Standard Grade Biology – Revision Notes
... • Living things need energy to grow, move, reproduce etc. They get this energy from Aerobic Respiration. • Aerobic Respiration – glucose + oxygen ⇒ carbon dioxide + water + energy • Metabolism – the sum of all chemical processes in a living organism that keeps it alive. ...
... • Living things need energy to grow, move, reproduce etc. They get this energy from Aerobic Respiration. • Aerobic Respiration – glucose + oxygen ⇒ carbon dioxide + water + energy • Metabolism – the sum of all chemical processes in a living organism that keeps it alive. ...
Primary productivity
... • Secondary and tertiary consumers~ carnivores • Detrivores/detritus~ special consumers that derive nutrition from non-living organic matter ...
... • Secondary and tertiary consumers~ carnivores • Detrivores/detritus~ special consumers that derive nutrition from non-living organic matter ...
Biogeochemical Cycles Matter cycles and energy flows through
... this liquid water is converted to water vapor (gas). 4. The evaporated water in the air condenses into clouds. When cooled, the clouds release rain, snow, and other forms of precipitation back into the ...
... this liquid water is converted to water vapor (gas). 4. The evaporated water in the air condenses into clouds. When cooled, the clouds release rain, snow, and other forms of precipitation back into the ...
Study Guide Ch - Cobb Learning
... 6. Both ____________ and __________ are examples of ________ transport because the do NOT require energy. 7. When a red blood cell has it’s normal doughnut shape, the concentration of water in the solution around the cell is the ______ as inside the cell. 8. In the concentration of water is lower th ...
... 6. Both ____________ and __________ are examples of ________ transport because the do NOT require energy. 7. When a red blood cell has it’s normal doughnut shape, the concentration of water in the solution around the cell is the ______ as inside the cell. 8. In the concentration of water is lower th ...
A B C - admms
... Unit Review, Introduction to Plants 1. During which process do plants capture light energy and carbon dioxide along with water to produce glucose? a. fertilization b. reproduction c. photosynthesis d. cellular respiraton 2. Where would you expect to see a plant that does not have a vascular system? ...
... Unit Review, Introduction to Plants 1. During which process do plants capture light energy and carbon dioxide along with water to produce glucose? a. fertilization b. reproduction c. photosynthesis d. cellular respiraton 2. Where would you expect to see a plant that does not have a vascular system? ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Aerobic Cellular Respiration
... Respiration: the life process by which organisms convert the chemical energy stored in food to a form of energy more easily utilized by the cell Process of Cell Respiration: a biochemical process used by cells to release energy from organic molecules (food) such as glucose ~this energy is stored in ...
... Respiration: the life process by which organisms convert the chemical energy stored in food to a form of energy more easily utilized by the cell Process of Cell Respiration: a biochemical process used by cells to release energy from organic molecules (food) such as glucose ~this energy is stored in ...
Biology Objective 3
... The process of change over time. • There are natural variations in all populations. • As climate changes occur, and as pressures in terms of food, space, shelter and predation occur, some variations allow a species to ...
... The process of change over time. • There are natural variations in all populations. • As climate changes occur, and as pressures in terms of food, space, shelter and predation occur, some variations allow a species to ...
Water Cycle
... 1a. The creature has a large wide head............................go to 2 1b. The creature has a small narrow head..........................go to 11 2a. It has 3 eyes ................................................go to 3 2b. It has 2 eyes ................................................go to 7 3a. ...
... 1a. The creature has a large wide head............................go to 2 1b. The creature has a small narrow head..........................go to 11 2a. It has 3 eyes ................................................go to 3 2b. It has 2 eyes ................................................go to 7 3a. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration uses oxygen (O2) to break down food Fermentation does not use oxygen Cellular respiration releases more energy from food than Fermentation. So most eukaryotes (ex: plants & animals) get their energy through cellular respiration ...
... Cellular Respiration uses oxygen (O2) to break down food Fermentation does not use oxygen Cellular respiration releases more energy from food than Fermentation. So most eukaryotes (ex: plants & animals) get their energy through cellular respiration ...
Cycles
... The Earth is considered a closed system. This means that there is little or no input of new materials from outside the system. Organics = H and C, often O and N (proteins, fats, sugars) Inorganics – not containing C and H Nutrients can be in the biotic environment or abiotic environment. ...
... The Earth is considered a closed system. This means that there is little or no input of new materials from outside the system. Organics = H and C, often O and N (proteins, fats, sugars) Inorganics – not containing C and H Nutrients can be in the biotic environment or abiotic environment. ...
PP Ch_ 2-3 Modified - Maria Regina High School
... some are used for transport around an organism The Shape of a protein is incredibly important ...
... some are used for transport around an organism The Shape of a protein is incredibly important ...
Biology Semester Test
... _____ 55. A round organelle containing digestive enzymes and used to clean up the cell and reuse parts is the a. Vacuole b. Nuclelous c. Lysosome d. Chloroplast _____ 56. The jelly-like substance composing the interior of the cell is the a. Nucleus b. Cytoplasm c. Lysosome d. Mitochondria _____ 57. ...
... _____ 55. A round organelle containing digestive enzymes and used to clean up the cell and reuse parts is the a. Vacuole b. Nuclelous c. Lysosome d. Chloroplast _____ 56. The jelly-like substance composing the interior of the cell is the a. Nucleus b. Cytoplasm c. Lysosome d. Mitochondria _____ 57. ...
Plants
... Pollen gets transported to the sticky stigma. Pollen grain makes a pollen tube and the sperm travels downwards through the pollen tube towards the ovule. The sperm and egg join during fertilization. Ovule develops into a seed, seed coat, and stored food. The fertilized egg (zygote) becomes the seed’ ...
... Pollen gets transported to the sticky stigma. Pollen grain makes a pollen tube and the sperm travels downwards through the pollen tube towards the ovule. The sperm and egg join during fertilization. Ovule develops into a seed, seed coat, and stored food. The fertilized egg (zygote) becomes the seed’ ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... The Nitrogen Cycle • Organisms require nitrogen to produce amino acids. • Nitrogen makes up 78% of the atmosphere, but most organisms can not use this form of nitrogen, and must have the fixed form. • The nitrogen cycle produces the fixed form of nitrogen these organisms need. ...
... The Nitrogen Cycle • Organisms require nitrogen to produce amino acids. • Nitrogen makes up 78% of the atmosphere, but most organisms can not use this form of nitrogen, and must have the fixed form. • The nitrogen cycle produces the fixed form of nitrogen these organisms need. ...
A2 Biology notes – AQA unit 4: Populations and
... series of molecules, each of which has a greater affinity for the electrons than the previous; the electrons move along the chain in a series of redox reactions. - Chlorophyll in plants is found in two photosystems. Electrons from photosystem II inter an electron transport chain where the energy re ...
... series of molecules, each of which has a greater affinity for the electrons than the previous; the electrons move along the chain in a series of redox reactions. - Chlorophyll in plants is found in two photosystems. Electrons from photosystem II inter an electron transport chain where the energy re ...
ecology - Algonac Community Schools
... Predation: when one species relies upon another for food Migration: movement of a population during different times of the year ...
... Predation: when one species relies upon another for food Migration: movement of a population during different times of the year ...
Practice AP Multiple Choice Exam 1 Do NOT write on this! 1. Which
... 72. Process in which O2 is released as a by-product of redox reactions. 73. Process in which CO2 is released as a by-product of redox reactions. 74. Process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into other organic molecules. 75. Process found in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 76. P ...
... 72. Process in which O2 is released as a by-product of redox reactions. 73. Process in which CO2 is released as a by-product of redox reactions. 74. Process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into other organic molecules. 75. Process found in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 76. P ...
DESERT PLANT ADAPTATIONS Environmental Stresses for Desert
... CAM photosynthesis used by many succulent species ...
... CAM photosynthesis used by many succulent species ...
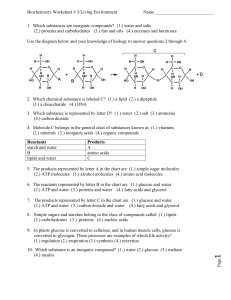
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 8. Simple sugars and starches belong to the class of compounds called (1.) lipids (2.) carbohydrates (3.) proteins (4.) nucleic acids ...
... 8. Simple sugars and starches belong to the class of compounds called (1.) lipids (2.) carbohydrates (3.) proteins (4.) nucleic acids ...
COMMUNICATION
... needs to be quite long. The colon also needs to be long so that it can process the extensive amounts of faecal matter produced as a by-product of cellulose digestion. ...
... needs to be quite long. The colon also needs to be long so that it can process the extensive amounts of faecal matter produced as a by-product of cellulose digestion. ...
Name ______ Period ______________ Date ______________
... Because the first product of the cycle is citric acid 8. List the products of the Krebs cycle. CO2, ATP, NADH, FADH2 9. Briefly explain the electron transport chain reaction in the mitochondria and where it takes place. What fuels the electron transport chain? The ATP, NADH, and FADH2 from the Krebs ...
... Because the first product of the cycle is citric acid 8. List the products of the Krebs cycle. CO2, ATP, NADH, FADH2 9. Briefly explain the electron transport chain reaction in the mitochondria and where it takes place. What fuels the electron transport chain? The ATP, NADH, and FADH2 from the Krebs ...
Biobowl
... Chapter 8 – Photosynthesis 50. Where does oxygen fit into PS? 51. What is the source of hydrogens with which CO2 is reduced during PS? 52. What is the difference between an absorption spectrum and an action spectrum? 53. Put these in the correct order for non-cyclic electron flow: PSI; PSII, NADP, w ...
... Chapter 8 – Photosynthesis 50. Where does oxygen fit into PS? 51. What is the source of hydrogens with which CO2 is reduced during PS? 52. What is the difference between an absorption spectrum and an action spectrum? 53. Put these in the correct order for non-cyclic electron flow: PSI; PSII, NADP, w ...
Ecology Notesheet
... Ex: Nitrogen is often limiting in water; if there is suddenly as input of N (fertilizer runoff), organisms can ...
... Ex: Nitrogen is often limiting in water; if there is suddenly as input of N (fertilizer runoff), organisms can ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.