Adv Bio Cellular Respiration Objectives
... 9. Identify the location where the reactions of the Krebs cycle take place 10. List the molecules which enter and those which are produced by the Krebs cycle 11. Explain at what point in cellular respiration that glucose is completely oxidized 12. Explain (in very general terms) how the exergonic sl ...
... 9. Identify the location where the reactions of the Krebs cycle take place 10. List the molecules which enter and those which are produced by the Krebs cycle 11. Explain at what point in cellular respiration that glucose is completely oxidized 12. Explain (in very general terms) how the exergonic sl ...
Additional Science Module B4 – What You Should Know
... 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 I can recall the main stages of photosynthesis: a. light energy absorbed by the green chemical chlorophyll b. energy used to bring about the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose (a sugar) c. oxygen produced as a waste product I can recall that gluc ...
... 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 I can recall the main stages of photosynthesis: a. light energy absorbed by the green chemical chlorophyll b. energy used to bring about the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose (a sugar) c. oxygen produced as a waste product I can recall that gluc ...
plants - Cloudfront.net
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
Unit 3 Notes
... 1. Light strikes the photosystem II 2. An electron in the photosystem reaction centre is ‘excited’. 3. The electron is passed to an electron-accepting molecule. a. Gain electron = reduced = has greater energy 4. The reaction centre in the photosystem is now missing an electron – which has to be repl ...
... 1. Light strikes the photosystem II 2. An electron in the photosystem reaction centre is ‘excited’. 3. The electron is passed to an electron-accepting molecule. a. Gain electron = reduced = has greater energy 4. The reaction centre in the photosystem is now missing an electron – which has to be repl ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: How do leaves help a plant
... a. Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to make sugar for food in the leaves where chlorophyll captures light energy. b. Plant cells use cellular respiration which means they use oxygen with food for growth, repairs and reproduction. c. Plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide for ph ...
... a. Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to make sugar for food in the leaves where chlorophyll captures light energy. b. Plant cells use cellular respiration which means they use oxygen with food for growth, repairs and reproduction. c. Plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide for ph ...
2. What are the main properties that fats, proteins, and
... within the leaves. 31. What are the main products of the light-dependent reaction? Generally, the light-dependent reactions remove low energy electrons from water when chlorophyll absorbs energy; these electrons move down an electron transport system to produce ATP from ADP and (P); energized electr ...
... within the leaves. 31. What are the main products of the light-dependent reaction? Generally, the light-dependent reactions remove low energy electrons from water when chlorophyll absorbs energy; these electrons move down an electron transport system to produce ATP from ADP and (P); energized electr ...
4 Necessities of Life
... • large molecules made up of subunits called nucleotides. • sometimes called the blueprints of life because they have all the information needed for a cell to make proteins. • DNA is the most important nucleic acid and the most important molecule for life on the planet ...
... • large molecules made up of subunits called nucleotides. • sometimes called the blueprints of life because they have all the information needed for a cell to make proteins. • DNA is the most important nucleic acid and the most important molecule for life on the planet ...
Bioenergetics Test Study Guide - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... machinery of pigments and proteins called photosystem II and photosystem I. Notice that photosystem II occurs first. The products of the light-dependent reaction are oxygen, ATP, and NADPH. PS II Light and water enter the thylakoids within the photosystem II machinery. The light is absorbed by a spe ...
... machinery of pigments and proteins called photosystem II and photosystem I. Notice that photosystem II occurs first. The products of the light-dependent reaction are oxygen, ATP, and NADPH. PS II Light and water enter the thylakoids within the photosystem II machinery. The light is absorbed by a spe ...
mid-term-exam-versio..
... 118. _____ The G1 phase features normal cell function and growth; and cells that do not pass the G1 checkpoint remain permanently in G1, sometimes referred to as G0. 119. _____ The S phase features the synthesis of RNA known as RNA replication. FALSE 120. _____ The G2 phase features additional produ ...
... 118. _____ The G1 phase features normal cell function and growth; and cells that do not pass the G1 checkpoint remain permanently in G1, sometimes referred to as G0. 119. _____ The S phase features the synthesis of RNA known as RNA replication. FALSE 120. _____ The G2 phase features additional produ ...
6th Grade Science Semester Final Multiple Choice (1pt each) A
... 75. What organelle in a cell is responsible for producing ATP, the cells energy? 76. What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? 77. What organelle has the responsibility of storage? 78. What is an extremely important property of lipids? 79. This type of transport requires the use of some cell ...
... 75. What organelle in a cell is responsible for producing ATP, the cells energy? 76. What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? 77. What organelle has the responsibility of storage? 78. What is an extremely important property of lipids? 79. This type of transport requires the use of some cell ...
Homework 3 BSC 1005 Fall 2011
... a. thylakoids. b. cytoplasm. c. grana. d. stroma. 45.Two products of the light-dependent reactions, which become reactants for the lightindependent reactions, are a. ATP and NADP. b. CO2 and H2O. c. O2 and ATP. d. ATP and NADPH2. 46.O2 is a product of the a. light-dependent reactions. b. light-indep ...
... a. thylakoids. b. cytoplasm. c. grana. d. stroma. 45.Two products of the light-dependent reactions, which become reactants for the lightindependent reactions, are a. ATP and NADP. b. CO2 and H2O. c. O2 and ATP. d. ATP and NADPH2. 46.O2 is a product of the a. light-dependent reactions. b. light-indep ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... White bread is a simple carbohydrate (little nutritional value, digested more quickly, converted to fat more quickly) Whole grain bread is a complex carbohydrate (high in fiber, vitamins and minerals, provide more energy, digested slowly) ...
... White bread is a simple carbohydrate (little nutritional value, digested more quickly, converted to fat more quickly) Whole grain bread is a complex carbohydrate (high in fiber, vitamins and minerals, provide more energy, digested slowly) ...
B4 - ME School of Excellence
... • Carbon dioxide is removed from the environment by green plants for photosynthesis • The carbon is used to make carbohydrates, proteins and fats which make up the body of ...
... • Carbon dioxide is removed from the environment by green plants for photosynthesis • The carbon is used to make carbohydrates, proteins and fats which make up the body of ...
C 4 plants
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
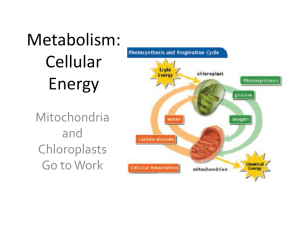
Cellular Energy
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
Gas Stoichiometry Worksheet
... Gas Stoichiometry Practice For problems 1-3, assume that the reactions are being performed at a pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 298 K. ...
... Gas Stoichiometry Practice For problems 1-3, assume that the reactions are being performed at a pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 298 K. ...
AP Biology Ch 9 Cell Respiration J. Dolce Study Questions Identify
... Where does the Kreb’s cycle take place? Describe what happens to pyruvate before it enters the Kreb’s Cycle. Where is the Electron Transport Chain located? Describe the role of the Electron Transport Chain. What happens to the electrons and H+? What is chemiomosis and how is it generated? How does t ...
... Where does the Kreb’s cycle take place? Describe what happens to pyruvate before it enters the Kreb’s Cycle. Where is the Electron Transport Chain located? Describe the role of the Electron Transport Chain. What happens to the electrons and H+? What is chemiomosis and how is it generated? How does t ...
Handout
... systems, the different complexes can substitute for one another, and the structures of their protein components reveal that they are evolutionarily related. ...
... systems, the different complexes can substitute for one another, and the structures of their protein components reveal that they are evolutionarily related. ...
PACKET 12: PLANT STRUCTURE & REPRODUCTION A. PLANT STRUCTURE 1.
... --BUT –Once the guard cells have lost water, the opening closes, so that no more water will be lost from the leaf. ...
... --BUT –Once the guard cells have lost water, the opening closes, so that no more water will be lost from the leaf. ...
Multiple Choice Review- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 17. The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis during oxidative phosphorylation is a. The flow of electrons down the electron transport chain b. That attraction of electrons to Oxygen c. The proton gradient created across the membrane d. ATP from glycolysis 18. The final electron acceptor ...
... 17. The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis during oxidative phosphorylation is a. The flow of electrons down the electron transport chain b. That attraction of electrons to Oxygen c. The proton gradient created across the membrane d. ATP from glycolysis 18. The final electron acceptor ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.