Quiz8ch8.doc
... 10. ____________________ is the process in which hydrogen ions move down their concentration gradient through ATP-synthesizing enzymes. a. substrate level phosphorylation b. facilitated diffusion c. outer phosphorylation d. chemiosmosis ...
... 10. ____________________ is the process in which hydrogen ions move down their concentration gradient through ATP-synthesizing enzymes. a. substrate level phosphorylation b. facilitated diffusion c. outer phosphorylation d. chemiosmosis ...
... a. Lipids mix with water. b. Lipids store energy. c. Lipids include fats and oils. d. Lipids make up cell membranes. 33. The molecules that form much of the cell membrane are ______________________. 34. When your body uses up all of its carbohydrates, it can get stored energy from __________________ ...
ENZYMES
... 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen quickly ...
... 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen quickly ...
Microbial Metabolism
... Electron Tower • A redox reaction needs a reducing and oxidizing half-reaction • Reactions with stronger tendency to give up electrons are higher (more negative) on the tower • To determine which direction the reactions go, see which is “higher” on the electron tower • Note the position of importan ...
... Electron Tower • A redox reaction needs a reducing and oxidizing half-reaction • Reactions with stronger tendency to give up electrons are higher (more negative) on the tower • To determine which direction the reactions go, see which is “higher” on the electron tower • Note the position of importan ...
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with one fatty acid molecule replaced by phosphate, choline, or other group. Important to membrane structure. Carotenoids - red and yellow plant pigmen ...
... organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with one fatty acid molecule replaced by phosphate, choline, or other group. Important to membrane structure. Carotenoids - red and yellow plant pigmen ...
Ch. 8 Photosynthesis
... to find out if plants grew by taking material out of the soil • Joseph Priestley placed a glass jar over a burning candle and watched as the flame went out. He put a live plant in the jar, and guess what happened? • Jan Ingenhousz showed that the effect observed by Priestley occurred only when the p ...
... to find out if plants grew by taking material out of the soil • Joseph Priestley placed a glass jar over a burning candle and watched as the flame went out. He put a live plant in the jar, and guess what happened? • Jan Ingenhousz showed that the effect observed by Priestley occurred only when the p ...
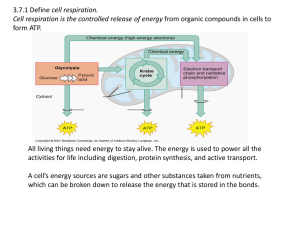
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... anaerobic in the absence of oxygen whereas aerobic in the presence of oxygen; both may produce 2 CO ; both produce ATP; aerobic releases considerably more ATP per glucose molecule than anaerobic; anaerobic/fermentation in plants produces alcohol / anaerobic in animals produces lactic acid neither pr ...
... anaerobic in the absence of oxygen whereas aerobic in the presence of oxygen; both may produce 2 CO ; both produce ATP; aerobic releases considerably more ATP per glucose molecule than anaerobic; anaerobic/fermentation in plants produces alcohol / anaerobic in animals produces lactic acid neither pr ...
Structure and function of mitochondria (Slide
... Releases carbon as CO2 H+ ions captured by NAD Releases 2 ATP Provides > 20 proteins for metabolic processes Refer to p127 in Biozone Look at position on flowchart ...
... Releases carbon as CO2 H+ ions captured by NAD Releases 2 ATP Provides > 20 proteins for metabolic processes Refer to p127 in Biozone Look at position on flowchart ...
Concept 1 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... molecule is not needed, so it is joined with another oxygen from a second split water molecule to form O2. The oxygen can then be released by the plant through its stroma, or sent to the mitochondria for use in cellular respiration. c. Describe the journey of a carbon dioxide molecule in photosynthe ...
... molecule is not needed, so it is joined with another oxygen from a second split water molecule to form O2. The oxygen can then be released by the plant through its stroma, or sent to the mitochondria for use in cellular respiration. c. Describe the journey of a carbon dioxide molecule in photosynthe ...
Biol 2022 Spring 2017 Study Guide Exam 1 Lecture 1 Definition of a
... Cell walls, primary and secondary. Four main components of cell walls, know what they are made of, such as cellulose is 1,4 linked glucose, and where they are synthesized. ER and Golgi, the main organelles responsible for synthesizing cell wall components and also delivering then to the cell wall ...
... Cell walls, primary and secondary. Four main components of cell walls, know what they are made of, such as cellulose is 1,4 linked glucose, and where they are synthesized. ER and Golgi, the main organelles responsible for synthesizing cell wall components and also delivering then to the cell wall ...
EOC PRACTICE QUESTIONS #5
... Organisms with the most energy in a food web are the ____. They have the greatest impact on the ecosystem because without them there would not be food and energy for the others. • Producers (autotrophs) ...
... Organisms with the most energy in a food web are the ____. They have the greatest impact on the ecosystem because without them there would not be food and energy for the others. • Producers (autotrophs) ...
-The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved
... -During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence? -Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located? -The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to _____. -During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the ...
... -During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence? -Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located? -The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to _____. -During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the ...
Intro to Biochemistry Pratt & Cornely Chapter 1
... touch. What conclusions can you draw about the sign of the enthalpy change and the entropy change for this process? ...
... touch. What conclusions can you draw about the sign of the enthalpy change and the entropy change for this process? ...
Appendix A - SDSU Biology Department
... prokaryotes reigned supreme for at least two billion years. The prokaryotes are quite small, having an average size between 1 m and 5 m. These cells have no nuclei, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, or other eukaryotic organelles. The DNA of prokaryotes is a single, circular, double-stranded mo ...
... prokaryotes reigned supreme for at least two billion years. The prokaryotes are quite small, having an average size between 1 m and 5 m. These cells have no nuclei, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, or other eukaryotic organelles. The DNA of prokaryotes is a single, circular, double-stranded mo ...
Levels of Organization - Bremen High School District 228
... B. Bases – a solution with a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) ...
... B. Bases – a solution with a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) ...
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
... Most producers capture sunlight to produce carbohydrates by photosynthesis: ...
... Most producers capture sunlight to produce carbohydrates by photosynthesis: ...
1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling Crossword
... DNA and protein manufacture. Atmosphere composed of 78% of this gas (8) 7. The conversion of ammonia to nitrites and nitrates ...
... DNA and protein manufacture. Atmosphere composed of 78% of this gas (8) 7. The conversion of ammonia to nitrites and nitrates ...
document
... • 6 CO2 + 6 H2O+light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 • Carbon dioxide + Water + Light energy → Glucose + Oxygen • Photosynthesis is the same in all the plants. • During photosynthesis, sunlight energy is stored in carbohydrate for later use. • Most of the carbohydrates stay in the plant but some of it goes ...
... • 6 CO2 + 6 H2O+light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 • Carbon dioxide + Water + Light energy → Glucose + Oxygen • Photosynthesis is the same in all the plants. • During photosynthesis, sunlight energy is stored in carbohydrate for later use. • Most of the carbohydrates stay in the plant but some of it goes ...
Seed Plants (Pg 262-271)
... 2.provides support for the plant 3.holds up the leaves so they can be exposed to the sun. 12. What are annual rings? The patterns of circles that represents a trees yearly growth. 13. What is the job of the leaves? Captures the suns energy and carries out the food making process of photosynthesis. 1 ...
... 2.provides support for the plant 3.holds up the leaves so they can be exposed to the sun. 12. What are annual rings? The patterns of circles that represents a trees yearly growth. 13. What is the job of the leaves? Captures the suns energy and carries out the food making process of photosynthesis. 1 ...
Module B: Unit 2, Lesson 4 - Plant Processes
... visible light are seen as different colors. • Chlorophyll absorbs many wavelengths, but it reflects more green light than it reflects other colors of light. As a result, most plants look green. • The light energy captured in chloroplasts is changed and stored in the bonds of a sugar called glucose. ...
... visible light are seen as different colors. • Chlorophyll absorbs many wavelengths, but it reflects more green light than it reflects other colors of light. As a result, most plants look green. • The light energy captured in chloroplasts is changed and stored in the bonds of a sugar called glucose. ...
Biology-1 Exam Two You can write on this exam. Please put a W at
... 48. Carbon fixation a. occurs when carbon atoms from CO2 are incorporated into an organic molecule b. supplies the cell with ATP c. occurs during the light reactions d. provides the cell with a supply of NADPH molecules e. all of the above 49. What is the name of the organic compound that CO2 first ...
... 48. Carbon fixation a. occurs when carbon atoms from CO2 are incorporated into an organic molecule b. supplies the cell with ATP c. occurs during the light reactions d. provides the cell with a supply of NADPH molecules e. all of the above 49. What is the name of the organic compound that CO2 first ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.