weather test study guide
... They also use the history of weather to help predict what will happen in the future. 12. Which direction does air usually move across the United States? From west to east 13. Where do most weather changes occur? Along fronts; for example, we are likely to experience a change in weather when a cold f ...
... They also use the history of weather to help predict what will happen in the future. 12. Which direction does air usually move across the United States? From west to east 13. Where do most weather changes occur? Along fronts; for example, we are likely to experience a change in weather when a cold f ...
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems
... r = relative humidity, and T = is the air temperature in °K Note: 273.15°K = 0°C = 32°F. Question 3: The relative humidity is 70% at a noon-time temperature of 75°F (297°K). How much must the air cool for dew to form that night? Question 4: The relative humidity is 90% at a noon-time temperature of ...
... r = relative humidity, and T = is the air temperature in °K Note: 273.15°K = 0°C = 32°F. Question 3: The relative humidity is 70% at a noon-time temperature of 75°F (297°K). How much must the air cool for dew to form that night? Question 4: The relative humidity is 90% at a noon-time temperature of ...
The atmosphere! - Studentportalen
... •" The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
... •" The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
Weather Merit Badge
... and pushes the fluid above it out of the way. The fluid cools away from stove top and begins to sink. (cooler=more dense) ...
... and pushes the fluid above it out of the way. The fluid cools away from stove top and begins to sink. (cooler=more dense) ...
Atmosphere ppt - Bedford Middle School
... Temperature v. Heat Temperature – measurement of how fast or slow molecules move. Average energy of all the moving molecules. Measured by thermometer. ...
... Temperature v. Heat Temperature – measurement of how fast or slow molecules move. Average energy of all the moving molecules. Measured by thermometer. ...
Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer
... Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration WEATHER BASICS: ¾ Explain where the energy for Earth’s weather originates. ¾ Describe the basic directio ...
... Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration WEATHER BASICS: ¾ Explain where the energy for Earth’s weather originates. ¾ Describe the basic directio ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #1 (Chapters 1 and 2
... 22. What are the three important rules regarding radiation? ...
... 22. What are the three important rules regarding radiation? ...
The Atmosphere: Climate and Weather
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
File
... Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. What you may call weather is the water cycle at work. ...
... Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. What you may call weather is the water cycle at work. ...
Earth*s Atmosphere
... Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere so they help to moderate global temperatures. Without an atmosphere with greenhouse gases, Earth's temperatures would be frigid at night and scorching during the day. Important greenhouse gases include: ...
... Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere so they help to moderate global temperatures. Without an atmosphere with greenhouse gases, Earth's temperatures would be frigid at night and scorching during the day. Important greenhouse gases include: ...
Weather/Climate Vocabulary Matching
... forming high in the atmosphere, made of ice crystals. A sudden spark or energy discharge in the atmosphere. ...
... forming high in the atmosphere, made of ice crystals. A sudden spark or energy discharge in the atmosphere. ...
Bad Meteorology: The reason clouds form when air cools is because
... The air (mainly nitrogen and oxygen) no more has a holding capacity for water vapor, than, say, water vapor has for nitrogen. The atmosphere is a mixture of gases. While saturation (which involves bonds between different molecules) is a real phenomenon in liquids it does not describe the interactio ...
... The air (mainly nitrogen and oxygen) no more has a holding capacity for water vapor, than, say, water vapor has for nitrogen. The atmosphere is a mixture of gases. While saturation (which involves bonds between different molecules) is a real phenomenon in liquids it does not describe the interactio ...
Q: What is Weather
... Closely spaced isobars - lines on a map that connect places of equal air pressure - indicate a steep pressure gradient and high winds Widely spaced isobars indicate a weak pressure gradient and light winds. Influence of temperature on weather Temperature: measure of the motion of the molecules in a ...
... Closely spaced isobars - lines on a map that connect places of equal air pressure - indicate a steep pressure gradient and high winds Widely spaced isobars indicate a weak pressure gradient and light winds. Influence of temperature on weather Temperature: measure of the motion of the molecules in a ...
The atmosphere - Studentportalen
... • The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
... • The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
weather reviewScienc.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c) when the temperature stays the same for a long time d) season to season changes in the atmosphere 3. A high pressure system is associated with: a) heavy precipitation and overcast conditions b) thunder and lightning c) clear, cool weather d) none of the above 4. When there is low pressure, we can ...
... c) when the temperature stays the same for a long time d) season to season changes in the atmosphere 3. A high pressure system is associated with: a) heavy precipitation and overcast conditions b) thunder and lightning c) clear, cool weather d) none of the above 4. When there is low pressure, we can ...
L10 - atmo.arizona.edu
... Up to this point we’ve talked about moisture content in terms of the mass of moisture, mv, or the molar concentration of vapor, nv. This has been useful when determining the effective molecular weight for the ideal gas law. Because water vapor is tri-atomic, and light, it also has a higher heat capa ...
... Up to this point we’ve talked about moisture content in terms of the mass of moisture, mv, or the molar concentration of vapor, nv. This has been useful when determining the effective molecular weight for the ideal gas law. Because water vapor is tri-atomic, and light, it also has a higher heat capa ...
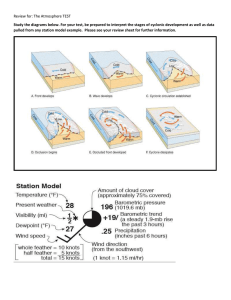
Review for: The Atmosphere TEST Study the diagrams below. For
... A cold, dense air mass displaces a warm air mass and forces the warm air to rise steeply When a warm and cold air mass meet’s what happens? Measures air pressure Measures wind speed Measures relative humidity Uses weather data to project upcoming weather conditions Captures visible and infrared (hea ...
... A cold, dense air mass displaces a warm air mass and forces the warm air to rise steeply When a warm and cold air mass meet’s what happens? Measures air pressure Measures wind speed Measures relative humidity Uses weather data to project upcoming weather conditions Captures visible and infrared (hea ...
Weather & Climate - s3.amazonaws.com
... 2. As air warms, relative humidity decreases 3. As air cools, relative humidity increases ...
... 2. As air warms, relative humidity decreases 3. As air cools, relative humidity increases ...
TZ Sensors - Rack Technologies
... Supply voltage: 9.0 – 32 VDC – powered via TZ Device Network Current Usage: < 4 mA | 4 mA | < 4 mA | < 15 mA Sinks up to an additional 10 mA 8115CF: Normally open, dry contact 8116CF: Pinout: NC, GND, NC, Temperature 8117CF: Pinout: V+, GND, Relative Humidity, NC ...
... Supply voltage: 9.0 – 32 VDC – powered via TZ Device Network Current Usage: < 4 mA | 4 mA | < 4 mA | < 15 mA Sinks up to an additional 10 mA 8115CF: Normally open, dry contact 8116CF: Pinout: NC, GND, NC, Temperature 8117CF: Pinout: V+, GND, Relative Humidity, NC ...
Meteorology_Study_Guide
... ______ 2. This layer contains 75% of the atmospheric gases and is where weather occurs ______ 3. This layer is where auroras form ______ 4. The layer above the stratosphere where temperature begins to fall again ______ 5. The boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere ______ 6. This layer shi ...
... ______ 2. This layer contains 75% of the atmospheric gases and is where weather occurs ______ 3. This layer is where auroras form ______ 4. The layer above the stratosphere where temperature begins to fall again ______ 5. The boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere ______ 6. This layer shi ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.