Unit 3 Macromolecules, Enzymes, and ATP
... • He was trying to make an inorganic salt called ammonium cyanate by mixing ammonium and cyanate ions but made urea instead. Urea is an organic compound that is found in the urine of mammals. • Scientists (Vitalists) were not convinced because the cyanate was extracted from animal blood. • Vitalism ...
... • He was trying to make an inorganic salt called ammonium cyanate by mixing ammonium and cyanate ions but made urea instead. Urea is an organic compound that is found in the urine of mammals. • Scientists (Vitalists) were not convinced because the cyanate was extracted from animal blood. • Vitalism ...
Lecture 16
... This is not an acid/base reaction, the H+ comes from the removal of a hydrogen atom with its electron, not just the proton AH2 and A together constitute a conjugate redox pair that can reduce another compound, B, or redox pair (B/BH2) by transfer of hydrogen atoms: AH2 + B A + BH2 ...
... This is not an acid/base reaction, the H+ comes from the removal of a hydrogen atom with its electron, not just the proton AH2 and A together constitute a conjugate redox pair that can reduce another compound, B, or redox pair (B/BH2) by transfer of hydrogen atoms: AH2 + B A + BH2 ...
Chapter 39 Student Misconceptions
... Both plants and animals respond to environmental stimuli. Which of the following statements are correct? a. The processes by which plants and animals perceive environmental changes are equally complex. b. The processes by which plants and animals perceive environmental changes are often homologous. ...
... Both plants and animals respond to environmental stimuli. Which of the following statements are correct? a. The processes by which plants and animals perceive environmental changes are equally complex. b. The processes by which plants and animals perceive environmental changes are often homologous. ...
ENVIRONMENTAL
... (3) Reducers Reducers are heterotrophic organisms like animals; they are fungi and bacterial that decompose dead organic matter. ...
... (3) Reducers Reducers are heterotrophic organisms like animals; they are fungi and bacterial that decompose dead organic matter. ...
Answer
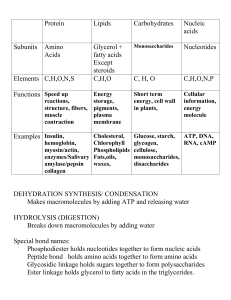
... 47. Are lipids polar or nonpolar? What happens to lipids when they are placed in water? Non polar, they separate from water 48. Compared to carbohydrates, what is true about the ratio of carbon & hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? If a compound has more bonds, what can it store more of in those bonds? ...
... 47. Are lipids polar or nonpolar? What happens to lipids when they are placed in water? Non polar, they separate from water 48. Compared to carbohydrates, what is true about the ratio of carbon & hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? If a compound has more bonds, what can it store more of in those bonds? ...
How Cells Obtain Energy Cell Respiration
... in the thylakoids Light energy is transferred to electrons in chlorophyll Electrons are lost from chlorophyll and are passed along a series of cytochrome molecules called an electron transport chain H2O breaks down to donate electrons lost from chlorophyll so chlorophyll can respond to more light en ...
... in the thylakoids Light energy is transferred to electrons in chlorophyll Electrons are lost from chlorophyll and are passed along a series of cytochrome molecules called an electron transport chain H2O breaks down to donate electrons lost from chlorophyll so chlorophyll can respond to more light en ...
powerpoint 24 Aug
... Tertiary structure is extremely important to the functioning of amylase. The tertiary structure is formed by the whole peptide chain (protein) folding and coiling around itself. This forms the active site (binding site) of the enzyme. The enzyme is held in a specific configuration (tertiary struct ...
... Tertiary structure is extremely important to the functioning of amylase. The tertiary structure is formed by the whole peptide chain (protein) folding and coiling around itself. This forms the active site (binding site) of the enzyme. The enzyme is held in a specific configuration (tertiary struct ...
Exam 2 Key
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
Basic Atomic Structure
... Reactions that give off heat (become hot) are called exothermic. Reactions that absorb heat (become cold) are called endothermic. Chemical indicators can be added to a reaction to tell many different things about the reaction – they usually change color to indicate a change that happened. ...
... Reactions that give off heat (become hot) are called exothermic. Reactions that absorb heat (become cold) are called endothermic. Chemical indicators can be added to a reaction to tell many different things about the reaction – they usually change color to indicate a change that happened. ...
Ecology Review Set
... 2. Explain the carbon cycle and how pollution relates to it. 3. What processes are involved in the hydrologic (water) cycle? 4. How does the carbon cycle relate to the oxygen cycle? 5. How is carbon released in to the atmosphere? 6. How is carbon released into the soil? 7. Define the terms biotic an ...
... 2. Explain the carbon cycle and how pollution relates to it. 3. What processes are involved in the hydrologic (water) cycle? 4. How does the carbon cycle relate to the oxygen cycle? 5. How is carbon released in to the atmosphere? 6. How is carbon released into the soil? 7. Define the terms biotic an ...
Summary/Reflection of Dan Freedman`s article, Science Education
... 2. The presence of a catalyst accelerates the rate of the reaction because it lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. 3. A catalyst is any substance that accelerates a reaction but does not undergo a chemical change itself. a. Since the catalyst is not changed by the re ...
... 2. The presence of a catalyst accelerates the rate of the reaction because it lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. 3. A catalyst is any substance that accelerates a reaction but does not undergo a chemical change itself. a. Since the catalyst is not changed by the re ...
unit 9 review sheet
... Carbon Dioxide Used – Plants and other photosynthetic organisms Nitrogen is maintained in the atmosphere through the nitrogen cycle. Water is maintained in the atmosphere through the water cycle. o As water vapor condenses in the atmosphere, impurities (such as dust and particulates) are remov ...
... Carbon Dioxide Used – Plants and other photosynthetic organisms Nitrogen is maintained in the atmosphere through the nitrogen cycle. Water is maintained in the atmosphere through the water cycle. o As water vapor condenses in the atmosphere, impurities (such as dust and particulates) are remov ...
Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes
... Biochemistry an enzyme name has two parts: ‐First part is the name of the substrates for the enzyme. ‐Second part is the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.This part ends with the suffix “ase”. Example: Lactate dehydrogenase ...
... Biochemistry an enzyme name has two parts: ‐First part is the name of the substrates for the enzyme. ‐Second part is the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.This part ends with the suffix “ase”. Example: Lactate dehydrogenase ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
GRADE 6 SCIENCE NOTES
... 4. Give an example of a stimulus and a response. The leaves of the Mimosa plant droop if we touch it .Touch is a stimulus while folding of the leaves is the response. 5. How are autotrophs different from heterotrophs? Autotrophs make their own food themselves.eg: Green Plants. Heterotrophs depend on ...
... 4. Give an example of a stimulus and a response. The leaves of the Mimosa plant droop if we touch it .Touch is a stimulus while folding of the leaves is the response. 5. How are autotrophs different from heterotrophs? Autotrophs make their own food themselves.eg: Green Plants. Heterotrophs depend on ...
midterm-review_slides
... General Energetics (be able to apply these concepts!) • Potential energy – stored energy/energy at rest • Kinetic energy –energy in motion • Conductionv-transfer of energy through solid matter • Convection – transfer of energy through a fluid • First law of thermodynamics – energy cannot be created ...
... General Energetics (be able to apply these concepts!) • Potential energy – stored energy/energy at rest • Kinetic energy –energy in motion • Conductionv-transfer of energy through solid matter • Convection – transfer of energy through a fluid • First law of thermodynamics – energy cannot be created ...
Flow of Energy - Big Spring ISD
... Plants use stored energy (food) when the resources they need to grow and thrive are unavailable. ...
... Plants use stored energy (food) when the resources they need to grow and thrive are unavailable. ...
Biology 123 SI-Dr. Raut`s Class Session 10
... from NADH to the first molecule of the electron transport chain in complex one. From there the electrons flow down the electron transport chain. Every time the electrons move to a molecule, that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is o ...
... from NADH to the first molecule of the electron transport chain in complex one. From there the electrons flow down the electron transport chain. Every time the electrons move to a molecule, that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is o ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... 5. Describe what would happen to a red blood cell in each of the following situations: a. It is placed in a solution with an extremely high concentration of salt. b. It is placed in distilled water. 6. What are some body systems that help organisms remove excess water? Explain how these systems work ...
... 5. Describe what would happen to a red blood cell in each of the following situations: a. It is placed in a solution with an extremely high concentration of salt. b. It is placed in distilled water. 6. What are some body systems that help organisms remove excess water? Explain how these systems work ...
2.3 and 2.4 Notes
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.