Semester 1 - TJ
... Characteristics of the major types of cells (plant, animal, bacteria) Key organelles in eukaryotic cells and their functions (jobs) How animal cells and plant cells get their ATP (Cellular Respiration) ...
... Characteristics of the major types of cells (plant, animal, bacteria) Key organelles in eukaryotic cells and their functions (jobs) How animal cells and plant cells get their ATP (Cellular Respiration) ...
Photosynthesis Modeling Activity
... cellulose, which are polymers of glucose. Other glucose molecules go on to cellular respiration which creates useable energy for the cells (ATP) from glucose. The sugars produced by photosynthesis are also used to make other plant molecules such as the amino acids which are the building blocks for p ...
... cellulose, which are polymers of glucose. Other glucose molecules go on to cellular respiration which creates useable energy for the cells (ATP) from glucose. The sugars produced by photosynthesis are also used to make other plant molecules such as the amino acids which are the building blocks for p ...
Mock Exam 2 1. Which of the following s
... a. NADPH oxygen gas carbon dioxide b. Water NADPH calvin cycle c. NADPH chlorophyll calvin cycle d. Water photosystem 1 photosystem 2 e. NADPH electron transport chain oxygen gas If a leaf was to become flaccid and the stomata closed, what aspect(s) of the plant would be affected ...
... a. NADPH oxygen gas carbon dioxide b. Water NADPH calvin cycle c. NADPH chlorophyll calvin cycle d. Water photosystem 1 photosystem 2 e. NADPH electron transport chain oxygen gas If a leaf was to become flaccid and the stomata closed, what aspect(s) of the plant would be affected ...
(18 pts) Pyruvate can be converted to a variety of othe
... possible to make those different products from the same starting molecule.) The molecule could undergo any of a variety of different chemical reactions. Each would lead to a different product. Starting with pyruvate, for example, a carbon-carbon bond break would lead to ethanol and carbon dioxide. R ...
... possible to make those different products from the same starting molecule.) The molecule could undergo any of a variety of different chemical reactions. Each would lead to a different product. Starting with pyruvate, for example, a carbon-carbon bond break would lead to ethanol and carbon dioxide. R ...
Document
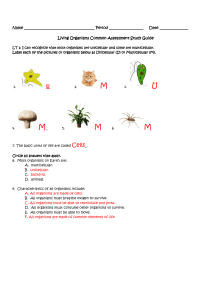
... 3. What part of a leaf helps to protect the plant? Epidermis 4. A leaf is an organ. 5. Name the components for photosynthesis to occur and the product. Sunlight + CO2+ Water --- Sugar + Oxygen (photosynthesis) 6. Name some plants that reproduce using spores. Mosses, ferns & duckweed 7. Explain what ...
... 3. What part of a leaf helps to protect the plant? Epidermis 4. A leaf is an organ. 5. Name the components for photosynthesis to occur and the product. Sunlight + CO2+ Water --- Sugar + Oxygen (photosynthesis) 6. Name some plants that reproduce using spores. Mosses, ferns & duckweed 7. Explain what ...
Chemolithotrophs
... inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Chemolithotrophs: reduced inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Phototrophs: use light energy and an electron donor molecule (H2O, H2S, organic). • Both may be autotrophs: fix CO2 into organic carbon via the Calvin Cycle. ...
... inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Chemolithotrophs: reduced inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Phototrophs: use light energy and an electron donor molecule (H2O, H2S, organic). • Both may be autotrophs: fix CO2 into organic carbon via the Calvin Cycle. ...
File
... a) Oxidation. Adding a carbon dioxide makes the products more oxidized. b) Reduction. Adding the hydrogens from the water results in a more reduced condition. ...
... a) Oxidation. Adding a carbon dioxide makes the products more oxidized. b) Reduction. Adding the hydrogens from the water results in a more reduced condition. ...
Lecture The Plant Cell and Physiological Processes
... Photo System I (PS I) Photo System II (PS II) Photo System II precedes Photo System I only because it was discovered first PS I and PS II are referred to as the "Z scheme” ...
... Photo System I (PS I) Photo System II (PS II) Photo System II precedes Photo System I only because it was discovered first PS I and PS II are referred to as the "Z scheme” ...
DEC 2016 BIO: some useful words File
... storage form of glucose in (most) bacteria, fungi and animals hyphae threads making up the main body (mycelium) of a multicellular fungus that perform saprotrophic nutrition autotrophic nutrition where the organism makes its own food by photosynthesis heterotrophic nutrition that consumes other orga ...
... storage form of glucose in (most) bacteria, fungi and animals hyphae threads making up the main body (mycelium) of a multicellular fungus that perform saprotrophic nutrition autotrophic nutrition where the organism makes its own food by photosynthesis heterotrophic nutrition that consumes other orga ...
Cell Processes Overview
... water on one side the membrane and a chemical solution on the other, the water will _______________ from high to __________ concentration of water. ...
... water on one side the membrane and a chemical solution on the other, the water will _______________ from high to __________ concentration of water. ...
Plantae - phsgirard.org
... Adaptations which allowed plants to grow on land: • Cuticle – waxy covering to prevent water loss ...
... Adaptations which allowed plants to grow on land: • Cuticle – waxy covering to prevent water loss ...
Living Organisms unit test study guide - Answer Key - Parkway C-2
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
Fast Facts 4 Plant Reproduction, Processes and Fungi 2010
... 3 Processes Necessary for Plants to Survive Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. ...
... 3 Processes Necessary for Plants to Survive Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. ...
file
... Autotrophic means the organism makes its own food from raw materials Example: plants Plants make their own food (sugars aka glucose, starch, cellulose aka carbohydrates!) Plants create their own energy by making their own food ...
... Autotrophic means the organism makes its own food from raw materials Example: plants Plants make their own food (sugars aka glucose, starch, cellulose aka carbohydrates!) Plants create their own energy by making their own food ...
Ecosystems Study Guide
... Natural Cycles A. Water cycle - evaporation= change from water to water vapor - condensation= water vapor condenses to form small droplets of water - precipitation= any form of water that falls from the sky - transpiration= some water within plants evaporates into the atmosphere B. Carbon cycle -beg ...
... Natural Cycles A. Water cycle - evaporation= change from water to water vapor - condensation= water vapor condenses to form small droplets of water - precipitation= any form of water that falls from the sky - transpiration= some water within plants evaporates into the atmosphere B. Carbon cycle -beg ...
8th Grade Sixth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an organic compound, either RNA or DNA, whose molecules are made up of one or two chains ...
... a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an organic compound, either RNA or DNA, whose molecules are made up of one or two chains ...
BCOR 11 Exploring Biology
... 32) All of the following are directly associated with photosystem II except A) extraction of hydrogen electrons from the splitting of water. B) release of oxygen. C) harvesting of light energy by chlorophyll. D) NADP+ reductase E) P680 reaction-center chlorophyll. 33) As a research scientist, you m ...
... 32) All of the following are directly associated with photosystem II except A) extraction of hydrogen electrons from the splitting of water. B) release of oxygen. C) harvesting of light energy by chlorophyll. D) NADP+ reductase E) P680 reaction-center chlorophyll. 33) As a research scientist, you m ...
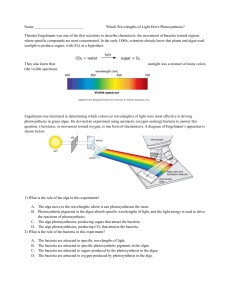
B) Alga`s photosynthetic pigments absorb photons at specific
... A. The number of bacteria clustered at each wavelength (color) was approximately proportional to the amount of oxygen being produced by that portion of the alga. B. Every photon absorbed by the alga was used to drive oxygen production by the alga. C. The algae absorbed the same number of photons at ...
... A. The number of bacteria clustered at each wavelength (color) was approximately proportional to the amount of oxygen being produced by that portion of the alga. B. Every photon absorbed by the alga was used to drive oxygen production by the alga. C. The algae absorbed the same number of photons at ...
Chapter 2-1 The Nature of Matter
... Primary- sequence of amino acids in a protein chain Secondary- amino acid within a chain is twisted or folded Tertiary- the chain itself is folded Quaternary- if a protein has more than one chain ...
... Primary- sequence of amino acids in a protein chain Secondary- amino acid within a chain is twisted or folded Tertiary- the chain itself is folded Quaternary- if a protein has more than one chain ...
Chapter 13 Introduction to Ecology Review
... 26. ___Hydrologic Cycle___ or water cycle is the circular pathway of water on Earth. Organism’s bodies are made mostly of __Water__. 27. _____Oxygen___ Cycle: cycles oxygen through the processes of respiration and photosynthesis. 28. __Carbon__ is the building block of life. __Carbon___ Cycle moves ...
... 26. ___Hydrologic Cycle___ or water cycle is the circular pathway of water on Earth. Organism’s bodies are made mostly of __Water__. 27. _____Oxygen___ Cycle: cycles oxygen through the processes of respiration and photosynthesis. 28. __Carbon__ is the building block of life. __Carbon___ Cycle moves ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.