* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PACKET 12: PLANT STRUCTURE & REPRODUCTION A. PLANT STRUCTURE 1.
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
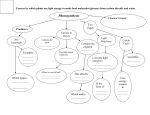
PACKET 12: A. PLANT STRUCTURE & REPRODUCTION PLANT STRUCTURE 1. WHAT IS A PLANT? A multicellular eukaryote Has a cell wall Carries out photosynthesis and makes its own food. (__________________) 2. WHAT DO PLANTS NEED TO SURVIVE? Sunlight Water & Minerals Gas Exchange Movement of Water & Nutrients 3. THE LEAVES OF PLANTS (How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis?) The Leaf The plant’s main organ of photosynthesis! Thin & Flat -- Tissues of the leaf help bring gases, water & nutrients to the cells _______________________ of the leaf that carry out photosynthesis. Leaf structure is also optimal for Gas Exchange and Water Balance. o o Pore like openings on the underside of the leaf - ______________ Allow CO2 & O2 to diffuse into and out of the leaf Controls water loss Structures responsible for opening & closing the stomata _______________ --If the guard cells are swollen with water the stoma can open because they can afford to lose some water. --BUT –Once the guard cells have lost water, the opening closes, so that no more water will be lost from the leaf. --This is why WILTING occurs if plants have lost too much water!! 4) PLANT TISSUES (How are materials moved throughout a plant? --vascular tissues: --there are two types of vascular tissues found in plants a) xylem: b) phloem: Label the plants below as either a monocot or dicot. ____________________ B. PLANT REPRODUCTION --Most types of plants reproduce: _________________________ --FLOWERING PLANTS (_____________________) MALE GAMETE + FEMALE GAMETE ______________________ ZYGOTE EMBRYO & SEED NEW PLANT 1. WHERE DOES SEXUAL REPRODUCTION TAKE PLACE?: _________________________ --A typical flower contains BOTH the male AND female parts! 2. POLLINATION: The transfer of pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female reproductive structure. HOW DOES THIS HAPPEN? 1. 2. 3. FERTILIZATION: The male and female reproductive structures combine to form a new cell. HOW DOES THIS HAPPEN? Pollen ( ___________________________________) lands on sticky stigma. The pollen then travels to the ovary. o Sperm #1: Fuses with the egg to form a ZYGOTE (becomes the EMBRYO) o Sperm #2: Becomes the ENDOSPERM (feeds the embryo) A SEED forms around this. o HOW ARE SEEDS DISPERSED? Animals Wind --Some types of plants reproduce via: _____________________________________ --This is called ______________________________________ C. Enables a single plant to produce many offspring genetically identical to itself! PLANT RESPONSES & ADAPTATIONS Plants grow in response to environmental factors: o Light o Moisture o Temperature o Gravity Plant body parts must be told what to do. Plant HORMONES control the responses of plants. The growth responses are called: **Read text pg. 646** _____________________ o Many plants are prey to plant-eating insects and other animals. o Plants try to defend themselves against insect attack by making compounds that have powerful effects on animals. --Examples: