Meteorology - School in the Park
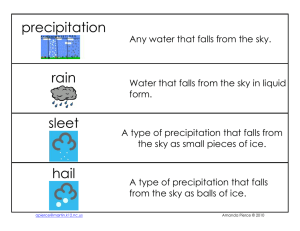
... Label the water cycle diagram by writing the following words in the correct boxes precipitation ...
... Label the water cycle diagram by writing the following words in the correct boxes precipitation ...
Lecture 5 (10/01) METR 1111
... The height contours from the first should approximately line up with the isobars from the second (except that they use fewer lines on one). To see this best, look in regions where the lines are closest together (greatest pressure gradient) and compare between the two maps A viewing tip: Click on the ...
... The height contours from the first should approximately line up with the isobars from the second (except that they use fewer lines on one). To see this best, look in regions where the lines are closest together (greatest pressure gradient) and compare between the two maps A viewing tip: Click on the ...
AIR MASSES AND FRONTS
... and a group of his colleagues concluded that storms are caused by the collision of large air masses that differ from one another in temperature and humidity. Storms occur in low pressure areas, but low pressure is not their cause. ...
... and a group of his colleagues concluded that storms are caused by the collision of large air masses that differ from one another in temperature and humidity. Storms occur in low pressure areas, but low pressure is not their cause. ...
1473227653.
... What is meant by saying that a body is moving with velocity , v relative to another. (1mark) A boat crosses a river 3km wide flowing at 4ms-1 to reach a point on the opposite bank 5km upstream. The boat’s speed in still water is 12ms-1. Find the direction in which the boat must be headed. (4marks) W ...
... What is meant by saying that a body is moving with velocity , v relative to another. (1mark) A boat crosses a river 3km wide flowing at 4ms-1 to reach a point on the opposite bank 5km upstream. The boat’s speed in still water is 12ms-1. Find the direction in which the boat must be headed. (4marks) W ...
Weather and Climate Notes
... Thermometers are used to measure air temperature Anemometers are used to measure wind speed Changes in wind speed indicate weather changes. Barometers measure air pressure. High pressure indicates fair or clear weather. Low pressure indicates stormy weather. A Wind Vane is used to determine wi ...
... Thermometers are used to measure air temperature Anemometers are used to measure wind speed Changes in wind speed indicate weather changes. Barometers measure air pressure. High pressure indicates fair or clear weather. Low pressure indicates stormy weather. A Wind Vane is used to determine wi ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 4 – Meteorology Review (CH 22
... 17. What form of radiation can people see? Which can’t we see? 18. How does radiation travel and at what speed does it travel? 19. What molecules are in the thermosphere and mesosphere and what do they absorb? 20. What affect does U.V. rays have in the stratosphere? 21. What absorbs infrared radiati ...
... 17. What form of radiation can people see? Which can’t we see? 18. How does radiation travel and at what speed does it travel? 19. What molecules are in the thermosphere and mesosphere and what do they absorb? 20. What affect does U.V. rays have in the stratosphere? 21. What absorbs infrared radiati ...
Intro to the Atmosphere
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
Es 241 P and Chem Pot
... And define the enthalpy of vaporization ~ the energy in the molecular bonds of the liquid ...
... And define the enthalpy of vaporization ~ the energy in the molecular bonds of the liquid ...
File
... • Meteorologist in Oklahoma: – Big picture first, then drill down to local. You can’t make an accurate forecast without understanding the big picture. (We call this the forecast funnel) ...
... • Meteorologist in Oklahoma: – Big picture first, then drill down to local. You can’t make an accurate forecast without understanding the big picture. (We call this the forecast funnel) ...
PPT
... -The moments of inertia around the x & z axes are very much larger than the moments of inertia around the y-axis. - The molecule also has 2 vibrational modes (position & velocity) but the vibrational modes are usually dominated by the rotational modes for atmospheric (troposphere/stratosphere) tempe ...
... -The moments of inertia around the x & z axes are very much larger than the moments of inertia around the y-axis. - The molecule also has 2 vibrational modes (position & velocity) but the vibrational modes are usually dominated by the rotational modes for atmospheric (troposphere/stratosphere) tempe ...
MME 2006 Metallurgical Thermodynamics
... to 1150 °C by adding solid copper at 25 C. 40000 kJ are lost during the time it takes to make the addition and the temperature to stabilize. What quantity of solid is used? ...
... to 1150 °C by adding solid copper at 25 C. 40000 kJ are lost during the time it takes to make the addition and the temperature to stabilize. What quantity of solid is used? ...
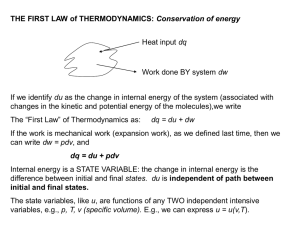
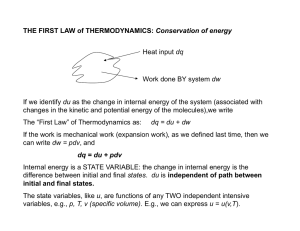
THE FIRST LAW of THERMODYNAMICS: Conservation of energy
... Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since dq = dw = 0, du = 0. Under these conditions, its clear that the volume of the gas changed, as ...
... Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since dq = dw = 0, du = 0. Under these conditions, its clear that the volume of the gas changed, as ...
Earth`s Climate System Today
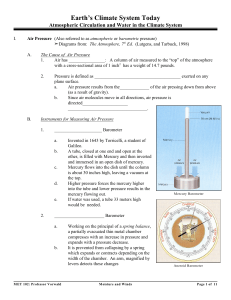
... second. Millibar values used in meteorology range from about 100 to 1050. At sea level, standard air pressure in millibars is 1013.2. Weather maps showing the pressure at the surface are drawn using millibars Standard pressure at seal level is 1013.2 mb (measured to the nearest tenth of a millibar f ...
... second. Millibar values used in meteorology range from about 100 to 1050. At sea level, standard air pressure in millibars is 1013.2. Weather maps showing the pressure at the surface are drawn using millibars Standard pressure at seal level is 1013.2 mb (measured to the nearest tenth of a millibar f ...
... Consider a column of gas Dz meters tall suspended somewhere in the atmosphere (here D symbolizes an interval or difference). The pressure acting on its bottom surface is higher than the pressure acting on its top surface. The pressure difference Dp exactly balances the weight (per unit area) of the ...
The Earth`s Atmosphere
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
Chap-3
... property of the system without loss or dissipation of energy. Due to these infinitesimal changes, the system is at rest during the whole process. Since it would take an infinite amount of time for the process to finish, perfectly reversible processes are impossible. However, if the system undergoing ...
... property of the system without loss or dissipation of energy. Due to these infinitesimal changes, the system is at rest during the whole process. Since it would take an infinite amount of time for the process to finish, perfectly reversible processes are impossible. However, if the system undergoing ...
Meteorology notes
... this scale is degrees Celsius. At standard air pressure, the Celsius scale sets the freezing point of water at 0 degrees Celsius (0°C) and the boiling point of water at 100 degrees Celsius (100°C). It is divide into equal increments of temperature based on the metric system. ...
... this scale is degrees Celsius. At standard air pressure, the Celsius scale sets the freezing point of water at 0 degrees Celsius (0°C) and the boiling point of water at 100 degrees Celsius (100°C). It is divide into equal increments of temperature based on the metric system. ...
Course 3: Pressure – Volume – Temperature Relationship of Pure
... Ideal gas equation of state is a model equation applicable to all gases to understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy ...
... Ideal gas equation of state is a model equation applicable to all gases to understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy ...
Chapter 1 - Weather Underground
... Most likely made of of hydrogen and helium So light they escaped to space ...
... Most likely made of of hydrogen and helium So light they escaped to space ...
chapter 3 - UniMAP Portal
... behavior of a gas quite accurately within some properly selected region. ...
... behavior of a gas quite accurately within some properly selected region. ...
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
... Not about to evaporate Heat added T Compressed liquid phase About to evaporate Heat added evaporation starts Saturated liquid phase ...
... Not about to evaporate Heat added T Compressed liquid phase About to evaporate Heat added evaporation starts Saturated liquid phase ...
Atmosphere
... Acid precipitation is another harmful side effect of the burning of fossil fuels. Air pollution can become a more serious problem as result of certain weather conditions. Temperature inversion is when a layering of warm air on top of cool air. Controlled by preventing air pollutants. ...
... Acid precipitation is another harmful side effect of the burning of fossil fuels. Air pollution can become a more serious problem as result of certain weather conditions. Temperature inversion is when a layering of warm air on top of cool air. Controlled by preventing air pollutants. ...
Vocabulary of Thermodynamics
... thermodynamic properties, all substances are assumed to be pure. A property of a substance is any measurable characteristic. Linear dimension, mass, electrical resistance, viscosity, thermal conductivity, temperature, pressure and color are examples of the properties of a substance. Not all properti ...
... thermodynamic properties, all substances are assumed to be pure. A property of a substance is any measurable characteristic. Linear dimension, mass, electrical resistance, viscosity, thermal conductivity, temperature, pressure and color are examples of the properties of a substance. Not all properti ...
Humidity

Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.There are three main measurements of humidity: absolute, relative and specific. Absolute humidity is the water content of air at a given temperature expressed in gram per cubic metre. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis.