File - Winnipeg Ground School
... weight of water present in the air. amount of moisture present in the air compared to the amount the air could hold at that temperature and pressure. 4. temperature to which the air must be lowered to bring about saturation. **HINT** Relative Humidity is a ratio! It’s always comparing how much water ...
... weight of water present in the air. amount of moisture present in the air compared to the amount the air could hold at that temperature and pressure. 4. temperature to which the air must be lowered to bring about saturation. **HINT** Relative Humidity is a ratio! It’s always comparing how much water ...
Meteorology 3/2/2016 Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the
... Meteorology 3/2/2016 1) Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the total volume of the atmosphere near the equator? __________ 2) Atmospheric layers are bounded by __________ 3) The height of the troposphere is highest at latitude __________ 4) The “standard” air pressure at the earth’s surface is _ ...
... Meteorology 3/2/2016 1) Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the total volume of the atmosphere near the equator? __________ 2) Atmospheric layers are bounded by __________ 3) The height of the troposphere is highest at latitude __________ 4) The “standard” air pressure at the earth’s surface is _ ...
Topic_VI_Meteorology
... making it a cooling process. 2. Condensation: gas (water vapor) to a liquid. Releases energy into the air. ...
... making it a cooling process. 2. Condensation: gas (water vapor) to a liquid. Releases energy into the air. ...
Ch 11/12/13 Earth`s Atmosphere Study Guide
... Why is the thermosphere said to be the hottest layer when it feels so cold up there? __________________________________________________________________ How much of the sun’s energy does Earth’s surface absorb? _______ What happens to the rest of it? __________________________________________________ ...
... Why is the thermosphere said to be the hottest layer when it feels so cold up there? __________________________________________________________________ How much of the sun’s energy does Earth’s surface absorb? _______ What happens to the rest of it? __________________________________________________ ...
WSO100 - NMEA 2000 Ultrasonic Wind and Weather
... direction, air temperature, barometric pressure, and relative humidity. The wind measurement is performed using ultrasonic sensors, which means there are no moving parts to wear out or to get caught in the rigging. The WSO100 accurately measures wind speed and direction even when tilted, making it i ...
... direction, air temperature, barometric pressure, and relative humidity. The wind measurement is performed using ultrasonic sensors, which means there are no moving parts to wear out or to get caught in the rigging. The WSO100 accurately measures wind speed and direction even when tilted, making it i ...
Psychrometer
... A psychrometer consists of two thermometers exposed side by side, the surface of the sensing element of one being covered by a thin film of water or ice and termed the wet or ice bulb, as appropriate. The sensing element of the second thermometer is simply exposed to the air and is termed the dry ...
... A psychrometer consists of two thermometers exposed side by side, the surface of the sensing element of one being covered by a thin film of water or ice and termed the wet or ice bulb, as appropriate. The sensing element of the second thermometer is simply exposed to the air and is termed the dry ...
doc - MMG @ UCD: Research
... the Newton (N) kg m s-2 (F=ma, mass x acceleration) A force of 1 N will cause an acceleration of 1 m s-2 in a mass of 1 kg b) the unit of pressure is Newtons per square meter, which is called the Pascal (Pa). 1 Pa 1 N m-2 kg m-1 s-2 c) the common meteorological unit of pressure is the millibar ...
... the Newton (N) kg m s-2 (F=ma, mass x acceleration) A force of 1 N will cause an acceleration of 1 m s-2 in a mass of 1 kg b) the unit of pressure is Newtons per square meter, which is called the Pascal (Pa). 1 Pa 1 N m-2 kg m-1 s-2 c) the common meteorological unit of pressure is the millibar ...
Γ = Γ ∙ (1)
... the adiabatic rate of 5.50F/1000 ft will be offset by a warming effect of about 2oF/1000 ft, leading to net cooling of around 3.50F/1000 ft. Equation (1) can be solved for every temperature that appears on a thermodynamic chart, resulting in a family of lines called moist adiabats. Since the moist a ...
... the adiabatic rate of 5.50F/1000 ft will be offset by a warming effect of about 2oF/1000 ft, leading to net cooling of around 3.50F/1000 ft. Equation (1) can be solved for every temperature that appears on a thermodynamic chart, resulting in a family of lines called moist adiabats. Since the moist a ...
Thermodynamic (I) PE200 Assignment #6
... 1.A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a initially at 160 kPa and 40 percent quality. Heat is now transferred to the refrigerant until the pressure reaches 700 kPa. Determine (a) the mass of the refrigerant in the tank and (b) the amount of heat transferred. Also, show the process on a P-v di ...
... 1.A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a initially at 160 kPa and 40 percent quality. Heat is now transferred to the refrigerant until the pressure reaches 700 kPa. Determine (a) the mass of the refrigerant in the tank and (b) the amount of heat transferred. Also, show the process on a P-v di ...
Air Pressure Review
... 4. A relative humidity of 25% means the air is holding only 25% of what it could hold at a given temp. 5. Relative humidity is 100% at the dew point. To change relative humidity 1. If the amount of moisture remains the same, cooled air will have a higher relative humidity. 2. If temp decreases, rela ...
... 4. A relative humidity of 25% means the air is holding only 25% of what it could hold at a given temp. 5. Relative humidity is 100% at the dew point. To change relative humidity 1. If the amount of moisture remains the same, cooled air will have a higher relative humidity. 2. If temp decreases, rela ...
1. The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surround the earth_
... 6. Why is air pressure greatest at the Earth’s surface? Because ...
... 6. Why is air pressure greatest at the Earth’s surface? Because ...
“Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
... Mid level - Prefixed with “alto” High level - Cirrus Cumulonimbus - Thunderstorms Valuable tool in forecasting ...
... Mid level - Prefixed with “alto” High level - Cirrus Cumulonimbus - Thunderstorms Valuable tool in forecasting ...
Atmosphere
... and it refers to the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place Climate is based on observations of weather that have been collected over many years to help describe a place or region ...
... and it refers to the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place Climate is based on observations of weather that have been collected over many years to help describe a place or region ...
Dry Rate Factors
... Humidity: High relative humidity (moisture content in the air) retards evaporation of liquids from the paint; relative humidity over 90% can cause extremely slow drying. Temperature: Low temperatures impede evaporation of liquids from paint; significant slowing of dry is generally observed with temp ...
... Humidity: High relative humidity (moisture content in the air) retards evaporation of liquids from the paint; relative humidity over 90% can cause extremely slow drying. Temperature: Low temperatures impede evaporation of liquids from paint; significant slowing of dry is generally observed with temp ...
Chapter 14
... Simple Heating and Cooling ( = constant) Many residential heating systems consist of a stove, a heat pump, or an electric resistance heater. The air in these systems is heated by circulating it through a duct that contains the tubing for the hot gases or the electric resistance wires. Cooling can ...
... Simple Heating and Cooling ( = constant) Many residential heating systems consist of a stove, a heat pump, or an electric resistance heater. The air in these systems is heated by circulating it through a duct that contains the tubing for the hot gases or the electric resistance wires. Cooling can ...
Chapter 19 Test Review Notes
... the same sea-level air pressure at a given time are called isobars. ...
... the same sea-level air pressure at a given time are called isobars. ...
Weather Vocabulary Words
... At night, land rapidly loses its heat. Water cools off more slowly. Warmer air rises above the water and is replaced by cooler air form above land A scientist that studies and measures the weather conditions The study of weather Is formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. Has characteristics ...
... At night, land rapidly loses its heat. Water cools off more slowly. Warmer air rises above the water and is replaced by cooler air form above land A scientist that studies and measures the weather conditions The study of weather Is formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. Has characteristics ...
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
... 3. Problem 3.4 d) and e) 4. a) Determine the mean molar mass of the atmosphere of Venus, which consists of 95% CO2 and 5% N2 by volume. b) What is the corresponding gas constant? c) The mean surface temperature T on Venus is a scorching 740K as compared to only 288K for Earth; the surface pressure i ...
... 3. Problem 3.4 d) and e) 4. a) Determine the mean molar mass of the atmosphere of Venus, which consists of 95% CO2 and 5% N2 by volume. b) What is the corresponding gas constant? c) The mean surface temperature T on Venus is a scorching 740K as compared to only 288K for Earth; the surface pressure i ...
The Earth and Its Atmosphere
... greenhouse effect = warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere; caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth. Water is the only substance that can be found naturally in the atmos ...
... greenhouse effect = warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere; caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth. Water is the only substance that can be found naturally in the atmos ...
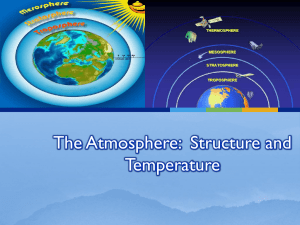
The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature
... What type of weather do you experience during the four seasons? What is the study of weather? What is another term that you associate with weather? Where does weather occur? What is our air made of? *lead them to water vapor is made in the atmosphere also = clouds/air ...
... What type of weather do you experience during the four seasons? What is the study of weather? What is another term that you associate with weather? Where does weather occur? What is our air made of? *lead them to water vapor is made in the atmosphere also = clouds/air ...
Unit 2 Meteorology Test
... 27. Snow on the ground prevents polar climates from gaining heat by what mechanism? A heating by greenhouse gases B heat spread from the equator C reflection of solar radiation D release of heat from Earth’s core 28. Which of the following best explains why temperature decreases as altitude increase ...
... 27. Snow on the ground prevents polar climates from gaining heat by what mechanism? A heating by greenhouse gases B heat spread from the equator C reflection of solar radiation D release of heat from Earth’s core 28. Which of the following best explains why temperature decreases as altitude increase ...
1/12/2012 Chap. 1 - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... information is related to: a) weather; b) climate; c) neither; d) either. Q: Today’s maximum temperature is 75oF. This information is related to: a) weather; b) climate; c) neither; d) either. ...
... information is related to: a) weather; b) climate; c) neither; d) either. Q: Today’s maximum temperature is 75oF. This information is related to: a) weather; b) climate; c) neither; d) either. ...
Weather Lab Powerpoint Charts
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.