Anaerobic Energy Systems
... Anaerobic energy system = energy system within the body that does not require the use of oxygen It consists of the ATP-PC system and the Lactic Acid/Anaerobic Glycolysis system All three energy pathways (ATP-PC, Lactic Acid & Aerobic energy systems) operate at any one time and can overlap. The ...
... Anaerobic energy system = energy system within the body that does not require the use of oxygen It consists of the ATP-PC system and the Lactic Acid/Anaerobic Glycolysis system All three energy pathways (ATP-PC, Lactic Acid & Aerobic energy systems) operate at any one time and can overlap. The ...
Exam 1 454 Study Guide
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
Microbial Metabolism
... products of the pathway Related to synthesis of microbial cells in the growth phase Include alcohols, amino acids, nucleotides, organic acids, polyols, vitamins, and enzymes ...
... products of the pathway Related to synthesis of microbial cells in the growth phase Include alcohols, amino acids, nucleotides, organic acids, polyols, vitamins, and enzymes ...
Sample Exam 1
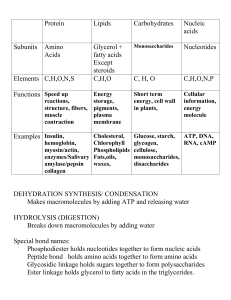
... 27. A fatty acid molecule that has a double bond between 2 adjacent carbon atoms is: a. a monosaccharide. b. unsaturated. c. polar. d. saturated. e. a nucleotide. 28. A triglyceride is made by bonding ____________ and ____________. a. cholesterol, fatty acids. b. fatty acids, glycerol c. glucose an ...
... 27. A fatty acid molecule that has a double bond between 2 adjacent carbon atoms is: a. a monosaccharide. b. unsaturated. c. polar. d. saturated. e. a nucleotide. 28. A triglyceride is made by bonding ____________ and ____________. a. cholesterol, fatty acids. b. fatty acids, glycerol c. glucose an ...
Systemic Response to Injury and Metabolic Support
... can tolerate 10 days of partial starvation before any significant protein catabolism occurs ...
... can tolerate 10 days of partial starvation before any significant protein catabolism occurs ...
AP Biology – PowerPoint Notes - Chapter 6
... ATP goes through a cycle: energy from glucose breakdown drives ATP buildup and then ATP breakdown provides energy for cellular work. o Endergonic ‐ absorbing energy o Exergonic – releasing energy ...
... ATP goes through a cycle: energy from glucose breakdown drives ATP buildup and then ATP breakdown provides energy for cellular work. o Endergonic ‐ absorbing energy o Exergonic – releasing energy ...
Study Guide
... cause certain chemical reactions that may interfere with a cell’s normal functioning (can lead to cell death) B. Buffers • Weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH • Produced naturally by the body to maintain homeostasis II. Carbon Compounds (S ...
... cause certain chemical reactions that may interfere with a cell’s normal functioning (can lead to cell death) B. Buffers • Weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH • Produced naturally by the body to maintain homeostasis II. Carbon Compounds (S ...
Document
... List a few additional processes that occur in living organisms which require the energy. • generating nerve impulses in the nervous system • contraction of muscle fibers ...
... List a few additional processes that occur in living organisms which require the energy. • generating nerve impulses in the nervous system • contraction of muscle fibers ...
HW #23 KEY 1. Adenosine triphosphate is the energy currency of
... 24. Explain why the Calvin cycle depends on light reactions. The Calvin cycle depends on light-dependent reactions to provide the energy (ATP and NADPH) needed for glucose production. 27. Describe two alternative photosynthesis pathways found in plants. Suggest how these adaptations might help plant ...
... 24. Explain why the Calvin cycle depends on light reactions. The Calvin cycle depends on light-dependent reactions to provide the energy (ATP and NADPH) needed for glucose production. 27. Describe two alternative photosynthesis pathways found in plants. Suggest how these adaptations might help plant ...
Systems Biology Study Group Chapter 3
... • Conformational changes in enzyme molecule • Example: Hexokinase – Catalyzes phosphorylation of glucose – Inhibited by ATP, product of glycolysis – Stimulated by ADP, product of ATP stored energy consumption ...
... • Conformational changes in enzyme molecule • Example: Hexokinase – Catalyzes phosphorylation of glucose – Inhibited by ATP, product of glycolysis – Stimulated by ADP, product of ATP stored energy consumption ...
Unit 2 PPT - Faculty Sites
... • This leaves an energy ‘hole’ which is filled by splitting water into 2 H+ and ½ O2. (Oh, that’s where Oxygen comes from!) When the energized electrons fall they release energy that is captured as they are transferred through a series of electron transport molecules. • They then arrive at Photosyst ...
... • This leaves an energy ‘hole’ which is filled by splitting water into 2 H+ and ½ O2. (Oh, that’s where Oxygen comes from!) When the energized electrons fall they release energy that is captured as they are transferred through a series of electron transport molecules. • They then arrive at Photosyst ...
Name: ____ ______ Unit 4: Living Things Metabolize Section A
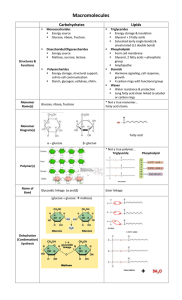
... macromolecule: Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, proteins. State unique characteristics for each. Identify the monomer and polymer of each organic macromolecule. ...
... macromolecule: Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, proteins. State unique characteristics for each. Identify the monomer and polymer of each organic macromolecule. ...
Slide 1
... Carbohydrates—monosaccharides Lipids—fatty acids Proteins—amino acids Nucleic acids—nucleotides ...
... Carbohydrates—monosaccharides Lipids—fatty acids Proteins—amino acids Nucleic acids—nucleotides ...
Final Review
... 62. Explain energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high energy charge. Chemical energy is stored in ATP only for a short time-ATP is quickly hydrolyzed. This chemical energy is used to do chemical, mechanical and electrical work in the body and to maintain body temperature ...
... 62. Explain energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high energy charge. Chemical energy is stored in ATP only for a short time-ATP is quickly hydrolyzed. This chemical energy is used to do chemical, mechanical and electrical work in the body and to maintain body temperature ...
Chem 2B
... 62. Explain energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high energy charge. Chemical energy is stored in ATP only for a short time-ATP is quickly hydrolyzed. This chemical energy is used to do chemical, mechanical and electrical work in the body and to maintain body temperature ...
... 62. Explain energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high energy charge. Chemical energy is stored in ATP only for a short time-ATP is quickly hydrolyzed. This chemical energy is used to do chemical, mechanical and electrical work in the body and to maintain body temperature ...
protein/power point
... HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates vs Lipids ...
... HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates vs Lipids ...
Organic molecules
... • Monomers: one unit of a compound -smaller, simple molecule that can join together to form larger molecule Mono = single; mer = part • Polymers: many monomers combined -complex molecule formed when 2 or more monomers combine poly = many • Macromolecules -Many large molecules combined -Formed by pol ...
... • Monomers: one unit of a compound -smaller, simple molecule that can join together to form larger molecule Mono = single; mer = part • Polymers: many monomers combined -complex molecule formed when 2 or more monomers combine poly = many • Macromolecules -Many large molecules combined -Formed by pol ...
chapter_6_mod_2009
... (sugar) called photosynthetic autotroph Use the energy from inorganic chemical reaction to make larger organic molecules called chemosynthetic autotroph Heterotrophs Obtain their energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which they must obtain f ...
... (sugar) called photosynthetic autotroph Use the energy from inorganic chemical reaction to make larger organic molecules called chemosynthetic autotroph Heterotrophs Obtain their energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which they must obtain f ...
notes for cell resp - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... A. AcetylCoA enters the cycle and combines with oxaloacetate to form a six carbon citrate (citric acid) B. Rearrangement of the molecule yield NADH and CO2 C. Loss of the CoA drives GDP to GTP which drives ADP to ATP D. FAD is reduced to FADH2 E. More rearrangements produce NADH and oxaloacetate F. ...
... A. AcetylCoA enters the cycle and combines with oxaloacetate to form a six carbon citrate (citric acid) B. Rearrangement of the molecule yield NADH and CO2 C. Loss of the CoA drives GDP to GTP which drives ADP to ATP D. FAD is reduced to FADH2 E. More rearrangements produce NADH and oxaloacetate F. ...
Ch 26 Powerpoint
... • 1 – NADH dehydrogenase complex – FMN & 5 Fe-S centers – start – NADH + H+ is oxidized to NAD+ and FMN is reduced to ...
... • 1 – NADH dehydrogenase complex – FMN & 5 Fe-S centers – start – NADH + H+ is oxidized to NAD+ and FMN is reduced to ...
2106lecture 11a powerpoint
... Oxygen debt-recovery oxygen consumptionthe difference between oxygen consumption in the post-exercise recovery phase and the oxygen consumption at rest Fuel source is limited to glucose and produces a relatively small amount of ATP relative to aerobic metabolism All out effort for 60-120 seconds ...
... Oxygen debt-recovery oxygen consumptionthe difference between oxygen consumption in the post-exercise recovery phase and the oxygen consumption at rest Fuel source is limited to glucose and produces a relatively small amount of ATP relative to aerobic metabolism All out effort for 60-120 seconds ...
Completed Note
... Store & transmit genetic material Direct synthesis of new proteins & organic molecules RNA Translates DNA into functional proteins Several types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA…) ATP Stores potential energy in its phosphate bonds Releases energy when converted to ...
... Store & transmit genetic material Direct synthesis of new proteins & organic molecules RNA Translates DNA into functional proteins Several types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA…) ATP Stores potential energy in its phosphate bonds Releases energy when converted to ...
An Introduction to Metabolism
... pH: optimal 6-8, but exceptions exist (pepsin and trypsin) Cofactors/coenzymes: inorganic or organic helpers ...
... pH: optimal 6-8, but exceptions exist (pepsin and trypsin) Cofactors/coenzymes: inorganic or organic helpers ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.