* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
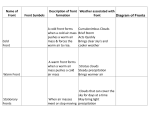
Unit 6 Study Guide : Meteorology Test Date: _______________ 1. List the four main layers of the atmosphere and their temperature trend with height from closest to the ground to highest. Also list where each of the following occurs: weather, meteors burning up, ozone layer, the northern lights/aurora. 2. Which main layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer? How does ozone protect us? 3. Which layer do you think contains the most mass? Why? (Hint – think about air pressure relative to altitude!) 4. Why does temperature decrease in the troposphere? What type of heat transfer is occurring here? 5. The chemical formula for ozone is _________ 6. UV radiation breaks down ___________ in our atmosphere. 7. Describe each form of heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation) and which substances (solid, liquid, or gas) they occur in. 8. When radiation strikes an object, it can be _______________, _______________, or ________________ . 9. Describe what happens in each of the following: a. reflection b. scattering 10. Air masses move from _______ air pressure to _______ air pressure. This is what causes _____. 11. A rising barometer reading indicates a(n) __________ (increase/decrease) in air pressure, which will be associated with _____ (hot/cold) temperatures and _______ (humid/dry) air. 12. If you were to see a weather forecast on TV what would represent the cold fronts and warm fronts? Draw the symbols for each. 13. Which two properties characterize an air mass? 14. What type of air mass effects NC and the eastern coast of the US the most? 15. What type of air mass would originate over northern Canada? 16. What type of air mass would be associated with cold, wet conditions? 17. What type of air mass would have a great effect on weather in the southwestern portion of the US? 18. How do you know which direction a front is moving when you are looking at the symbol on a weather map? 19. If a warm air mass moves over a cold air mass, describe the type of precipitation you would expect. 20. If a cold air mass collides with a warm air mass, describe the type of precipitation you would expect. 21. Warm air is _______ (choose: more/less) dense than cold air. 22. What is the ultimate source of energy that drives wind? 23. What do the contour-‐type “lines” near high and low fronts, on a weather map, indicate? What does it mean if these lines are closely spaced? 24. As air rises it will ________ (expand/contract) and ________ (warm/cool) but never loose heat energy. When the _______ _______ is reached, water droplets will coalesce (condense) and form a _________. 25. What is the difference between absolute humidity and relative humidity? 26. What happens to relative humidity as temperature of the air increases? 27. What does it mean if the air is “saturated”? WHY does the air need to be saturated in order for clouds to form? What is the phase change that water goes through to form clouds? 28. What causes dew to form on the grass outside most mornings? (Be DESCRIPTIVE, here!). When you wake up and see frost on the grass outside, what happened? (Hint – think about temperature relative to dew point and the phase changes of water!) 29. In the Northern hemisphere, wind is deflected to the _______ (right/left) and therefore windbelts spin ________(clockwise/counterclockwise). 30. In the Southern hemisphere, wind is deflected to the _____ (right/left) and therefore windbelts spin ____ (cw/ccw) 31. Draw a global wind belt diagram and label all of the correct pressure zones (subtropical high, subpolar low, polar high, equatorial low) and wind belts (tradewinds, westerlies, easterlies). Draw in arrows to show where the air is moving. These arrows should be curved – why? 32. Label the correct phase changes: S ! L _______________, L ! S = ______________, L ! G __________, G -‐! L ___________, G ! S _______________, S! G ___________________ 33. What type of cloud produces t-‐storms/hail? 34. What type of air rises at a front where two air masses meet? What does the uplift of air usually produce? 35. Hurricane intensity is classified according to ____________________________________________. 36. What causes a hurricane to lose energy when it moves onto land? 37. What is the difference between a typhoon and a hurricane? 38. Cloudy, rainy weather would be associated with ___________ (high/low) air pressure systems. 39. The ultimate source of energy driving all weather systems on Earth is ___________. 40. Using the diagram below, match each letter with the description of what is occurring at that point. 41. _____ i. This area is probably experiencing some cloud coverage, and will soon have hot humid days with some light precipitation. _____ ii. This area will experience gusty winds. _____ iii. This area will be experiencing some violent storms followed by cold clear days. _____ iv. This area is a high pressure zone.