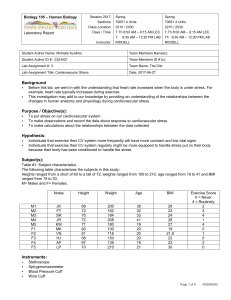
1 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Introduction
... – sugars are partially degraded ...
... – sugars are partially degraded ...
The citric acid cycle • Also known as the Kreb`s cycle
... If ____________ conditions exist, we get < 10% of the energy generated under aerobic conditions • Can you determine what the exact amount of energy is under these conditions?? ...
... If ____________ conditions exist, we get < 10% of the energy generated under aerobic conditions • Can you determine what the exact amount of energy is under these conditions?? ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint and animations
... = organisms that can make ATP using either fermentation or cellular respiration Ex: yeast and many bacteria With oxygen pyruvate → Krebs cycle ...
... = organisms that can make ATP using either fermentation or cellular respiration Ex: yeast and many bacteria With oxygen pyruvate → Krebs cycle ...
Transaminase. There are many types for each amino acid. They are
... Oxidative phosphorylation (ox-phos). A fixed amount of ATP is generated depending on how much oxidation occurs. The P/O ratio, for example, is the molar amount of ATP generated per atom of oxygen that gets reduced. This ratio is ~3. ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation (ox-phos). A fixed amount of ATP is generated depending on how much oxidation occurs. The P/O ratio, for example, is the molar amount of ATP generated per atom of oxygen that gets reduced. This ratio is ~3. ...
Adv. Bio. Ch 9 Glyco and Resp
... Proteins must be broken down to individual amino acids which ...
... Proteins must be broken down to individual amino acids which ...
EnERGY TRANSFORMATIONS IN NATURE
... Chemoautotrophs are primarily bacteria that are found in rare ecosystems where sunlight is not available, such as in those associated with dark caves or hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean . Many chemoautotrophs in hydrothermal vents use hydrogen sulfide (H 2S), which is released from the ...
... Chemoautotrophs are primarily bacteria that are found in rare ecosystems where sunlight is not available, such as in those associated with dark caves or hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean . Many chemoautotrophs in hydrothermal vents use hydrogen sulfide (H 2S), which is released from the ...
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
PowerPoint Learning Quest
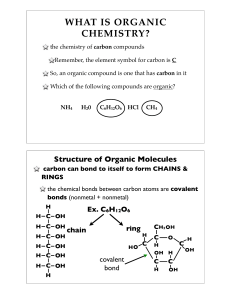
... responsible for the creation of these organic molecules, however, hydrolysis is responsible for the digestion or breakdown of these food molecules. Notice how water molecules are either removed or added to complete the bonding process. Observe figures 3.7 and 3.11 ...
... responsible for the creation of these organic molecules, however, hydrolysis is responsible for the digestion or breakdown of these food molecules. Notice how water molecules are either removed or added to complete the bonding process. Observe figures 3.7 and 3.11 ...
Ch8_CellularRespiration
... Energy from Glucose • Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration break glucose and other carbon compounds apart. • Energy released from broken bonds is harnessed to make ATP to run cell processes. • ALL Eukaryotic organisms (including plants) carry out cellular respiration ALL ...
... Energy from Glucose • Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration break glucose and other carbon compounds apart. • Energy released from broken bonds is harnessed to make ATP to run cell processes. • ALL Eukaryotic organisms (including plants) carry out cellular respiration ALL ...
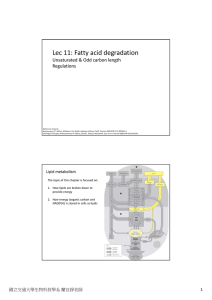
Lec 11: Fatty acid degradation
... • Recall that Fatty acid cannot convert to sugars in humans and most mammals. • acetyl‐CoA formed in the liver can go to TCA cycle for direct energy generation, or can be used to make ketone bodies which is then transported to other tissues for utilization. (acetone is not utilized, it is a degradat ...
... • Recall that Fatty acid cannot convert to sugars in humans and most mammals. • acetyl‐CoA formed in the liver can go to TCA cycle for direct energy generation, or can be used to make ketone bodies which is then transported to other tissues for utilization. (acetone is not utilized, it is a degradat ...
Energy Conversion Pathways 1. Substrate level phosphorylation
... Normally, animals eat every day which provides fuel for thermoregulation and ATP synthesis. Hibernating animals are dependent on stored fat for energy to keep cells alive and on thermongenin-mediated futile cycling to create sufficient thermoregulation. 33. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is requi ...
... Normally, animals eat every day which provides fuel for thermoregulation and ATP synthesis. Hibernating animals are dependent on stored fat for energy to keep cells alive and on thermongenin-mediated futile cycling to create sufficient thermoregulation. 33. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is requi ...
Lecture 7- 24 October 2013 Vitamins in metabolism and regulation
... B class-roles in metabolism and regulation of metabolism Niacin-part of co-enzymes NAD(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP(its phosphate form)-used in energy metabolism Biotin-part of coenzyme used in energy metabolism, fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism and glycogen synthesis Pantothenic ...
... B class-roles in metabolism and regulation of metabolism Niacin-part of co-enzymes NAD(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP(its phosphate form)-used in energy metabolism Biotin-part of coenzyme used in energy metabolism, fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism and glycogen synthesis Pantothenic ...
Table of Contents
... Figure 7.9 The Citric Acid Cycle Releases Much More Free Energy Than Glycolysis Does ...
... Figure 7.9 The Citric Acid Cycle Releases Much More Free Energy Than Glycolysis Does ...
Molecular Madness
... C O • Lactic acid builds up too fast and changes H OHthe pH of muscle cells C CH3 • Change in pH slows performance and ...
... C O • Lactic acid builds up too fast and changes H OHthe pH of muscle cells C CH3 • Change in pH slows performance and ...
The neutral theory of molecular evolution
... proposal may not seem particularly controversial now, it generated enormous controversy at the time, because at the time many paleoanthropologists interpreted the evidence to indicate humans diverged from apes as much as 30 million years ago. One year after Zuckerkandl and Pauling’s paper, Harris [ ...
... proposal may not seem particularly controversial now, it generated enormous controversy at the time, because at the time many paleoanthropologists interpreted the evidence to indicate humans diverged from apes as much as 30 million years ago. One year after Zuckerkandl and Pauling’s paper, Harris [ ...
Chem 150 quiz #6
... 17. What is the total net yield of ATP obtained when 5 glucose molecules are catabolized through glycolysis? (Note: The end product of glycolysis has not entered the TCA cycle yet.) a. 2 ATP b. 28 – 29 ATP c. 30 – 32 ATP d. 18 ATP e. none of the above 18. How many molecules of pyruvate would be obta ...
... 17. What is the total net yield of ATP obtained when 5 glucose molecules are catabolized through glycolysis? (Note: The end product of glycolysis has not entered the TCA cycle yet.) a. 2 ATP b. 28 – 29 ATP c. 30 – 32 ATP d. 18 ATP e. none of the above 18. How many molecules of pyruvate would be obta ...
Amino acid catabolism I
... 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are catabolized 2. urea cycle enzymes: extrahepatic arginine synthesis ...
... 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are catabolized 2. urea cycle enzymes: extrahepatic arginine synthesis ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.