Name Date Period 1. What are the end products of aerobic cell
... How many ATP molecules (net yield) are produced per molecule of glucose as a direct result of glycolysis? A. ...
... How many ATP molecules (net yield) are produced per molecule of glucose as a direct result of glycolysis? A. ...
File
... Pasteur observed that yeast consumes far more glucose when growing under anaerobic conditions than when growing under aerobic conditions. Scientists now know that the rate of ATP production by anaerobic glycolysis can be up to 100 times faster than that of oxidative phosphorylation, but much glucose ...
... Pasteur observed that yeast consumes far more glucose when growing under anaerobic conditions than when growing under aerobic conditions. Scientists now know that the rate of ATP production by anaerobic glycolysis can be up to 100 times faster than that of oxidative phosphorylation, but much glucose ...
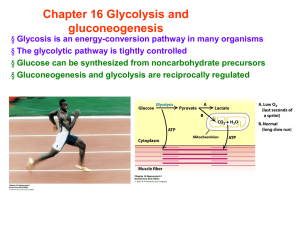
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Try sucrose (non-reducing sugar), sucrose was rapidly fermented into alcohol by the yeast juice, sucrose fermentation Fermentation could take place outside living cells 1860 Louis Pasteur: fermentation is inextricably tied to living cells. Open the door to modern biochemistry ...
... Try sucrose (non-reducing sugar), sucrose was rapidly fermented into alcohol by the yeast juice, sucrose fermentation Fermentation could take place outside living cells 1860 Louis Pasteur: fermentation is inextricably tied to living cells. Open the door to modern biochemistry ...
chapter 8 notes - 8.4 and 8.5 - APBio09-10
... b. Enzyme stretches the substrate toward transition state form i. Stretches and bends chemical bonds that must be broken in reaction ii. Ea is directly related to the difficulty of breaking the substrate’s bonds iii. Distorting the bonds helps the substrate approach transition and lowers the free en ...
... b. Enzyme stretches the substrate toward transition state form i. Stretches and bends chemical bonds that must be broken in reaction ii. Ea is directly related to the difficulty of breaking the substrate’s bonds iii. Distorting the bonds helps the substrate approach transition and lowers the free en ...
Article - International Journal of Biomedicine
... is regulated in accordance with the current needs of the body, tissues and cells on any of the central metabolic pathways – a catabolic or anabolic one. At the same time, all the reactions are adjusted so that they are carried out most economically, i.e., with the least possible expenditure of energ ...
... is regulated in accordance with the current needs of the body, tissues and cells on any of the central metabolic pathways – a catabolic or anabolic one. At the same time, all the reactions are adjusted so that they are carried out most economically, i.e., with the least possible expenditure of energ ...
10-3 Getting Energy to Make ATP
... iv. ATP is used for cell processes, growth, repair, movement, homeostasis etc… ...
... iv. ATP is used for cell processes, growth, repair, movement, homeostasis etc… ...
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
... ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
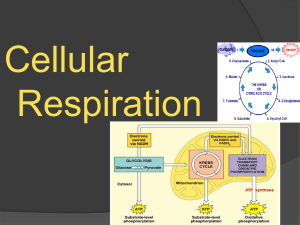
Chapter 9 - Cellular Respiration
... • Not an efficient method of ATP production. • AKA: fermentation. • Two primary types: – Lactic Acid Fermentation – Alcohol Fermentation ...
... • Not an efficient method of ATP production. • AKA: fermentation. • Two primary types: – Lactic Acid Fermentation – Alcohol Fermentation ...
Chemistry of Opioids
... o Partial agonist activity @ μ receptor due to metabolite nor-buprenorphine o Partial antagonist activity@ κ receptor o Antihyperalgesic effect: κ receptor antagonistic activity o ↓Adverse effects: ↓respiratory depression, not altered by age or renal dysfunction Meperidine o Binds to P-site: phenoli ...
... o Partial agonist activity @ μ receptor due to metabolite nor-buprenorphine o Partial antagonist activity@ κ receptor o Antihyperalgesic effect: κ receptor antagonistic activity o ↓Adverse effects: ↓respiratory depression, not altered by age or renal dysfunction Meperidine o Binds to P-site: phenoli ...
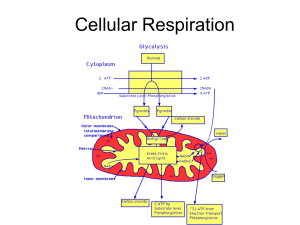
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration - Chemistry
... In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. ...
... In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. ...
bodylogix.com gnc.ca bodylogix.com gnc.ca gnc.ca
... GNC Pro Performance Lean Muscle Meal Ready-To-Drink Lean Muscle Meals RTDs are an excellent tasting liquid nutrition formula designed for endurance and recovery. Lean Muscle Meal RTDs are packed with 25g of protein, 3g of fiber, 27 vitamins and minerals – all only 170 calories. Lean Muscle Meal allo ...
... GNC Pro Performance Lean Muscle Meal Ready-To-Drink Lean Muscle Meals RTDs are an excellent tasting liquid nutrition formula designed for endurance and recovery. Lean Muscle Meal RTDs are packed with 25g of protein, 3g of fiber, 27 vitamins and minerals – all only 170 calories. Lean Muscle Meal allo ...
HB Cell Respiration Questions
... Concept 7.4 Electrons “fall” from food to oxygen during cellular respiration. (pg 145-147) Cellular respiration is an aerobic process, meaning that it requires oxygen. Although cellular respiration is different from breathing (called respiration), the two processes are related. Breathing brings oxyg ...
... Concept 7.4 Electrons “fall” from food to oxygen during cellular respiration. (pg 145-147) Cellular respiration is an aerobic process, meaning that it requires oxygen. Although cellular respiration is different from breathing (called respiration), the two processes are related. Breathing brings oxyg ...
Lecture 4 - IISER Pune
... Chiral ligands in organometallic compounds that serve as catalysts for hydrogenaOons and other reacOons Significance of chiral ligands: industrial synthesis each year of approximately 3500 tons of (-)-menthol using an ...
... Chiral ligands in organometallic compounds that serve as catalysts for hydrogenaOons and other reacOons Significance of chiral ligands: industrial synthesis each year of approximately 3500 tons of (-)-menthol using an ...
Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
... Metabolism 6.2 Carbohydrate Catabolism in the Presence of Oxygen Releases a Large Amount of Energy 6.3 Carbohydrate Catabolism in the Absence of Oxygen Releases a Small Amount of Energy ...
... Metabolism 6.2 Carbohydrate Catabolism in the Presence of Oxygen Releases a Large Amount of Energy 6.3 Carbohydrate Catabolism in the Absence of Oxygen Releases a Small Amount of Energy ...
HUMAN BIOCHEMISTRY
... Benefits and Concerns of Genetically Modified Foods Crops and animals can be genetically modified to provide more food, be more resistant to disease, or be more tolerant to heavy metals (among many other characteristics). Genetic engineering involves the process of selecting a single gene for a ...
... Benefits and Concerns of Genetically Modified Foods Crops and animals can be genetically modified to provide more food, be more resistant to disease, or be more tolerant to heavy metals (among many other characteristics). Genetic engineering involves the process of selecting a single gene for a ...
Microbiology bio 123
... Enzymes are organic catalysts, and therefore determine everything that a cell does. Once a reaction is completed, the enzyme can be reused because it is not changed by the reaction. The types of enzymes we produce determine what kinds of catabolic pathways we use. Enzymatic reactions are reversible. ...
... Enzymes are organic catalysts, and therefore determine everything that a cell does. Once a reaction is completed, the enzyme can be reused because it is not changed by the reaction. The types of enzymes we produce determine what kinds of catabolic pathways we use. Enzymatic reactions are reversible. ...
Lactate Inflection Point & Recovery
... Exercise intensities beyond the LIP are associated with fatigue The greater the exercise intensity above the inflection point, the more rapid the fatigue This fatigue is generally considered to be a consequence of a greater reliance on the anaerobic systems to supply the adenosine triphosphate ...
... Exercise intensities beyond the LIP are associated with fatigue The greater the exercise intensity above the inflection point, the more rapid the fatigue This fatigue is generally considered to be a consequence of a greater reliance on the anaerobic systems to supply the adenosine triphosphate ...
PDF
... from litter-mates were allowed to equilibrate for 1 h in oxygenated KrebsRinger bicarbonate solution which contained 5 x 10~ 3 M glucose. The inhibitor was added to the medium after one hour of equilibration. One chamber was supplied with oxygen and the other an anaerobic gas phase consisting of 95 ...
... from litter-mates were allowed to equilibrate for 1 h in oxygenated KrebsRinger bicarbonate solution which contained 5 x 10~ 3 M glucose. The inhibitor was added to the medium after one hour of equilibration. One chamber was supplied with oxygen and the other an anaerobic gas phase consisting of 95 ...
NOTES: Ch 9, part 4
... ● Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the Krebs cycle ● Fats are digested to glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ● An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
... ● Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the Krebs cycle ● Fats are digested to glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ● An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
Photosynthesis and alternate pathways
... Because PEP carboxylase’s binding affinity for CO2 is high, C4 plants have the ability to continue to fix carbon for a while even when their stomates are closed. That makes the water use efficiency of C4s much higher than that for C3s. That same affinity means that far less PEP carboxylase protein ...
... Because PEP carboxylase’s binding affinity for CO2 is high, C4 plants have the ability to continue to fix carbon for a while even when their stomates are closed. That makes the water use efficiency of C4s much higher than that for C3s. That same affinity means that far less PEP carboxylase protein ...
Biology Clicker Questions
... Grow fertilizer on plant growth. Group A is given fertilizer once a week for 4 weeks. Group B is given no fertilizer. The plant height of both groups is measured daily. Which of the following is a possible source of error? A. B. C. D. ...
... Grow fertilizer on plant growth. Group A is given fertilizer once a week for 4 weeks. Group B is given no fertilizer. The plant height of both groups is measured daily. Which of the following is a possible source of error? A. B. C. D. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.