Document
... • There are nine essential amino acids, that are not easily made by animals and must be included in their diet. They are found in first class proteins which come from animal sources (meat, fish, eggs)… • There are also non-essential amino acids: they can be synthesised from any protein including pla ...
... • There are nine essential amino acids, that are not easily made by animals and must be included in their diet. They are found in first class proteins which come from animal sources (meat, fish, eggs)… • There are also non-essential amino acids: they can be synthesised from any protein including pla ...
vascular plants
... •Organisms have the ability to produce offspring that have similar characteristics as the parents. There are two basic types of reproduction: •Asexual reproduction: involves only one parent and produces offspring that is identical to the parent. •Sexual reproduction: involves two parents. The egg (f ...
... •Organisms have the ability to produce offspring that have similar characteristics as the parents. There are two basic types of reproduction: •Asexual reproduction: involves only one parent and produces offspring that is identical to the parent. •Sexual reproduction: involves two parents. The egg (f ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... Plants can release more O2 in photosynthesis than they consume in respiration because they do not respire all of the glucose they produce. For example, plants may store glucose as starch or cellulose. ...
... Plants can release more O2 in photosynthesis than they consume in respiration because they do not respire all of the glucose they produce. For example, plants may store glucose as starch or cellulose. ...
Document
... Relationship in which two organisms live together in close association Some bacteria in the soil change nitrogen compounds into nitrogen gas. This process is called____. ______________is converted into fossil fuels such as gas, peat, or coal When an organism dies, it is eventually eaten by _________ ...
... Relationship in which two organisms live together in close association Some bacteria in the soil change nitrogen compounds into nitrogen gas. This process is called____. ______________is converted into fossil fuels such as gas, peat, or coal When an organism dies, it is eventually eaten by _________ ...
3. While You wait – Plant Science
... • Proper temperature – 45 degrees for lettuce, 70 degrees for pepper ...
... • Proper temperature – 45 degrees for lettuce, 70 degrees for pepper ...
respir532
... The pumping of H+ ions into the INTERMEMBRANE SPACE represents _______________________ potential energy that is harnessed to make ATP. As H+ ions escape through ion channels ATP SYNTHASE back into the matrix, ________________ spins and adds a phosphate to ADP to ATP form _______ ...
... The pumping of H+ ions into the INTERMEMBRANE SPACE represents _______________________ potential energy that is harnessed to make ATP. As H+ ions escape through ion channels ATP SYNTHASE back into the matrix, ________________ spins and adds a phosphate to ADP to ATP form _______ ...
Science 7 – Unit 2 Plants for Food and Fibre – Study Guide
... Leaves – the energy producers of the plants Leaves contain chlorophyll the pigment that makes them green. Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves. CO2 + H2O + Sunlight + nutrients ----- sugar + O2 Gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen enter and leave the plant through little openings in the leaves ...
... Leaves – the energy producers of the plants Leaves contain chlorophyll the pigment that makes them green. Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves. CO2 + H2O + Sunlight + nutrients ----- sugar + O2 Gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen enter and leave the plant through little openings in the leaves ...
Electrons - davis.k12.ut.us
... The sugar portion of the molecule is a pentose sugar, ribose. Nitrogen base thymine in DNA is replaced by uracil in RNA. ...
... The sugar portion of the molecule is a pentose sugar, ribose. Nitrogen base thymine in DNA is replaced by uracil in RNA. ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
End of Course Exam 6th Grade Review Answer Key
... DNA, cells, reproduce, respond to stimuli, use energy, grow and develop 2. Describe the 7 levels of organization going from smallest to largest. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism 3. What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? Pro: single c ...
... DNA, cells, reproduce, respond to stimuli, use energy, grow and develop 2. Describe the 7 levels of organization going from smallest to largest. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism 3. What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? Pro: single c ...
the release of energy in cells by the combination of food and oxygen
... Respiration – the release of energy in cells by the combination of food and oxygen Gills – organs used by water animals to obtain oxygen from the water Spiracles – holes along the abdomen of insects used to take in oxygen Carbon dioxide – a gaseous waste product of respiration which is exhaled from ...
... Respiration – the release of energy in cells by the combination of food and oxygen Gills – organs used by water animals to obtain oxygen from the water Spiracles – holes along the abdomen of insects used to take in oxygen Carbon dioxide – a gaseous waste product of respiration which is exhaled from ...
10B - Plant Systems Review
... 45. What conclusions can you draw from a plant that has lots of stomata? 46. What happens to the guard cells when the plant is lacking water? When it has plenty of water? 47. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in a desert? 48. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it li ...
... 45. What conclusions can you draw from a plant that has lots of stomata? 46. What happens to the guard cells when the plant is lacking water? When it has plenty of water? 47. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in a desert? 48. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it li ...
Interdependence among Living Organisms and the
... These different populations that live together are interdependent on one another for survival. Therefore, the interdependence among living organisms and the environment creates a balanced ecosystem. ...
... These different populations that live together are interdependent on one another for survival. Therefore, the interdependence among living organisms and the environment creates a balanced ecosystem. ...
Respiration and Fermentation
... Respiration and Fermentation 1. Some bacteria can use carbon dioxide rather than oxygen as the prime oxidizing molecule and therefore produce methane (CH4) rather than water as a waste product. (T/F) 2. Autotrophs are organisms which can go out and hunt for their own food, unlike plants which stay i ...
... Respiration and Fermentation 1. Some bacteria can use carbon dioxide rather than oxygen as the prime oxidizing molecule and therefore produce methane (CH4) rather than water as a waste product. (T/F) 2. Autotrophs are organisms which can go out and hunt for their own food, unlike plants which stay i ...
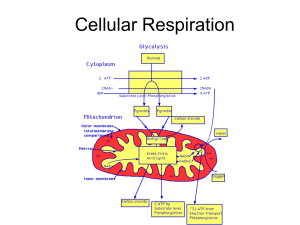
Cellular Respiration
... Carried out by your muscles when you’re exercising hard (need ATP) and can’t get oxygen into you fast enough (can’t do aerobic respiration) Causes muscle cramps and soreness ...
... Carried out by your muscles when you’re exercising hard (need ATP) and can’t get oxygen into you fast enough (can’t do aerobic respiration) Causes muscle cramps and soreness ...
BioH_Cellular Respiration
... Each protein in the chain has a higher attraction for electrons than the one before it, causing electrons to be pulled “down” the chain. The last protein of the chain passes its electrons to oxygen, which also picks up a pair of H+ from the surroundings to form water (oxygen is the “final electron a ...
... Each protein in the chain has a higher attraction for electrons than the one before it, causing electrons to be pulled “down” the chain. The last protein of the chain passes its electrons to oxygen, which also picks up a pair of H+ from the surroundings to form water (oxygen is the “final electron a ...
Catabolism
... simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy. ...
... simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy. ...
Plants – Chapters 22-25
... In leaves covered by _________________________ - waxy layer o _________________________ tissue – conducts nutrients through plant _________________________ - conducts water Composed of dead cells called ____________________ and _________________________that act as pipes. ____________________ ...
... In leaves covered by _________________________ - waxy layer o _________________________ tissue – conducts nutrients through plant _________________________ - conducts water Composed of dead cells called ____________________ and _________________________that act as pipes. ____________________ ...
Ecology Pre-Test on Part A
... 1. The appearance of new kinds of organisms during ecological succession A. depends upon new kinds of organisms previously inhabiting the community B. has no relationship to the presence of other organisms C. affects the kind of organisms that later inhabit the community D. both A and C are correct ...
... 1. The appearance of new kinds of organisms during ecological succession A. depends upon new kinds of organisms previously inhabiting the community B. has no relationship to the presence of other organisms C. affects the kind of organisms that later inhabit the community D. both A and C are correct ...
Chapter 7 Notes - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... pumped against their concentration gradient (uphill). ...
... pumped against their concentration gradient (uphill). ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... Enzymes are large protein molecules which act as biological catalysts – they speed up reactions in the body by reducing the activation energy of the reaction. The molecule on which an enzyme acts is called a substrate, and the place on the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site. ...
... Enzymes are large protein molecules which act as biological catalysts – they speed up reactions in the body by reducing the activation energy of the reaction. The molecule on which an enzyme acts is called a substrate, and the place on the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.