* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Goal 3 Weather and Climate vocab
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Convective storm detection wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
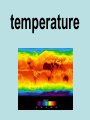
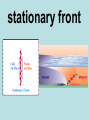
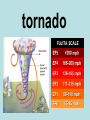
weather The state of the atmosphere: considering wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture, pressure, and other factors. forecast A prediction of what the future weather will be like. atmosphere The layer of air that surrounds the earth. temperature A measurement of the amount of heat something contains. weather pattern When the weather repeats itself several days in a row. climate The average weather over a long period of time. almanac A book that contains weather data and forecasts. water cycle The journey water takes as it circulates from the land to the sky and back again. water vapor Water in its gaseous stateinstead of liquid or solid. It is totally invisible. condensation When a gas becomes a liquid. evaporation When a liquid becomes a gas. precipitation Any liquid or solid form of water that falls from the atmosphere. For example: rain, snow, hail, or sleet. stratus Flat, featureless clouds low in the atmosphere that cover the sky like a blanket. They indicate rain. cirrus High level clouds made mostly of ice crystals. They indicate fair weather. cumulonimbus Clouds that bring summer storms, usually with thunder, lighting, and strong winds. cumulus Mid-level, puffy clouds. They indicate fair weather. fog Clouds that form at ground level. wind isobars Air flowing from high pressure to low pressure . beaufort scale A scale that relates the wind speed to its effects, classified from force 0 to force 12. prevailing winds The speed and direction of wind over a particular point on the earth's surface. Westerlies The global winds that carry weather over the United States, traveling from West to East. Easterlies Global winds at the poles of the earth. These global winds sometimes affect our weather during the winter months. air mass A massive bubble of air that has the same temperature and pressure throughout. air pressure The force of air pushing down on Earth. barometer A device used to measure air pressure. aneroid barometer A barometer that uses liquid. isobar A line drawn on a weather map that connects locations with the same air pressure. front Where air masses meet, but do not mix and rain or storms occur. cold front The leading edge of a moving mass of cold air, brings thunderstorms, and leaves behind cooler air. warm front The leading edge of a moving mass of warm air, brings rain showers, leaves behind warmer air. occluded front Where a cold front catches up to and overtakes a warm front. stationary front When a cold and a warm air mass meet, but neither moves. tornado A narrow, violent funnel cloud that may form during a thunderstorm with winds greater than 65 kph. hurricane A large rotating windstorm with a calm central eye and winds greater than 75 mph. meteorologist isobars A person who studies the weather. meteorology The study of the earth’s atmosphere and what happens in it. station model A weather symbol that represents the state of the weather at a particular place. rain gauge A device used to measure the amount of precipitation in a given area.