Leaves and Photosynthesis
... There are veins in the leaves to transport water and sugar around. ...
... There are veins in the leaves to transport water and sugar around. ...
Cells need to produce new cells in order to
... 8. The process by which plants use carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water to make glucose and oxygen is called a. Osmosis b. Photosynthesis c. Cellular respiration ...
... 8. The process by which plants use carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water to make glucose and oxygen is called a. Osmosis b. Photosynthesis c. Cellular respiration ...
Chapter 5 Test Review
... 7. plants use sun to form glucose, animals eat plants, animals eat other animals 8. cellular respiration Section 2 1. photosynthesis 2. chlorophyll 3. red (675 nm) and blue (450 nm) 4. green wavelengths (525 nm) are reflected 5. oxygen gas (O2) 6. enter the electron transport chain of the thylakoid ...
... 7. plants use sun to form glucose, animals eat plants, animals eat other animals 8. cellular respiration Section 2 1. photosynthesis 2. chlorophyll 3. red (675 nm) and blue (450 nm) 4. green wavelengths (525 nm) are reflected 5. oxygen gas (O2) 6. enter the electron transport chain of the thylakoid ...
PowerPoint Presentation - THE CARBON CYCLE
... The same carbon atoms are used over and over on earth. They cycle between the earth & the atmosphere. ...
... The same carbon atoms are used over and over on earth. They cycle between the earth & the atmosphere. ...
Chapter 8 Photosynthesis.notebook
... when light is absorbed by the chlorophyll, the electrons gain energy cells need a way to transport these highenergy electrons cells use an electron carriers electron transport chain molecules to transport highenergy electrons from chlorophyll to another molecule electron transport NADP+ ...
... when light is absorbed by the chlorophyll, the electrons gain energy cells need a way to transport these highenergy electrons cells use an electron carriers electron transport chain molecules to transport highenergy electrons from chlorophyll to another molecule electron transport NADP+ ...
6CO2 + 6H2O sunlight C 6H12O6 + 6O2 Name
... 2. What process is the equation above showing? photosynthesis 3. Where does the process you answered in #2 occur (what organelle in the cell?) chloroplast 4. Define: Autotroph organism that can make its own food (plants) Heterotroph organism that cannot make its own food (animals) 5. Explain how you ...
... 2. What process is the equation above showing? photosynthesis 3. Where does the process you answered in #2 occur (what organelle in the cell?) chloroplast 4. Define: Autotroph organism that can make its own food (plants) Heterotroph organism that cannot make its own food (animals) 5. Explain how you ...
BIOLOGY PRACTICE QUESTIONS GROUP II 1.To separate the
... 36. Phase II is often referred to as (a) oxidation (b) hydrolysis (c) carbon fixation (d) aerobic respiration 37. A three-carbon sugar formed during phase II is (a) carbon dioxide (b) glucose (c) ATP (d) PGAL 38. The reaction in phase I occurs in the (a) grana (b) stroma (c) Golgi apparatus (d) cel ...
... 36. Phase II is often referred to as (a) oxidation (b) hydrolysis (c) carbon fixation (d) aerobic respiration 37. A three-carbon sugar formed during phase II is (a) carbon dioxide (b) glucose (c) ATP (d) PGAL 38. The reaction in phase I occurs in the (a) grana (b) stroma (c) Golgi apparatus (d) cel ...
abiotic components - Southgate Schools
... called photosynthesis Have a cell wall of cellulose ...
... called photosynthesis Have a cell wall of cellulose ...
Photosynthesis
... • When RuBP is oxidized, it produces only 1 molecule of 3-PGA. • This process is called photorespiration. ...
... • When RuBP is oxidized, it produces only 1 molecule of 3-PGA. • This process is called photorespiration. ...
File
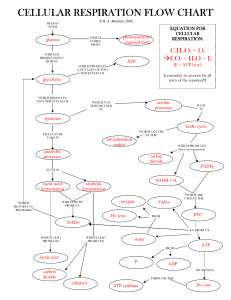
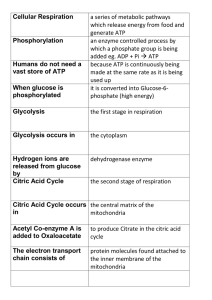
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
Molecular Biology
... carbon (carbon dioxide) with ATP and NADPH produced in the light dependent reaction ...
... carbon (carbon dioxide) with ATP and NADPH produced in the light dependent reaction ...
Unit 1: Cells - Loudoun County Public Schools
... breakdown of organic molecules to release energy stored by photosynthesis. Understand that PLANT use both Photosynthesis (obtain food) & Respiration (obtain energy). The product of Photosynthesis becomes the reactants in Respiration and the products of Respiration become the reactants in Photosynthe ...
... breakdown of organic molecules to release energy stored by photosynthesis. Understand that PLANT use both Photosynthesis (obtain food) & Respiration (obtain energy). The product of Photosynthesis becomes the reactants in Respiration and the products of Respiration become the reactants in Photosynthe ...
Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Essential Concepts
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars that can then be either used by the plant or by heterotrophs. The general reaction, which should be memorized, is : 6CO2 + 6H2O light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Written out, this equation states that 6 molecules of ...
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars that can then be either used by the plant or by heterotrophs. The general reaction, which should be memorized, is : 6CO2 + 6H2O light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Written out, this equation states that 6 molecules of ...
7th Grade - Vernon Independent School District
... Species- all organisms of the same kind that adapted to a ...
... Species- all organisms of the same kind that adapted to a ...
Student review sheet
... 3rd trophic levels Explain the cycling of nutrients (S.A.-1) Water cycle Water evaporates from ocean and lakes and is turned into water vapor in the air Plants lose water through leaves by transpiration Water vapor forms clouds Precipitation Water flows back into ocean or seeps into the gr ...
... 3rd trophic levels Explain the cycling of nutrients (S.A.-1) Water cycle Water evaporates from ocean and lakes and is turned into water vapor in the air Plants lose water through leaves by transpiration Water vapor forms clouds Precipitation Water flows back into ocean or seeps into the gr ...
Test Review – Ch
... Energy required for cellular activity, when breaking phosphate bond 5. What happens during photosynthesis? Light reactions (thylakoid membrane): energy from sun absorbed by chlorophyll, excites electrons, water split into hydrogen ions, free electrons, and oxygen which is released, ADP and NADP+ con ...
... Energy required for cellular activity, when breaking phosphate bond 5. What happens during photosynthesis? Light reactions (thylakoid membrane): energy from sun absorbed by chlorophyll, excites electrons, water split into hydrogen ions, free electrons, and oxygen which is released, ADP and NADP+ con ...
Photosynthesis
... • All energy on earth comes from the sun. • We depend on: – Plants – Algae (underwater plants) – Cyanobacteria (photosynthetic bacteria) • To provide this energy to us! ...
... • All energy on earth comes from the sun. • We depend on: – Plants – Algae (underwater plants) – Cyanobacteria (photosynthetic bacteria) • To provide this energy to us! ...
Photosynthesis
... Glycolysis requires NAD+ since no oxygen is available. The electrons from NADH are added to pyruvate to either produce alcohol (in plants and yeast) or lactate (in animals and bacteria). That produces NAD+ from which glucose can be broken down to make ATP. This is useful during strenuous exercise. D ...
... Glycolysis requires NAD+ since no oxygen is available. The electrons from NADH are added to pyruvate to either produce alcohol (in plants and yeast) or lactate (in animals and bacteria). That produces NAD+ from which glucose can be broken down to make ATP. This is useful during strenuous exercise. D ...
Standard 6: ECOLOGY – REVIEW OF BASICS
... Nitrogen Cycle: □ All organisms need nitrogen in proteins and nucleic acids. □ Plants and animals cannot use nitrogen gas found in air. □ Bacteria in soil or on the roots of legumes (plants like beans and clover) can take nitrogen from the air and put it in a form usable by plants. □ Animals get the ...
... Nitrogen Cycle: □ All organisms need nitrogen in proteins and nucleic acids. □ Plants and animals cannot use nitrogen gas found in air. □ Bacteria in soil or on the roots of legumes (plants like beans and clover) can take nitrogen from the air and put it in a form usable by plants. □ Animals get the ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS -
... Chlorophyll is the magic compound that can grab that sunlight and start the whole process. Chlorophyll is actually quite a varied compound. There are four (4) types: a, b, c, and d. Chlorophyll can also be found in many microorganisms and even some prokaryotic cells. However, as far as plants are ...
... Chlorophyll is the magic compound that can grab that sunlight and start the whole process. Chlorophyll is actually quite a varied compound. There are four (4) types: a, b, c, and d. Chlorophyll can also be found in many microorganisms and even some prokaryotic cells. However, as far as plants are ...
QUIZ - OrgSites.com
... _____ 1. Taxonomy includes: A. stuffing dead animals. B. Classification of large numbers of things into groups. C. Preparation of income tax forms. D. The method of describing the different ways parts of plants work. _____ 2. The largest group of organisms is the taxa called: A. Phylum. B. Class. C. ...
... _____ 1. Taxonomy includes: A. stuffing dead animals. B. Classification of large numbers of things into groups. C. Preparation of income tax forms. D. The method of describing the different ways parts of plants work. _____ 2. The largest group of organisms is the taxa called: A. Phylum. B. Class. C. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.