BIO00004C Molecular biology and biochemistry (PDF , 72kb)
... different sugar nutrients, regulation of glycogen metabolism; detailed discussion of glycolysis, the TCA cycle and the role of fermentation; regulation of these pathways, how energy generation is balanced with the efficient turnover of available nutrients; how and why cells choose one pathway over a ...
... different sugar nutrients, regulation of glycogen metabolism; detailed discussion of glycolysis, the TCA cycle and the role of fermentation; regulation of these pathways, how energy generation is balanced with the efficient turnover of available nutrients; how and why cells choose one pathway over a ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) ...
... Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of _________________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ______________, _____________, and _________________. 3. Proteins are made of ___________________ 4. ______________ are made of nucleotides. 5. Examples of lipids include _________________________ ...
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of _________________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ______________, _____________, and _________________. 3. Proteins are made of ___________________ 4. ______________ are made of nucleotides. 5. Examples of lipids include _________________________ ...
Chapter 11
... contractions of large muscle groups – Raises heart rate giving the heart an effective workout ...
... contractions of large muscle groups – Raises heart rate giving the heart an effective workout ...
Nutrition PowerPoint
... Oxygen debt now Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC) These terms refer to a lack of oxygen while training Oxygen Deficit. While exercising intensely the body is sometimes unable to fulfill all of its energy needs. In order to make up the difference without sacrificing the output, the body ...
... Oxygen debt now Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC) These terms refer to a lack of oxygen while training Oxygen Deficit. While exercising intensely the body is sometimes unable to fulfill all of its energy needs. In order to make up the difference without sacrificing the output, the body ...
Chapter 6: Metabolism of Microorganisms
... Other Nutrients Represent Potential Energy Sources • Many mono-, di-, and polysaccharides can be energy sources for prokaryotes • They must all be prepared before being processed by • glycolysis • the Krebs cycle • oxidative phosphorylation • Chemical bonds in fats store large amounts of energy, mak ...
... Other Nutrients Represent Potential Energy Sources • Many mono-, di-, and polysaccharides can be energy sources for prokaryotes • They must all be prepared before being processed by • glycolysis • the Krebs cycle • oxidative phosphorylation • Chemical bonds in fats store large amounts of energy, mak ...
Photosynthesis
... can take place with or without oxygen glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) Uses 2 ATP molecules but produces 4 ATP molecules = a net gain of 2 ATPs ...
... can take place with or without oxygen glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) Uses 2 ATP molecules but produces 4 ATP molecules = a net gain of 2 ATPs ...
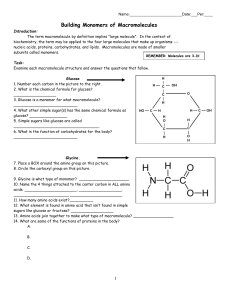
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
Biology 2.3 Carbon Compounds
... Store and transmit genetic information DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid RNA= ribonucleic acid ...
... Store and transmit genetic information DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid RNA= ribonucleic acid ...
Chapter 9 – Molecular Geometry and hybridization I. Molecular
... C. pOH = -log [OH-] D. [OH-] = 10-pOH E. [H+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 ...
... C. pOH = -log [OH-] D. [OH-] = 10-pOH E. [H+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 ...
notes - Main
... 1. Fasting means going without food for many hours or a few days whereas starvation implies weeks or months of food deprivation or inadequate food intake. a. Catabolism of stored triglycerides and structural proteins can provide energy for several weeks. b. The amount of adipose tissue determines th ...
... 1. Fasting means going without food for many hours or a few days whereas starvation implies weeks or months of food deprivation or inadequate food intake. a. Catabolism of stored triglycerides and structural proteins can provide energy for several weeks. b. The amount of adipose tissue determines th ...
Metabolism 2010edit
... Metabolism • Coordination of chemical processes across whole organism – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulat ...
... Metabolism • Coordination of chemical processes across whole organism – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulat ...
ch25 Metabolism
... 1. Fasting means going without food for many hours or a few days whereas starvation implies weeks or months of food deprivation or inadequate food intake. a. Catabolism of stored triglycerides and structural proteins can provide energy for several weeks. b. The amount of adipose tissue determines th ...
... 1. Fasting means going without food for many hours or a few days whereas starvation implies weeks or months of food deprivation or inadequate food intake. a. Catabolism of stored triglycerides and structural proteins can provide energy for several weeks. b. The amount of adipose tissue determines th ...
9.6 Respiration 4 (Control and other metabolites)
... Metabolism • Coordination of chemical processes across whole organism – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulat ...
... Metabolism • Coordination of chemical processes across whole organism – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulat ...
Main Concepts Muscle structure, Oxidation of fats, Muscle types
... Type 1 (slow twitch) muscle cells which gain their energy from aerobic respiration Type 2 (fast twitch) muscle cells which gain their energy from anaerobic respiration. 11. Glycogen is stored in small granules in muscle tissue. This can readily be broken down to glucose which is available for glycol ...
... Type 1 (slow twitch) muscle cells which gain their energy from aerobic respiration Type 2 (fast twitch) muscle cells which gain their energy from anaerobic respiration. 11. Glycogen is stored in small granules in muscle tissue. This can readily be broken down to glucose which is available for glycol ...
Chem 371-001 - Loyola University Chicago
... be dropped. Alternately, the final can be scaled back to 100 while keep the first three scores in your total score. Either way the highest possible total will be 400. The letter grade will be determined by strictly and precisely using the following scale: Grading Sale: A AB+ B BC+ C CD+ D F ...
... be dropped. Alternately, the final can be scaled back to 100 while keep the first three scores in your total score. Either way the highest possible total will be 400. The letter grade will be determined by strictly and precisely using the following scale: Grading Sale: A AB+ B BC+ C CD+ D F ...
Biochemistry PPT - Effingham County Schools
... Water, pH and Biological Molecules What’s so special about water? It is a great solvent. ...
... Water, pH and Biological Molecules What’s so special about water? It is a great solvent. ...
2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.