Name
... The sun heats the ground by radiation. The ground re-radiates energy to the carbon dioxide and water vapor in the atmosphere. Also, air in contact with the ground absorbs energy by conduction. As the air gains energy, the air molecules move more rapidly and this warm air rises because it is less den ...
... The sun heats the ground by radiation. The ground re-radiates energy to the carbon dioxide and water vapor in the atmosphere. Also, air in contact with the ground absorbs energy by conduction. As the air gains energy, the air molecules move more rapidly and this warm air rises because it is less den ...
Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Initial Training Modules
... Lapse rate describes variation of temperature with height. Normally the temperature decreases with height (Troposphere), such as when we climb a mountain This describes an unstable situation (cold heavy air above warm light air) thus we have atmospheric overturning with weather (thunderstorms) ...
... Lapse rate describes variation of temperature with height. Normally the temperature decreases with height (Troposphere), such as when we climb a mountain This describes an unstable situation (cold heavy air above warm light air) thus we have atmospheric overturning with weather (thunderstorms) ...
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 2a: Cloud formation & physical processes SSEC
... Lapse rate describes variation of temperature with height. Normally the temperature decreases with height (Troposphere), such as when we climb a mountain This describes an unstable situation (cold heavy air above warm light air) thus we have atmospheric overturning with weather (thunderstorms) ...
... Lapse rate describes variation of temperature with height. Normally the temperature decreases with height (Troposphere), such as when we climb a mountain This describes an unstable situation (cold heavy air above warm light air) thus we have atmospheric overturning with weather (thunderstorms) ...
Section 6.2
... using a line marked with triangles. • The triangles point in the direction the front is ...
... using a line marked with triangles. • The triangles point in the direction the front is ...
6.2 Cloud formation
... using a line marked with triangles. • The triangles point in the direction the front is ...
... using a line marked with triangles. • The triangles point in the direction the front is ...
Air Masses and Weather
... and humidity are nearly uniform. The temperature and humidity of an air mass depend on where the air mass originates. For example, in polar regions, the lack of sunlight in winter causes the ground to be very cold. If an air mass stays in a polar region for days or weeks, it becomes cold as well. In ...
... and humidity are nearly uniform. The temperature and humidity of an air mass depend on where the air mass originates. For example, in polar regions, the lack of sunlight in winter causes the ground to be very cold. If an air mass stays in a polar region for days or weeks, it becomes cold as well. In ...
Study guide for Exam 4
... differences between cyclones and anticyclones. Know the wind belts of the world, how they form and how they influence the climate of the world. Be able to use the major air masses of the United States to explain weather systems. Be able to define sea breeze, land breeze, cold front and warm front an ...
... differences between cyclones and anticyclones. Know the wind belts of the world, how they form and how they influence the climate of the world. Be able to use the major air masses of the United States to explain weather systems. Be able to define sea breeze, land breeze, cold front and warm front an ...
What is the atmosphere?
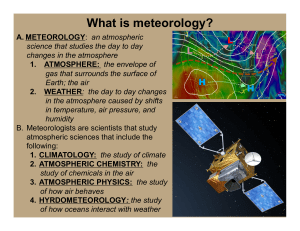
... energy in the air 2. AIR PRESSURE: the amount of pressure (weight) the air exerts due to the concentration of air 3. WIND: air that moves from high to low pressure 4. MOISTURE: the amount of evaporated water in the air B. All four of these factors are influence directly or indirectly by the sun’ ...
... energy in the air 2. AIR PRESSURE: the amount of pressure (weight) the air exerts due to the concentration of air 3. WIND: air that moves from high to low pressure 4. MOISTURE: the amount of evaporated water in the air B. All four of these factors are influence directly or indirectly by the sun’ ...
NSTA Meteorology Reading 8 • Weather`s Central Actor: Water
... ‣ The total quantity of water in all forms in Earth’s hydrosphere is constant - Hydrologic Change aka The Water Cycle ‣ Water evaporates or transpires into the atmosphere ‣ In the atmosphere, it condenses and returns to Earth’s surface as precipitation ‣ May be temporarily stored in glaciers, lakes, ...
... ‣ The total quantity of water in all forms in Earth’s hydrosphere is constant - Hydrologic Change aka The Water Cycle ‣ Water evaporates or transpires into the atmosphere ‣ In the atmosphere, it condenses and returns to Earth’s surface as precipitation ‣ May be temporarily stored in glaciers, lakes, ...
Earth – The Water Planet
... Mountain regions display many interesting weather patterns. One example is the valley wind which originates on south-facing slopes (north-facing in the southern hemisphere). When the slopes and the neighboring air are heated the density of the air decreases, and the air ascends towards the top follo ...
... Mountain regions display many interesting weather patterns. One example is the valley wind which originates on south-facing slopes (north-facing in the southern hemisphere). When the slopes and the neighboring air are heated the density of the air decreases, and the air ascends towards the top follo ...
Chapter 2-C
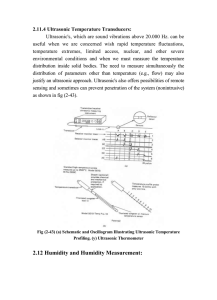
... the two filament resistors (reference filament and measuring filament R3 and R4 The resistor R2 is adjusted to yield a balanced The bridge is first calibrated by allowing the same gas to surround the two filament resistors (reference filament and measuring filament R3 and R4 The resistor R2 is adjus ...
... the two filament resistors (reference filament and measuring filament R3 and R4 The resistor R2 is adjusted to yield a balanced The bridge is first calibrated by allowing the same gas to surround the two filament resistors (reference filament and measuring filament R3 and R4 The resistor R2 is adjus ...
Weather Unit Foldable - Cole`s Science Pages
... – Temperature decreases as altitude increases 140 to 76 degrees F – All weather happens here – This is the ONLY layer living things can live in – 16 km above sea level ...
... – Temperature decreases as altitude increases 140 to 76 degrees F – All weather happens here – This is the ONLY layer living things can live in – 16 km above sea level ...
Do the Dewpoint! - UNI ScholarWorks
... scientific inquiry, properties of earth materials, and changes in earth and sky. Teacher Notes: To reach the activity maps go to http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities/level1/ Dew point is the temperature to which air must be lowered to make it saturated, or when it can hold no more water molecules. (T ...
... scientific inquiry, properties of earth materials, and changes in earth and sky. Teacher Notes: To reach the activity maps go to http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities/level1/ Dew point is the temperature to which air must be lowered to make it saturated, or when it can hold no more water molecules. (T ...
What is meteorology?
... Pressure variations at sea level do not usually exceed 4% of the normal average value (that is 1013 millibar): lower values (up to 900 millibar) can be registered in the eye of tropical cyclones. With the exception of some small local variations, atmospheric pressure and density decrease with altitu ...
... Pressure variations at sea level do not usually exceed 4% of the normal average value (that is 1013 millibar): lower values (up to 900 millibar) can be registered in the eye of tropical cyclones. With the exception of some small local variations, atmospheric pressure and density decrease with altitu ...
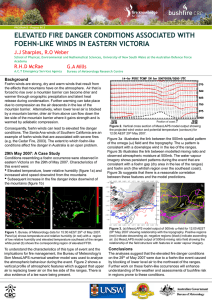
Foehn winds and effect on fire weather: Victorian Case Study File
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
Properties of pure substances: introduction, PV diagrams with phase
... – A surface in p,v,T (or u,p,v) space or more commonly its projections on (p,v), (T,v) and (p,T) planes. – Tables of properties ...
... – A surface in p,v,T (or u,p,v) space or more commonly its projections on (p,v), (T,v) and (p,T) planes. – Tables of properties ...
Chapter 16 Outline (Weather) fill in PART 1
... i. Barometer (tool used to measure pressure) 1. Mercury (less common) 2. Aneroid “without liquid” (more current tool) d. Weather related air pressure (generally speaking) i. Air pressure rises as __________________________of air come together in upper atmosphere ______________________________ on low ...
... i. Barometer (tool used to measure pressure) 1. Mercury (less common) 2. Aneroid “without liquid” (more current tool) d. Weather related air pressure (generally speaking) i. Air pressure rises as __________________________of air come together in upper atmosphere ______________________________ on low ...
METEOROLOGY
... Inversion in the stratosphere is due to heating of stratosphere from the absorption of UV rays by O3; absence of O3 ---- air would become colder with height • Mesosphere: Extremely thin air, low pressure and density; average temp. ~-90°C; • Thermosphere: Hot layer above Mesosphere; very few atoms an ...
... Inversion in the stratosphere is due to heating of stratosphere from the absorption of UV rays by O3; absence of O3 ---- air would become colder with height • Mesosphere: Extremely thin air, low pressure and density; average temp. ~-90°C; • Thermosphere: Hot layer above Mesosphere; very few atoms an ...
Powerpoint
... • Stratosphere: From the top of tropopause to until the temperature remains constant (~50 km); • Tropopause height varies – higher in the equatorial region & decreases poleward; tropopause is higher in summer and lower in winter at all latitudes; • In some regions, tropopause breaks, leading to stra ...
... • Stratosphere: From the top of tropopause to until the temperature remains constant (~50 km); • Tropopause height varies – higher in the equatorial region & decreases poleward; tropopause is higher in summer and lower in winter at all latitudes; • In some regions, tropopause breaks, leading to stra ...
Weather Unit Foldable
... Tornadoes and thunderstorms in southern US Fewer than normal hurricanes in the Atlantic ...
... Tornadoes and thunderstorms in southern US Fewer than normal hurricanes in the Atlantic ...
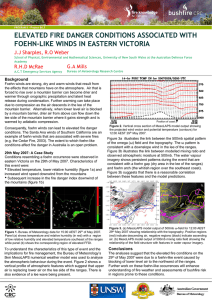
Foehn Winds in Eastern Victoria
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
ppt
... In the infrared portion of the spectrum, emitted energy from the earthatmosphere system predominates From “Weather Satellites”, Rao et. al (1990), AMS publication ...
... In the infrared portion of the spectrum, emitted energy from the earthatmosphere system predominates From “Weather Satellites”, Rao et. al (1990), AMS publication ...
4th Grade Weather and Water Cycle Vocabulary
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.