Analysis of metabolic pathways and fluxes in a newly discovered
... investigated the central metabolism of this bacterium using both in vitro enzyme assays and 13C-based flux analysis to provide insights into the physiological properties of this extremophile and explore its metabolism for bio-ethanol or other bioprocess applications. Our findings show that glucose m ...
... investigated the central metabolism of this bacterium using both in vitro enzyme assays and 13C-based flux analysis to provide insights into the physiological properties of this extremophile and explore its metabolism for bio-ethanol or other bioprocess applications. Our findings show that glucose m ...
BCHM 562, Biochemistry II
... between these two states. FAD can be reduced to the FADH2, whereby it accepts two H atoms. 3. FMN functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases such as NADH dehydrogenase. 4. During catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) ...
... between these two states. FAD can be reduced to the FADH2, whereby it accepts two H atoms. 3. FMN functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases such as NADH dehydrogenase. 4. During catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) ...
Analysis of energy metabolism in acetic acid bacteria during
... In both A. aceti and A. pasteurianus, the genes for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzymes were found to be significantly repressed when ethanol was present in the medium, even in the presence of glucose or acetate.1,2) Acetobacter species are able to produce proton motive force that is used for ...
... In both A. aceti and A. pasteurianus, the genes for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzymes were found to be significantly repressed when ethanol was present in the medium, even in the presence of glucose or acetate.1,2) Acetobacter species are able to produce proton motive force that is used for ...
Ratios and Rates - Creating, Learning, and Laughing with Mrs
... Unit Rate: A unit rate is a rate that has a denominator of ___________ unit. To write an equivalent rate, find an equivalent rate with a denominator of ____________ unit. To find a unit rate, _____________ the distance or frequency by the amount of time or number of units Examples: Write each situat ...
... Unit Rate: A unit rate is a rate that has a denominator of ___________ unit. To write an equivalent rate, find an equivalent rate with a denominator of ____________ unit. To find a unit rate, _____________ the distance or frequency by the amount of time or number of units Examples: Write each situat ...
Cellular Respiration
... •First, fat must by hydrolyzed into glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol can enter glycolysis after either being converted to glucose (via gluconeogenesis) or changed into dihydroxyacetonephosphate (DHAP). -The fatty acids are broken down to two-carbon units (acetyl-CoA) in a process called boxida ...
... •First, fat must by hydrolyzed into glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol can enter glycolysis after either being converted to glucose (via gluconeogenesis) or changed into dihydroxyacetonephosphate (DHAP). -The fatty acids are broken down to two-carbon units (acetyl-CoA) in a process called boxida ...
Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics
... Adenosine triphosphate is a high-energy compound or nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) formed by adding two additional phosphate groups to a nucleotide containing the base adenine and the pentose monosaccharide ribose. Sometimes referred to as the energy currency within cells, ATP is formed and used on a ...
... Adenosine triphosphate is a high-energy compound or nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) formed by adding two additional phosphate groups to a nucleotide containing the base adenine and the pentose monosaccharide ribose. Sometimes referred to as the energy currency within cells, ATP is formed and used on a ...
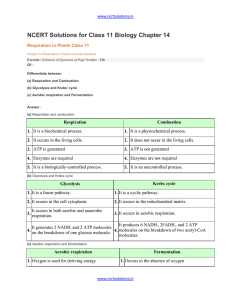
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... termed as amphibolic pathway as it involves both anabolism and catabolism. ...
... termed as amphibolic pathway as it involves both anabolism and catabolism. ...
Respiration
... It is the process of producing some of the remaining energy (ATP) from the Pyruvate molecules. It occurs mainly in mitochondrial matrix if oxygen is present. It is the main source for preparing most of the cellular NADH (storing energy molecule), and for producing some more of the cellular ATP. It i ...
... It is the process of producing some of the remaining energy (ATP) from the Pyruvate molecules. It occurs mainly in mitochondrial matrix if oxygen is present. It is the main source for preparing most of the cellular NADH (storing energy molecule), and for producing some more of the cellular ATP. It i ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
Name - straubel
... At the end of this process, how many Ps are present in the products? ______ What is the name of these molecules? _______________________________ 4. Four molecules of ATP are produced by what process? ______________ _____________________ Since ____ ATP were used to start glycolysis, what is the net A ...
... At the end of this process, how many Ps are present in the products? ______ What is the name of these molecules? _______________________________ 4. Four molecules of ATP are produced by what process? ______________ _____________________ Since ____ ATP were used to start glycolysis, what is the net A ...
Human skin contact with cold materials: Pain and Thermal sensation
... with the skin and clothing is warmed – the air can be moved by a draught -”forced” – or the buoyancy of the warmer air - “natural” Responsible for 70-80% of heat loss in the cold Near to 100% when immersed in water ...
... with the skin and clothing is warmed – the air can be moved by a draught -”forced” – or the buoyancy of the warmer air - “natural” Responsible for 70-80% of heat loss in the cold Near to 100% when immersed in water ...
Anaerobic Respiration - University of Indianapolis
... During heavy exercise, ATP production will switch from aerobic respiration to anerobic respiration ...
... During heavy exercise, ATP production will switch from aerobic respiration to anerobic respiration ...
9/2/08 Transcript I - UAB School of Optometry
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
Unit 06 Lecture Notes: Metabolism and Respiration
... 2) Respiratory mechanism delivers oxygen to blood 3) Blood delivers oxygen to tissues 4) Tissues give CO2 (waste) to blood 5) Blood gives CO2 to respiratory mechanism 6) Respiratory mechanism releases CO2 to external environment! B. Cells then take O2 and carry out cellular respiration, CO2 being wa ...
... 2) Respiratory mechanism delivers oxygen to blood 3) Blood delivers oxygen to tissues 4) Tissues give CO2 (waste) to blood 5) Blood gives CO2 to respiratory mechanism 6) Respiratory mechanism releases CO2 to external environment! B. Cells then take O2 and carry out cellular respiration, CO2 being wa ...
Document
... Phototroph: an organism that obtains energy from sunlight for the synthesis of organic compounds (they convert the solar energy to chemical one) Chemotroph: an organism that cannot harvest and convert the solar energy, instead of it take up organic compounds and oxydize them to gain energy. Source o ...
... Phototroph: an organism that obtains energy from sunlight for the synthesis of organic compounds (they convert the solar energy to chemical one) Chemotroph: an organism that cannot harvest and convert the solar energy, instead of it take up organic compounds and oxydize them to gain energy. Source o ...
Aerobic respiration - Wesleyan
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
photosynthesis
... The photosynthesis word equation. That light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts and used to make sugar from carbon dioxide. Oxygen is a bye-product. The rate of photosynthesis may by limited by: low temperature, shortage of carbon dioxide, shortage of light. The glucose produced in ph ...
... The photosynthesis word equation. That light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts and used to make sugar from carbon dioxide. Oxygen is a bye-product. The rate of photosynthesis may by limited by: low temperature, shortage of carbon dioxide, shortage of light. The glucose produced in ph ...
factors in photosynthesis
... The photosynthesis word equation. That light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts and used to make sugar from carbon dioxide. Oxygen is a bye-product. The rate of photosynthesis may by limited by: low temperature, shortage of carbon dioxide, shortage of light. The glucose produced in ph ...
... The photosynthesis word equation. That light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts and used to make sugar from carbon dioxide. Oxygen is a bye-product. The rate of photosynthesis may by limited by: low temperature, shortage of carbon dioxide, shortage of light. The glucose produced in ph ...
ap nucleic acids, proteins and enzymes
... Speed up Biochemical Reactions 3.4 Regulation of Metabolism Occurs by Regulation of Enzymes ...
... Speed up Biochemical Reactions 3.4 Regulation of Metabolism Occurs by Regulation of Enzymes ...
PoL2e Ch03 Lecture-Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Speed up Biochemical Reactions 3.4 Regulation of Metabolism Occurs by Regulation of Enzymes ...
... Speed up Biochemical Reactions 3.4 Regulation of Metabolism Occurs by Regulation of Enzymes ...
B-Metabolism of Sulphur containing amino acids
... Functions of Nitric Oxide - It acts as vasodilator and causes relaxation of smooth muscles. - It has important role in regulation of blood flow and maintaining blood pressure. - It is involved in penile erection. - Acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and peripheral autonomic nervous system - Ma ...
... Functions of Nitric Oxide - It acts as vasodilator and causes relaxation of smooth muscles. - It has important role in regulation of blood flow and maintaining blood pressure. - It is involved in penile erection. - Acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and peripheral autonomic nervous system - Ma ...
Nutrisi & Pertumbuhan Mikrobia
... energy and hydrogen atoms or electrons. • Nutrient molecules frequently cannot cross selectively permeable plasma membranes through passive diffusion. They must be transported by one of three major mechanisms involving the use of membrane carrier proteins. ...
... energy and hydrogen atoms or electrons. • Nutrient molecules frequently cannot cross selectively permeable plasma membranes through passive diffusion. They must be transported by one of three major mechanisms involving the use of membrane carrier proteins. ...
structural
... III. Lipids A. Fats - structure -unsaturated fats (no double bonds) Plant and fish oils Kinked; don’t pack – liquid at room temperature. “Hydrogenation” can make them saturated and solid, but the process also produces trans-fats (trans conformation around double bond) which may contribute MORE to a ...
... III. Lipids A. Fats - structure -unsaturated fats (no double bonds) Plant and fish oils Kinked; don’t pack – liquid at room temperature. “Hydrogenation” can make them saturated and solid, but the process also produces trans-fats (trans conformation around double bond) which may contribute MORE to a ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.