Photosynthesis/Cell Resp Notes
... Cells recycle the ADP to make new ATP to store more energy for future use Many proteins have spots where ATP attaches to provide energy for the protein to do its job, then the ADP is released for recycling Photosynthesis Process that uses the sun’s energy to make glucose Carried out by green ...
... Cells recycle the ADP to make new ATP to store more energy for future use Many proteins have spots where ATP attaches to provide energy for the protein to do its job, then the ADP is released for recycling Photosynthesis Process that uses the sun’s energy to make glucose Carried out by green ...
Cellular Respiration
... The chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP requires that the electron transport in the inner mitochondrial membrane be coupled to proton transport across the same membrane. ...
... The chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP requires that the electron transport in the inner mitochondrial membrane be coupled to proton transport across the same membrane. ...
Macromolecules Review Worksheet Answer Key
... Part B. Identify the specific molecule (use the above terms) from each description. Some terms may be used more than once. 11. glycogen ...
... Part B. Identify the specific molecule (use the above terms) from each description. Some terms may be used more than once. 11. glycogen ...
1 - vanleerscience
... 11. A dominant gene that codes for red eye color in fruit flies is represented by the symbol W, while the recessive white eye gene is represented by the symbol w. If a parent fly with the genotype WW is crossed with a parent of the genotype Ww, what percentage of the offspring will have red eyes? a ...
... 11. A dominant gene that codes for red eye color in fruit flies is represented by the symbol W, while the recessive white eye gene is represented by the symbol w. If a parent fly with the genotype WW is crossed with a parent of the genotype Ww, what percentage of the offspring will have red eyes? a ...
Cell Benchmark Study Guide 2013
... Plants take in __CO2__ from the atmosphere to create glucose in the process of photosynthesis. This process happens inside the ____chloroplast__ of a plant cell. _ O2__ is a waste product of photosynthes ...
... Plants take in __CO2__ from the atmosphere to create glucose in the process of photosynthesis. This process happens inside the ____chloroplast__ of a plant cell. _ O2__ is a waste product of photosynthes ...
Plant Study Guide – Answer Key
... xylem, and are responsible for translocation of nutrients and water throughout the plant. Vascular tissues provide support and rigidity to the plant, other than the circulation of food and water. Non-vascular - They do not have vascular systems and are called lower plants. These plants do not contai ...
... xylem, and are responsible for translocation of nutrients and water throughout the plant. Vascular tissues provide support and rigidity to the plant, other than the circulation of food and water. Non-vascular - They do not have vascular systems and are called lower plants. These plants do not contai ...
Topic 3 – The Chemistry of Life
... lower activity above and below optimum pH / graph showing this too acidic / base pH can determine enzyme change shape of active site / tertiary structure altered substrate cannot bind to active site / enzyme-substrate complex cannot hydrogen / ionic bonds in the enzyme / active site are br ...
... lower activity above and below optimum pH / graph showing this too acidic / base pH can determine enzyme change shape of active site / tertiary structure altered substrate cannot bind to active site / enzyme-substrate complex cannot hydrogen / ionic bonds in the enzyme / active site are br ...
Respiration - Mayfield City Schools
... • How do the electrons get transported to the special proteins involved? carried by carrier molecules NADH, FADH2 • What is the primary function of the chain? to make ATP ...
... • How do the electrons get transported to the special proteins involved? carried by carrier molecules NADH, FADH2 • What is the primary function of the chain? to make ATP ...
Chapter 35 and 36 Notes
... •Illustrates how the energy transfers between trophic levels –illustrates the ____________________________ at each trophic level. –only ________________ of the energy of the previous trophic level is utilized by the next level –90% is lost as ________________. 36.3 Nutrients Cycle through Ecosystems ...
... •Illustrates how the energy transfers between trophic levels –illustrates the ____________________________ at each trophic level. –only ________________ of the energy of the previous trophic level is utilized by the next level –90% is lost as ________________. 36.3 Nutrients Cycle through Ecosystems ...
KPN PowerPoint
... however, plants do not really eat anything. Fertilizers are often called “plant food,” but it is incorrect to label fertilizers as food. ...
... however, plants do not really eat anything. Fertilizers are often called “plant food,” but it is incorrect to label fertilizers as food. ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes
... Overview: Life Is Work • Living cells require energy from outside sources • Some animals, such as the chimpanzee, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants ...
... Overview: Life Is Work • Living cells require energy from outside sources • Some animals, such as the chimpanzee, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants ...
Structure of Plants
... 1. Photosynthesis • Plants convert radiant energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (sugar) • Process that plants use to produce their food WATER + CARBON DIOXIDE + SUNLIGHT = GLUCUSE + OXYGEN ...
... 1. Photosynthesis • Plants convert radiant energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (sugar) • Process that plants use to produce their food WATER + CARBON DIOXIDE + SUNLIGHT = GLUCUSE + OXYGEN ...
III. Cells and Energy
... (from the atmosphere) and hydrogen (from NADPH) to form glucose in a series of reactions called the Calvin Cycle ...
... (from the atmosphere) and hydrogen (from NADPH) to form glucose in a series of reactions called the Calvin Cycle ...
Botany 1st Semester Exam Study Guide ANSWERS
... 41. _______________ is a structure that is similar to roots.Rhizoid 42. _______________ tissue is important to ferns because it can _________________________.Xylem, it can transport water over long distances 43. List the four groups of gymnosperms. Gnetophytes, Conifers, Ginkoes, Cycads 44. Angiospe ...
... 41. _______________ is a structure that is similar to roots.Rhizoid 42. _______________ tissue is important to ferns because it can _________________________.Xylem, it can transport water over long distances 43. List the four groups of gymnosperms. Gnetophytes, Conifers, Ginkoes, Cycads 44. Angiospe ...
2016-2017 Carbon Cycle notes ppt
... An element The basis of life on Earth Present in rocks, oceans and the atmosphere ...
... An element The basis of life on Earth Present in rocks, oceans and the atmosphere ...
Botany Review Sheet
... b. taproots and fibrous roots c. woody stems and herbaceous stems d. photosynthesis and respiration 7. What is the equation of photosynthesis? (Label the reactants and the products.) ...
... b. taproots and fibrous roots c. woody stems and herbaceous stems d. photosynthesis and respiration 7. What is the equation of photosynthesis? (Label the reactants and the products.) ...
Photosynthesis: Converting Radiant Energy into Chemical Energy
... chlorophyll from the ground to the excited state? Does 680 nm light have enough energy? In the light reactions of photosynthesis, there are two steps; both involve chlorophyll acting as an electron pump that transfers an electron to an acceptor with a more negative redox potential. The two steps are ...
... chlorophyll from the ground to the excited state? Does 680 nm light have enough energy? In the light reactions of photosynthesis, there are two steps; both involve chlorophyll acting as an electron pump that transfers an electron to an acceptor with a more negative redox potential. The two steps are ...
ECOSYSTEMS
... Nitrogen is needed to build Protiens that make up structures in living organisms. 78% of the Earth’s Atmoshere Nitrogen atoms combine with other atoms causing – Nitrogen Fixation so Plants can use nitrogen and start it in the food chain. Bacteria decompose (breaks down) Waste Products and Dead organ ...
... Nitrogen is needed to build Protiens that make up structures in living organisms. 78% of the Earth’s Atmoshere Nitrogen atoms combine with other atoms causing – Nitrogen Fixation so Plants can use nitrogen and start it in the food chain. Bacteria decompose (breaks down) Waste Products and Dead organ ...
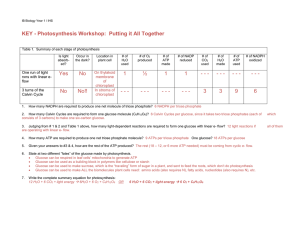
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
Photosynthesis Chloroplasts Light Reactions (photons → NADPH +
... Fluorescence - excited state decays to ground state by emitting photon, time frame ~10-8 s Exciton transfer (resonance energy transfer) - excited molecule transfers its excitation energy to nearby unexcited molecules, important in funneling light energy to photosynthetic reaction centers Photooxidat ...
... Fluorescence - excited state decays to ground state by emitting photon, time frame ~10-8 s Exciton transfer (resonance energy transfer) - excited molecule transfers its excitation energy to nearby unexcited molecules, important in funneling light energy to photosynthetic reaction centers Photooxidat ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.