* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
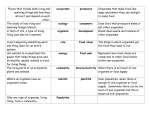
Ecosystems Study Guide I. II. III. Vocabulary a. Ecology- the study of living things(organisms) and how they interact with their environment b. Ecologist- person who studies ecosystems c. Ecosystem- groups of living things and the nonliving environment in which they live d. Biotic parts- living parts of an ecosystem (plants, trees flowers, grass, birds, other animals) e. Abiotic- nonliving parts of an environment f. Estuaries- bodies of water found in areas where freshwater from rivers and streams and salt water from the ocean meet g. Producers- organisms that use energy from the Sun to make their own food through a process called photosysenthesis (Plants) h. Consumers- get energy by eating other organisms (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores) i. Decomposers- get energy by breaking down nutrients in dead organisms j. Population- group of organisms of the same species living in the same place k. Community- made up of all the populations that live in the same area l. Habitat- physical space used by a population (habitat means home) m. Niche- describes an organism’s lifestyle (habitat, climate, and the types of food the organism eats) n. Predator- an organism that eats other organisms in order to live o. Prey- organism that is being eaten p. Parasite- live on or inside another organism to get energy q. Host- the organism that a parasite infects r. Food chain- show the path of energy as it flows from one organism to the next s. Food web- a diagram of several connected food chains Ecosystems A. Forest -temperate deciduous (trees lose their leaves each fall) -coniferous (trees produce seeds inside of cones) -tropical rainforests B. Grasslands-prairies, savannahs, plains C. Marine-oceans D. Coral Reefs-type of marine ecosystem F. Estuaries G. Lakes and Ponds Nonliving Factors in Ecosystems (Limiting Factors) A. Light B. Temperature C. Soil Composition (what the soil is made up of) IV. Living Factors in Ecosystems A. Predators and Prey relationships B. Parasites and Host C. Food Chains and Food Webs 1. producer---- primary consumer----secondary consumer---tertiary consumer V. Humans and Environmental Change A. Habitat Reduction Ex. People cutting down trees to put in buildings or roads B. Pollution C. Increased nutrients Natural Cycles A. Water cycle - evaporation= change from water to water vapor - condensation= water vapor condenses to form small droplets of water - precipitation= any form of water that falls from the sky - transpiration= some water within plants evaporates into the atmosphere B. Carbon cycle -begins with photosynthesis (in plants) -animal that eats the plants get the sugars through respiration -respiration breaks down the sugars and releases it as energy for the animal -the animals use the energy for their body processes and release the carbon dioxide into the air -the carbon dioxide that is released into the air is used by plants for photosythesis C. Nitrogen cycle VI.