Theory
... In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special form of heat exchanger because in addition to heat exchange, a material exchange also occurs as a result of evapo ...
... In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special form of heat exchanger because in addition to heat exchange, a material exchange also occurs as a result of evapo ...
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER
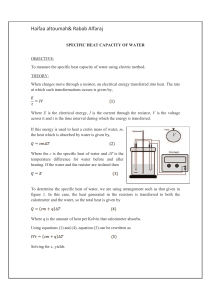
... To determine the specific heat of water, we are using arrangement such as that given in figure 1. In this case, the heat generated in the resistors is transferred to both the calorimeter and the water, so the total heat is given by ...
... To determine the specific heat of water, we are using arrangement such as that given in figure 1. In this case, the heat generated in the resistors is transferred to both the calorimeter and the water, so the total heat is given by ...
Structure of the Atmosphere
... Electrometeor - atmospheric electricity, i.e. lightning, auroras (Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) or Aurora Australis (Southern Lights)). ...
... Electrometeor - atmospheric electricity, i.e. lightning, auroras (Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) or Aurora Australis (Southern Lights)). ...
8 - Meteorology - Simone Damiano
... S c i e n c e s Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds, Cumulus Clouds, ...
... S c i e n c e s Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds, Cumulus Clouds, ...
1 Regional Climate Model 2 Calculating Cloud Base Heights
... formation would be if the air from lower elevations is lifted adiabatically. This is one of the reasons why we chose grid-points with elevation less than 800 m for this analysis. Furthermore, the horizontal grid resolution of the model is larger in size than any individual cloud, and the model RH do ...
... formation would be if the air from lower elevations is lifted adiabatically. This is one of the reasons why we chose grid-points with elevation less than 800 m for this analysis. Furthermore, the horizontal grid resolution of the model is larger in size than any individual cloud, and the model RH do ...
File
... 16. How does cloud cover affect albedo? Reflects solar radiation during day. Traps radiation at surface level at night. 17. ___________warm_________ air moves towards the poles and ________cold________ air moves towards the equator. 18. Label the major wind belts on the globe below. ...
... 16. How does cloud cover affect albedo? Reflects solar radiation during day. Traps radiation at surface level at night. 17. ___________warm_________ air moves towards the poles and ________cold________ air moves towards the equator. 18. Label the major wind belts on the globe below. ...
Meteorology Unit Test Study Guide
... 20. Which gas is more dense, a gas that has a density of 1.1 g/ml or a gas that has a density of 1.18 g/ml? The gas that has a density of 1.18 g/ml 21. Which type of air is denser, warm air or cool air? Explain. Cool air is denser because as air cools its molecules move closer together making it mor ...
... 20. Which gas is more dense, a gas that has a density of 1.1 g/ml or a gas that has a density of 1.18 g/ml? The gas that has a density of 1.18 g/ml 21. Which type of air is denser, warm air or cool air? Explain. Cool air is denser because as air cools its molecules move closer together making it mor ...
Weather Unit Notes - Lindbergh School District
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
Atmosphere and Weather Unit notes
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. ...
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. ...
Meteorology Test On a July day large cumulonimbus clouds are
... 19. What causes the outside of the windshield of a car to get icy on a cold autumn night when there is no rain? a. Moisture comes from inside the car b. Water vapor from the air condenses and freezes on the glass c. Water that is already on the glass evaporates and freezes d. Hydrogen and oxygen in ...
... 19. What causes the outside of the windshield of a car to get icy on a cold autumn night when there is no rain? a. Moisture comes from inside the car b. Water vapor from the air condenses and freezes on the glass c. Water that is already on the glass evaporates and freezes d. Hydrogen and oxygen in ...
Meteorology Test On a July day large cumulonimbus clouds are
... 19. What causes the outside of the windshield of a car to get icy on a cold autumn night when there is no rain? a. Moisture comes from inside the car b. Water vapor from the air condenses and freezes on the glass c. Water that is already on the glass evaporates and freezes d. Hydrogen and oxygen in ...
... 19. What causes the outside of the windshield of a car to get icy on a cold autumn night when there is no rain? a. Moisture comes from inside the car b. Water vapor from the air condenses and freezes on the glass c. Water that is already on the glass evaporates and freezes d. Hydrogen and oxygen in ...
Meteorology_Practice_Test
... 1. A ______ _______ is defined as the transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. 2. A ______ ______ is defined as the transition zone where a warm air mass is replacing a cold air mass. 3. ____________ is the evaporation of water from plants into the atmosphere. 4. ______ ...
... 1. A ______ _______ is defined as the transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. 2. A ______ ______ is defined as the transition zone where a warm air mass is replacing a cold air mass. 3. ____________ is the evaporation of water from plants into the atmosphere. 4. ______ ...
Corporate Profile
... Pressure is isotropic; at any point, it is the same in all directions Dalton’s law: total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures exerted by each individual gas ...
... Pressure is isotropic; at any point, it is the same in all directions Dalton’s law: total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures exerted by each individual gas ...
1AER200-MET1
... Humidity and Dew point • Warm air can hold more moisture. • The water vapor a volume of air can hold is governed by its temperature. • Air is said to be saturated when it contains the maximum amount of water it can hold at that temperature. • Dew point - the temperature to which unsaturated air mus ...
... Humidity and Dew point • Warm air can hold more moisture. • The water vapor a volume of air can hold is governed by its temperature. • Air is said to be saturated when it contains the maximum amount of water it can hold at that temperature. • Dew point - the temperature to which unsaturated air mus ...
Weather Tools and Symbols - Milton 7th Grade Advanced Science
... air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at a certain temperature. Meteorologists use % to show relative humidity ...
... air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at a certain temperature. Meteorologists use % to show relative humidity ...
Thermodynamics
... Thermodynamics is the study that concerns with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. ...
... Thermodynamics is the study that concerns with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. ...
notes for meteorofe - pams
... Ocean, occurring every 4 to 12 years and causing unusual global weather patterns. – Generally occurs in winter. – Winds get weaker, thus ocean gets warmer. – Thunderstorms that normally occur on the equator move eastward. • Southwest U.S. gets more water, Australia and Indonesia gets less (maybe). • ...
... Ocean, occurring every 4 to 12 years and causing unusual global weather patterns. – Generally occurs in winter. – Winds get weaker, thus ocean gets warmer. – Thunderstorms that normally occur on the equator move eastward. • Southwest U.S. gets more water, Australia and Indonesia gets less (maybe). • ...
4th Grade Weather and Water Cycle Vocabulary
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
File
... 6. UV radiation breaks down ___________ in our atmosphere. 7. Describe each form of heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation) and which substances (solid, liquid, or gas) they occur in. 8. When radiation ...
... 6. UV radiation breaks down ___________ in our atmosphere. 7. Describe each form of heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation) and which substances (solid, liquid, or gas) they occur in. 8. When radiation ...
WEATHER
... 2. water vapor (normally) condenses only onto a surface; ex. Dust, soot, sulfate the bigger the particle the bigger the ...
... 2. water vapor (normally) condenses only onto a surface; ex. Dust, soot, sulfate the bigger the particle the bigger the ...
Assimilation of high resolution dial water vapor data into the MM5
... Lidar systems are admittedly capable of closing gaps in the existing observational network, since they are able to observe parameters like temperature, wind, and water vapor with high spatial and temporal resolution as well as accuracy. LASE is an extensively characterized airborne DIAL system which ...
... Lidar systems are admittedly capable of closing gaps in the existing observational network, since they are able to observe parameters like temperature, wind, and water vapor with high spatial and temporal resolution as well as accuracy. LASE is an extensively characterized airborne DIAL system which ...
Weather - s3.amazonaws.com
... 2. As air warms, relative humidity decreases 3. As air cools, relative humidity increases ...
... 2. As air warms, relative humidity decreases 3. As air cools, relative humidity increases ...
The Difference Between Weather and Climate
... Air Pressure: the weight of air pushing on Earth’s surface Humidity: the amount of water vapor in the air Drought: a long period of very low rainfall; may last up to several years *** A drought can be very dangerous to people, animals, and plants, since we all need water to survive. ...
... Air Pressure: the weight of air pushing on Earth’s surface Humidity: the amount of water vapor in the air Drought: a long period of very low rainfall; may last up to several years *** A drought can be very dangerous to people, animals, and plants, since we all need water to survive. ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.