Science Test Review #2
... Period _____________ Date ____________ (19) Types of air masses: Tropical: warm; low pressure Polar: cold; high pressure Maritime: air mass that occurs over oceans Continental: air mass that occurs over land (20) Types of Storms: thunderstorms, tornados, etc. (21) Techniques to observe geolo ...
... Period _____________ Date ____________ (19) Types of air masses: Tropical: warm; low pressure Polar: cold; high pressure Maritime: air mass that occurs over oceans Continental: air mass that occurs over land (20) Types of Storms: thunderstorms, tornados, etc. (21) Techniques to observe geolo ...
Differential Heating, Convection, and Air Pressure
... Differential Heating, Convection, and Air Pressure Science Review Game ...
... Differential Heating, Convection, and Air Pressure Science Review Game ...
Regents Earth Science
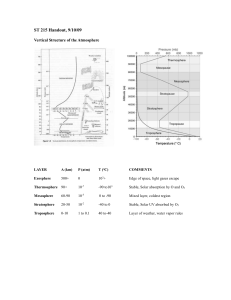
... Weather & the Atmosphere I. Structure of the Atmosphere A. Weather - the state of the atmosphere at a given time & place. B. Meteorology - the study of the atmosphere & the weather. C. Measuring the weather: 1. Wind speed - can be estimated by observing objects and relating that to the Beaufort scal ...
... Weather & the Atmosphere I. Structure of the Atmosphere A. Weather - the state of the atmosphere at a given time & place. B. Meteorology - the study of the atmosphere & the weather. C. Measuring the weather: 1. Wind speed - can be estimated by observing objects and relating that to the Beaufort scal ...
File
... Date when the sun is directly over the equator (0° latitude). On this day, at all places on the globe, night and day are of equal length--12 hours. Vernal (spring) Equinox (northern hemisphere) occurs on about March 21. Fall (autumnal) equinox (northern hemisphere) occurs on or about September 23 ...
... Date when the sun is directly over the equator (0° latitude). On this day, at all places on the globe, night and day are of equal length--12 hours. Vernal (spring) Equinox (northern hemisphere) occurs on about March 21. Fall (autumnal) equinox (northern hemisphere) occurs on or about September 23 ...
910 Handout, Structure and Composition
... Artificial satellites Air pollution Political boundaries It’s Your Atmosphere Only planet with abundant O2 atmosphere. Oceans cover 2/3 of planet. Natural greenhouse effect keeps urface temperatures 40 to -40 C allows three phases of water (ice, liquid, vapor) Hydrologic cycle recycles fresh water f ...
... Artificial satellites Air pollution Political boundaries It’s Your Atmosphere Only planet with abundant O2 atmosphere. Oceans cover 2/3 of planet. Natural greenhouse effect keeps urface temperatures 40 to -40 C allows three phases of water (ice, liquid, vapor) Hydrologic cycle recycles fresh water f ...
Chapter 16 Teal Weather Jeopardy 2015
... vapor in the air compared to the amount needed for the air to be saturated is ...
... vapor in the air compared to the amount needed for the air to be saturated is ...
Weather maps
... High Pressure and Clear Weather High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud ...
... High Pressure and Clear Weather High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud ...
what to know about meteorology list
... 11. The closer the air temperature is to the dew point, the higher the relative humidity. 12. Know this Process: Air is warmed, becomes less dense due to expansion; is forced upwards; expands and cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds ...
... 11. The closer the air temperature is to the dew point, the higher the relative humidity. 12. Know this Process: Air is warmed, becomes less dense due to expansion; is forced upwards; expands and cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds ...
Unit Test: Atmospheric Forces
... 1. What instruments measures atmospheric pressure 2. What has caused the destruction of the ozone layer? 3. Two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere 4. List the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and describe them in terms of wavelength. 5. What portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is MOS ...
... 1. What instruments measures atmospheric pressure 2. What has caused the destruction of the ozone layer? 3. Two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere 4. List the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and describe them in terms of wavelength. 5. What portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is MOS ...
Chapter 16,section 4 Water in the atmosphere
... • Clouds of all kinds form when water vapor in the air becomes liquid water or ice crystals. The process by which molecules of water vapor in the air become liquid water is called condensation. How does water condense? As you know, cold air can hold less water vapor than warm air. As air cools, the ...
... • Clouds of all kinds form when water vapor in the air becomes liquid water or ice crystals. The process by which molecules of water vapor in the air become liquid water is called condensation. How does water condense? As you know, cold air can hold less water vapor than warm air. As air cools, the ...
Meteorology Chapter 4 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... 1) If the air temperature remains constant, evaporating water into the air will ________ the dew point and ________ the relative humidity. a) increase, decrease b) not change, increase c) decrease, increase d) decrease, decrease e) increase, increase ...
... 1) If the air temperature remains constant, evaporating water into the air will ________ the dew point and ________ the relative humidity. a) increase, decrease b) not change, increase c) decrease, increase d) decrease, decrease e) increase, increase ...
Earth and Space Science Pre-Test
... 35. Warm moist air rises, expands due to decreasing pressure, cools, and condenses. This describes the formation of ________. ...
... 35. Warm moist air rises, expands due to decreasing pressure, cools, and condenses. This describes the formation of ________. ...
the Dew Point - Passport to Knowledge
... In 1751 French physicist Charles Le Roy sealed damp air in a glass container. As he observed the container, droplets of water began to appear on the surface of the glass. He heated the container and the droplets disappeared: conversely when he cooled the container the droplets reappeared. Le Roy’s e ...
... In 1751 French physicist Charles Le Roy sealed damp air in a glass container. As he observed the container, droplets of water began to appear on the surface of the glass. He heated the container and the droplets disappeared: conversely when he cooled the container the droplets reappeared. Le Roy’s e ...
5-SG - TeacherWeb
... High = out CW , cyclone Low = in CCW , anticyclone - weather related to H and L pressure sys. HUMIDITY - psychrometer, hygrometer - relative humidity, absolute humidity saturation, dew point - calculating RH and DP using ESRT - using DP and temp to forecast precip. (closer = > chance) - cloud format ...
... High = out CW , cyclone Low = in CCW , anticyclone - weather related to H and L pressure sys. HUMIDITY - psychrometer, hygrometer - relative humidity, absolute humidity saturation, dew point - calculating RH and DP using ESRT - using DP and temp to forecast precip. (closer = > chance) - cloud format ...
Humidity - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... Condensation • Condensation is the process by which a gas, such as water vapor, becomes a liquid. • Condensation will occur when the air is SATURATED, or has a relative humidity of 100%. The air can’t hold any more water vapor, so the water condensed out of the air. This commonly happens when moist ...
... Condensation • Condensation is the process by which a gas, such as water vapor, becomes a liquid. • Condensation will occur when the air is SATURATED, or has a relative humidity of 100%. The air can’t hold any more water vapor, so the water condensed out of the air. This commonly happens when moist ...
relative humidity
... • Condensation will occur when the air is SATURATED, or has a relative humidity of 100%. • The air can’t hold any more water vapor, so the water condensed out of the air. • This commonly happens when moist air is cooled, or comes in contact with a cool surface. ...
... • Condensation will occur when the air is SATURATED, or has a relative humidity of 100%. • The air can’t hold any more water vapor, so the water condensed out of the air. • This commonly happens when moist air is cooled, or comes in contact with a cool surface. ...
111 HUMIDITY INSTRUMENTS
... on the mirror and the light beam scatters instead of reflecting into a detector. Electronics in the instrument cool or heat the mirror to maintain the surface precisely at the dew point temperature, which is provided as an output. These are accurate instruments with relatively slow response. For col ...
... on the mirror and the light beam scatters instead of reflecting into a detector. Electronics in the instrument cool or heat the mirror to maintain the surface precisely at the dew point temperature, which is provided as an output. These are accurate instruments with relatively slow response. For col ...
Meteorology Test
... 16) An isobar is a line drawn on a weather map connecting points of equal pressure. 17) The Beaufort scale measures wind strength 18) The dry adiabatic lapse rate is 1 degree Celsius per 100m. 19) Pressure, relative humidity, and temperature 20) Virga is falling precipitation that evaporates before ...
... 16) An isobar is a line drawn on a weather map connecting points of equal pressure. 17) The Beaufort scale measures wind strength 18) The dry adiabatic lapse rate is 1 degree Celsius per 100m. 19) Pressure, relative humidity, and temperature 20) Virga is falling precipitation that evaporates before ...
DoubleJeopardy2
... The topsoil of a mature prairie has more of what material than The layers below? ...
... The topsoil of a mature prairie has more of what material than The layers below? ...
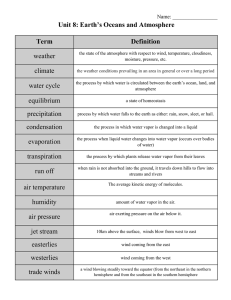
Unit 8: Earth`s Oceans and Atmosphere
... when rain is not absorbed into the ground, it travels down hills to flow into streams and rivers ...
... when rain is not absorbed into the ground, it travels down hills to flow into streams and rivers ...
Earth Science Weather Variable Review Sheet Topics: Air
... Know how to use the conversion temperature scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instrument used to take temperature. Air Pressure: Know how to use the conversion pressure scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instruments used to measure pressure. Understand the factors for air pressure: temperature, moistu ...
... Know how to use the conversion temperature scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instrument used to take temperature. Air Pressure: Know how to use the conversion pressure scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instruments used to measure pressure. Understand the factors for air pressure: temperature, moistu ...
DRACAENA MARGINATA
... bright yet indirect light. Too much light will cause the leaves to burn or bleach. ...
... bright yet indirect light. Too much light will cause the leaves to burn or bleach. ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.