Metabolic Processes Unit
... b. that reaction generates ATP. c. it replenishes the supply of NAD+. d. it allows NADH to move to the electron transport chain. e. none of the above. 19. Stomates open and close in response to a. carbon dioxide levels. b. glucose levels. c. light levels. d. oxygen levels. e. water levels. 20. Photo ...
... b. that reaction generates ATP. c. it replenishes the supply of NAD+. d. it allows NADH to move to the electron transport chain. e. none of the above. 19. Stomates open and close in response to a. carbon dioxide levels. b. glucose levels. c. light levels. d. oxygen levels. e. water levels. 20. Photo ...
Overview of mitochondria and plastids function in energy conversion
... carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose + oxygen + water Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first phase light-dependent reactions or photosynthetic reactions (also called the Light reactions) capture the energy of light g and use it to make high-energy g gy molecules. During the sec ...
... carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose + oxygen + water Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first phase light-dependent reactions or photosynthetic reactions (also called the Light reactions) capture the energy of light g and use it to make high-energy g gy molecules. During the sec ...
Plant Notes - cloudfront.net
... it turn into seeds Other animals eat the fruit and poop the seeds out far away from the parent plant, in some nice fertilizer so it can germinate ...
... it turn into seeds Other animals eat the fruit and poop the seeds out far away from the parent plant, in some nice fertilizer so it can germinate ...
National 4 -Energy from the sun Green plants are known as
... have light in order to carry out photosynthesis and produce glucose which is stored as starch. National 4 and 5- Affects of carbon dioxide on photosynthesis In order to make glucose, and subsequently starch, by photosynthesis plants must have carbon dioxide as a raw material. How much starch a plant ...
... have light in order to carry out photosynthesis and produce glucose which is stored as starch. National 4 and 5- Affects of carbon dioxide on photosynthesis In order to make glucose, and subsequently starch, by photosynthesis plants must have carbon dioxide as a raw material. How much starch a plant ...
Photosynthesis
... Aerobic conditions - pyruvate converts into molecules of water and carbon dioxid, the profit is ...
... Aerobic conditions - pyruvate converts into molecules of water and carbon dioxid, the profit is ...
Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
4.2 Carbon compounds and cells
... • Life as we know it is carbon based. • A carbon atom can form chemical bonds with other carbon atoms in long chains or rings. ...
... • Life as we know it is carbon based. • A carbon atom can form chemical bonds with other carbon atoms in long chains or rings. ...
Unit 4 Photosynthesis
... More ATP required to convert 3-Carbon in Sheath cell back into PEP Spend extra energy to run this reaction. Need PEP to bind CO2 to OAA ...
... More ATP required to convert 3-Carbon in Sheath cell back into PEP Spend extra energy to run this reaction. Need PEP to bind CO2 to OAA ...
2-4 outline cells and energy answers
... 6. During the second step of cellular respiration, the smaller molecules made during glycolysis are broken down. Large amounts of usable energy, called ATP, are ...
... 6. During the second step of cellular respiration, the smaller molecules made during glycolysis are broken down. Large amounts of usable energy, called ATP, are ...
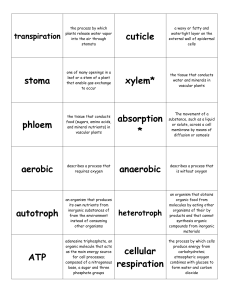
Explain what xylem and phloem are used for
... What is the function of the cuticle? The cuticle is a waxy covering that protects the plant from water loss. What is the function of stomata and guard cells? Explain the reasons why stomata open and close. Stomata and guard cells let carbon dioxide in and oxygen and water out of the leaves. Stomata ...
... What is the function of the cuticle? The cuticle is a waxy covering that protects the plant from water loss. What is the function of stomata and guard cells? Explain the reasons why stomata open and close. Stomata and guard cells let carbon dioxide in and oxygen and water out of the leaves. Stomata ...
Matching review Connect with lines
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
Title - Iowa State University
... c. Acetyl CoA is oxidized to two molecules of carbon dioxide, more ATP and NADH is produced, and FAD is reduced to form FADH2. d. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 move through the electron transport chain, and the energy released from this chain of redox reactions is used to create a proton gradient ac ...
... c. Acetyl CoA is oxidized to two molecules of carbon dioxide, more ATP and NADH is produced, and FAD is reduced to form FADH2. d. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 move through the electron transport chain, and the energy released from this chain of redox reactions is used to create a proton gradient ac ...
File
... Needed for Life • Most of the energy needed for life on Earth is gathered through photosynthesis • Plant, algae, and some blue/green bacteria do it. • Organisms that do not carry out photosynthesis (fungi, animals, some protists and bacteria) get their energy from photosynthetic organisms ...
... Needed for Life • Most of the energy needed for life on Earth is gathered through photosynthesis • Plant, algae, and some blue/green bacteria do it. • Organisms that do not carry out photosynthesis (fungi, animals, some protists and bacteria) get their energy from photosynthetic organisms ...
Answer Key - TeacherWeb
... 31. When electrons of a chlorophyll molecule are raised to a higher energy level, they enter the electron transport chain. ...
... 31. When electrons of a chlorophyll molecule are raised to a higher energy level, they enter the electron transport chain. ...
AP BIOLOGY QUIZ 2
... Why is this cyclic energy flow still important in photosynthetic organisms? a. It produces the majority of ATP required by the cell. b. It produces additional ATP to fuel the Calvin cycle. c. It produces glucose, while non-cyclic energy flow produces only ATP. d. It does not require chemiosmosis, as ...
... Why is this cyclic energy flow still important in photosynthetic organisms? a. It produces the majority of ATP required by the cell. b. It produces additional ATP to fuel the Calvin cycle. c. It produces glucose, while non-cyclic energy flow produces only ATP. d. It does not require chemiosmosis, as ...
review of ecology - Seekonk High School
... plants they eat (or eating other animals that ate the plants. □ Humans use fertilizers to provide nitrogen for plants. Water Cycle: □ Water evaporates from surface of the earth, condenses and falls as precipitation (rain or snow.) □ Water evaporation from surface of plants is transpiration. Carbon C ...
... plants they eat (or eating other animals that ate the plants. □ Humans use fertilizers to provide nitrogen for plants. Water Cycle: □ Water evaporates from surface of the earth, condenses and falls as precipitation (rain or snow.) □ Water evaporation from surface of plants is transpiration. Carbon C ...
INTERACTIVE GENETICS
... Van Helmont- Wondered if plants grew by taking mass out of the soil? - Measured the soil, planted a seed and watered the plant until it grew. - After 5 years, plants weighed 75 kg and the soil was unchanged! Concluded- water (hydrate) that made the plant grow! ...
... Van Helmont- Wondered if plants grew by taking mass out of the soil? - Measured the soil, planted a seed and watered the plant until it grew. - After 5 years, plants weighed 75 kg and the soil was unchanged! Concluded- water (hydrate) that made the plant grow! ...
photosynthesis Name: Date: 1. In most plants the process of
... in which the plant is growing. After increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in water, the student illuminated the plant and collected the bubbles of oxygen gas that were given o from the cut end of the submerged plant. ...
... in which the plant is growing. After increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in water, the student illuminated the plant and collected the bubbles of oxygen gas that were given o from the cut end of the submerged plant. ...
“Photosynthesis and Respiration Concept Map” Use the terms below
... Typically a concept map goes from general or big ideas to smaller more specific or detailed ideas. Additionally, a connecting phrase describes the relationship between each of the terms. Use all of the terms below (each should be in a box or bubble) to create a concept map about photosynthesis and r ...
... Typically a concept map goes from general or big ideas to smaller more specific or detailed ideas. Additionally, a connecting phrase describes the relationship between each of the terms. Use all of the terms below (each should be in a box or bubble) to create a concept map about photosynthesis and r ...
Intermediate Biology Unit 1
... production of lactic acid. Describe the effect of lactic acid on muscle cells and subsequent repayment of the oxygen debt. 4. State that anaerobic respiration in plants is irreversible and results in the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis 1. State that photosynthesis a series o ...
... production of lactic acid. Describe the effect of lactic acid on muscle cells and subsequent repayment of the oxygen debt. 4. State that anaerobic respiration in plants is irreversible and results in the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis 1. State that photosynthesis a series o ...
Ecology
... molecules by eating other organisms of their by products and that cannot synthesis organic compounds from inorganic materials ...
... molecules by eating other organisms of their by products and that cannot synthesis organic compounds from inorganic materials ...
Slide 1
... mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh). • An important process called cellular respiration takes place inside a mitochondrion. ...
... mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh). • An important process called cellular respiration takes place inside a mitochondrion. ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... phosphorylations using 2 ATP Sugar cleavage occurs Oxidations (dehydrogenations) occur 2 ATP form. Aerobic or anaerobic respiration may ...
... phosphorylations using 2 ATP Sugar cleavage occurs Oxidations (dehydrogenations) occur 2 ATP form. Aerobic or anaerobic respiration may ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.