is lighter (18O more negative) 18O, ‰ ...
... • Modern Ice Averages 18OSMOW = -25‰ but it depends on location • During Ice Ages it was colder and therefore ice is lighter (18O more negative) 18O, ‰ ...
Natural Causes for Climate Change
... contact with the Earth’s surface, and hence its temperature structure is determined by energy transmitted to and from the surface. Weather occurs in the troposphere. ...
... contact with the Earth’s surface, and hence its temperature structure is determined by energy transmitted to and from the surface. Weather occurs in the troposphere. ...
Outgassing from Volcanoes Layers of the Atmosphere
... Students know water vapor in the air moves from one place to another and can form fog or clouds, which are tiny droplets of water or ice, and can fall to Earth as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. ...
... Students know water vapor in the air moves from one place to another and can form fog or clouds, which are tiny droplets of water or ice, and can fall to Earth as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. ...
Overview of the Earth`s Atmosphere
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
Climate Science Study Guide
... a. A sea breeze flows from the ocean toward the land at night because the land and ocean lose heat at the same rate. b. A sea breeze flows from the land toward the ocean at night because the land and ocean lose heat at the same rate. c. A sea breeze forms at night because the ocean cools faster than ...
... a. A sea breeze flows from the ocean toward the land at night because the land and ocean lose heat at the same rate. b. A sea breeze flows from the land toward the ocean at night because the land and ocean lose heat at the same rate. c. A sea breeze forms at night because the ocean cools faster than ...
Classroom Teacher Preparation Earth Science 16: Weather
... This lesson provides an introduction to weather and its key components that influence it. Key components include temperature, humidity, pressure, ocean currents and air currents. The four main types of precipitation are also included in th th the lesson. This lesson was designed to focus on weather ...
... This lesson provides an introduction to weather and its key components that influence it. Key components include temperature, humidity, pressure, ocean currents and air currents. The four main types of precipitation are also included in th th the lesson. This lesson was designed to focus on weather ...
File - Mr. Lloyd`s 7th grade science!
... 6.) Advection of the wind moves cool air _____________________________ warm air, or warm air ________________________________cool air. This is because warm air is less dense than the cooler air (more water vapor in warm air). 7.) Increase in temperature cause a column of air to _____________________ ...
... 6.) Advection of the wind moves cool air _____________________________ warm air, or warm air ________________________________cool air. This is because warm air is less dense than the cooler air (more water vapor in warm air). 7.) Increase in temperature cause a column of air to _____________________ ...
Study guide for Atmosphere, Weather, and Climate Test (Chap 24)
... _________(a) Snow melts in a narrow warm air layer aloft, but has time to refreeze before hitting the ground _________(b) Snow melts in a deep (thick) warm air layer aloft, but does not have time to refreeze while falling. So this type of precip freezes on the ground and on surfaces. _________(c) Th ...
... _________(a) Snow melts in a narrow warm air layer aloft, but has time to refreeze before hitting the ground _________(b) Snow melts in a deep (thick) warm air layer aloft, but does not have time to refreeze while falling. So this type of precip freezes on the ground and on surfaces. _________(c) Th ...
Weather & Climate
... which then creates WINDS Winds blow this cooling or warming effect over the land ...
... which then creates WINDS Winds blow this cooling or warming effect over the land ...
File - Winnipeg Ground School
... d) clean air turbulence 12) The amount of water vapor that a given volume of air can contain at a given pressure is governed by a) the temperature b) the stability c) the relative humidity d) the lapse rate 13) A horizontal layer of cloud in the lower layers of the atmosphere from which continuous p ...
... d) clean air turbulence 12) The amount of water vapor that a given volume of air can contain at a given pressure is governed by a) the temperature b) the stability c) the relative humidity d) the lapse rate 13) A horizontal layer of cloud in the lower layers of the atmosphere from which continuous p ...
What is Weather.
... the actual temperature outside to the temp the body would feel if exposed to the air and wind. This adjusted temperature indicates the potential danger of frostbite in the outside air. ...
... the actual temperature outside to the temp the body would feel if exposed to the air and wind. This adjusted temperature indicates the potential danger of frostbite in the outside air. ...
Earth Science Spring Semester Final Answer Key
... d. carbon dioxide 34. A compound contains two or more a. elements physically combined. b. simple substances. c. elements chemically combined. d. nuclei combined with electrons 35. Crystallization from cooling magma describes one way that a. atoms bond. b. ions combine. c. protons attract electrons. ...
... d. carbon dioxide 34. A compound contains two or more a. elements physically combined. b. simple substances. c. elements chemically combined. d. nuclei combined with electrons 35. Crystallization from cooling magma describes one way that a. atoms bond. b. ions combine. c. protons attract electrons. ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.