CHEM 214 Elementary Biochemistry
... discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of the structures and chemical reactivity of biomolecules, with particular emphasis on the ...
... discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of the structures and chemical reactivity of biomolecules, with particular emphasis on the ...
Cellular Respiration
... H which combine with O to make H2O The excess energy stored in the electrons of H is slowly released and used to make ATP before they combine with the O Therefore, the energy that came from the sun and was stored in the organic molecule sugar, is now temporarily stored in ATP until the energy is use ...
... H which combine with O to make H2O The excess energy stored in the electrons of H is slowly released and used to make ATP before they combine with the O Therefore, the energy that came from the sun and was stored in the organic molecule sugar, is now temporarily stored in ATP until the energy is use ...
Assessment
... _____ 1. Which of the following statements is true for all cells? a. They use solar energy. b. They use photosynthesis. c. They use chemical energy. _____ 2. Which phrase best describes the function of the ATP molecule? a. carries energy b. absorbs energy c. converts energy _____ 3. Where does the c ...
... _____ 1. Which of the following statements is true for all cells? a. They use solar energy. b. They use photosynthesis. c. They use chemical energy. _____ 2. Which phrase best describes the function of the ATP molecule? a. carries energy b. absorbs energy c. converts energy _____ 3. Where does the c ...
Organic Compounds
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 essential amino acids. All amino acids have the same Amino group and carboxyl groups, but each amino acid has its own unique R- group. Only 20 amino acids can combine in different arrangements to form all of the many different kinds of pr ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 essential amino acids. All amino acids have the same Amino group and carboxyl groups, but each amino acid has its own unique R- group. Only 20 amino acids can combine in different arrangements to form all of the many different kinds of pr ...
Organic Molecules
... Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in the liver and muscles but only have about a one day supply. ...
... Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in the liver and muscles but only have about a one day supply. ...
Chapter 2 - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... Many humans are lactose-intolerant, meaning they cannot digest milk products containing the disaccharide lactose. Use the information learned in this chapter to hypothesize a cause of lactose ...
... Many humans are lactose-intolerant, meaning they cannot digest milk products containing the disaccharide lactose. Use the information learned in this chapter to hypothesize a cause of lactose ...
Honors Biology Notes:
... chemistry of life is organized into ________________________________________________________ – metabolism: collection of reactions that occur in organisms; facilitated by _____________________ – two general categories of reactions: • ____________________: breakdown of macromolecules into monomers, r ...
... chemistry of life is organized into ________________________________________________________ – metabolism: collection of reactions that occur in organisms; facilitated by _____________________ – two general categories of reactions: • ____________________: breakdown of macromolecules into monomers, r ...
powerpoint 24 Aug
... amylase to break down starch it must bind the starch. It can only bind starch because its tertiary structure results in the formation of a binding site. Quaternary structure would be more than one peptide chain associated with each other to form a functioning protein, but amylase is just one pepti ...
... amylase to break down starch it must bind the starch. It can only bind starch because its tertiary structure results in the formation of a binding site. Quaternary structure would be more than one peptide chain associated with each other to form a functioning protein, but amylase is just one pepti ...
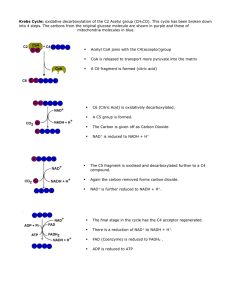
Krebs Cycle
... reduction of NAD (g) C4 to C4 with the reduction of coenzymes FAD and NAD. ATP is made ...
... reduction of NAD (g) C4 to C4 with the reduction of coenzymes FAD and NAD. ATP is made ...
STUDY GUIDE
... c. Organic molecules: i. Carbohydrates ii. Nucleic acids iii. Proteins (enzymes) d. Cellular organelles i. Chloroplast ii. Mitochondria iii. Ribosomes iv. Vacuole v. Nucleus o Explain how energy flows into and out of an organism: a. Illustrate light energy chemical energy (glucose) b. Illustrate c ...
... c. Organic molecules: i. Carbohydrates ii. Nucleic acids iii. Proteins (enzymes) d. Cellular organelles i. Chloroplast ii. Mitochondria iii. Ribosomes iv. Vacuole v. Nucleus o Explain how energy flows into and out of an organism: a. Illustrate light energy chemical energy (glucose) b. Illustrate c ...
Ch 26 Notes
... Need to maintain normal blood glucose level [90-100mg/100mL] Very important for nervous system - can only use glucose for energy. EVENTS: Liver glycogen is converted to glucose - lasts about 4 hrs. Muscle glycogen is converted to lactic acid glucose in liver Adipose breaks triglycerides to glycero ...
... Need to maintain normal blood glucose level [90-100mg/100mL] Very important for nervous system - can only use glucose for energy. EVENTS: Liver glycogen is converted to glucose - lasts about 4 hrs. Muscle glycogen is converted to lactic acid glucose in liver Adipose breaks triglycerides to glycero ...
What is metabolism? The sum of all chemical reactions that occur as
... Microorganisms also differ in the types of fermentation products they produce (given they can ferment a particular carbohydrate). These differences in fermentation by-products (acid or acid-gas) is also based on the presence/absence of appropriate enzymes. We make extensive use of these differences ...
... Microorganisms also differ in the types of fermentation products they produce (given they can ferment a particular carbohydrate). These differences in fermentation by-products (acid or acid-gas) is also based on the presence/absence of appropriate enzymes. We make extensive use of these differences ...
Vitamins and Minerals
... E. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid. 1. This one-step reaction involves hydrogen transfer, which regenerates NAD and allows for continued function of the glycolysis pathway. 2. Lactate production occurs in cells with few or no mitochondria and in muscle cells during hi ...
... E. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid. 1. This one-step reaction involves hydrogen transfer, which regenerates NAD and allows for continued function of the glycolysis pathway. 2. Lactate production occurs in cells with few or no mitochondria and in muscle cells during hi ...
Ch. 2 - The Chemistry of Life
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ◦ Composed of a nucleotide built from ribose sugar, adenine base, and three phosphate groups ◦ Supplies chemical energy used by all cells ◦ Energy is released by breaking high energy phosphate bonds ◦ ATP is replenished by oxidation (breakdown) of food fuels; primarily s ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ◦ Composed of a nucleotide built from ribose sugar, adenine base, and three phosphate groups ◦ Supplies chemical energy used by all cells ◦ Energy is released by breaking high energy phosphate bonds ◦ ATP is replenished by oxidation (breakdown) of food fuels; primarily s ...
Name: #: Cellular Respiration Review 2 Process Where does it
... 6. Write the complete overall chemical equation for cellular respiration using chemical symbols instead of words: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + 36ATP 7. Why do we say there is a ‘net’ gain of 2 ATP at the end of glycolysis? Glycolysis produces 4ATP but since it needs 2 ATP to start, the cell only in ...
... 6. Write the complete overall chemical equation for cellular respiration using chemical symbols instead of words: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + 36ATP 7. Why do we say there is a ‘net’ gain of 2 ATP at the end of glycolysis? Glycolysis produces 4ATP but since it needs 2 ATP to start, the cell only in ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
... which can join together to make a protein. 17. Phosholipids makes up cell membranes. 18. Fats are made of an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chain, then it is said to be saturate ...
... which can join together to make a protein. 17. Phosholipids makes up cell membranes. 18. Fats are made of an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chain, then it is said to be saturate ...
Teacher Quality Grant - Gulf Coast State College
... to keep H’s and OH’s that you may remove in order to show that water is also a product of this reaction. ...
... to keep H’s and OH’s that you may remove in order to show that water is also a product of this reaction. ...
Energy
... ∆G = ∆H – T∆S Spontaneous reactions release free energy, which is available to do work. Exergonic reactions have A negative G value. Endergonic reactions are a nonspontaneous reaction or process that absorbs free energy and has a positive ∆G. ...
... ∆G = ∆H – T∆S Spontaneous reactions release free energy, which is available to do work. Exergonic reactions have A negative G value. Endergonic reactions are a nonspontaneous reaction or process that absorbs free energy and has a positive ∆G. ...
THE Macromolecules PowerPoint - Panhandle Area Educational
... to keep H’s and OH’s that you may remove in order to show that water is also a product of this reaction. ...
... to keep H’s and OH’s that you may remove in order to show that water is also a product of this reaction. ...
Intro to Biology & Biochemistry
... Unsaturated fats contain more double bonds & are easier for the body to attack. These are healthier for the body. These fats can be made saturated by hydrogenation such as in Crisco (trans fats). Lipases are enzymes that break down fats & oils. Lipids are essential for the body for cell ...
... Unsaturated fats contain more double bonds & are easier for the body to attack. These are healthier for the body. These fats can be made saturated by hydrogenation such as in Crisco (trans fats). Lipases are enzymes that break down fats & oils. Lipids are essential for the body for cell ...
Organic Compounds
... • Sugars are the simplest carbohydrates and are used to make energy (metabolism). • Monosaccharides are single (mono=one) sugars. • Ex) glucose (C6H12O6), and fructose (same formula but different structure than glucose). ...
... • Sugars are the simplest carbohydrates and are used to make energy (metabolism). • Monosaccharides are single (mono=one) sugars. • Ex) glucose (C6H12O6), and fructose (same formula but different structure than glucose). ...
3.1 METABOLIC PATHWAYS §3.1a Overview of
... of electrons from electron-rich half-cell (copper) to electron-deficient half-cell (iron) through an external circuit (eg a conducting wire)—how can we measure ∆ε? - A salt bridge (eg a soaked filter paper in an electrolyte such as KNO3) is necessary to prevent the build-up of charge difference acro ...
... of electrons from electron-rich half-cell (copper) to electron-deficient half-cell (iron) through an external circuit (eg a conducting wire)—how can we measure ∆ε? - A salt bridge (eg a soaked filter paper in an electrolyte such as KNO3) is necessary to prevent the build-up of charge difference acro ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.