AS 90715 version 2 Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
definition - Humble ISD
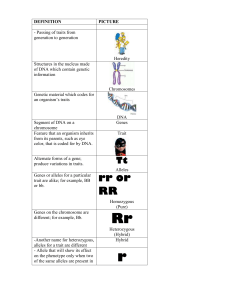
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
Extensions and Exceptions to Mendel*s Laws
... • Phenocopy: a characteristic that appears to be inherited but is environmentally caused Limb loss from thalidomide; infections ...
... • Phenocopy: a characteristic that appears to be inherited but is environmentally caused Limb loss from thalidomide; infections ...
Networks of Genes, Epistasis and a Functionally
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
What is another name for a polypeptide?
... Other mutations are caused by mutagens (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that ...
... Other mutations are caused by mutagens (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that ...
HW #1
... 10. What are Bateson’s three cases of non-Mendelian inheritance? Describe them in your own words. 11. What is Sutton’s key contribution to the world of genetics? Genetics Review 12. In a single sentence, define the following common genetic terms: A. Homozygous B. Heterozygous C. Aneuploidy D. ...
... 10. What are Bateson’s three cases of non-Mendelian inheritance? Describe them in your own words. 11. What is Sutton’s key contribution to the world of genetics? Genetics Review 12. In a single sentence, define the following common genetic terms: A. Homozygous B. Heterozygous C. Aneuploidy D. ...
LN #23
... 4c. Students know how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the gene or the sequence of amino acids in an encoded protein. ...
... 4c. Students know how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the gene or the sequence of amino acids in an encoded protein. ...
Mutations
... Mutation and Evolution • Mutations are recognized as the primary source of the hereditary variations that make evolution possible • Mutations may be either harmful or useful to a species • Mutations that help are continued because it is the survivors that reproduce and pass the traits on to their o ...
... Mutation and Evolution • Mutations are recognized as the primary source of the hereditary variations that make evolution possible • Mutations may be either harmful or useful to a species • Mutations that help are continued because it is the survivors that reproduce and pass the traits on to their o ...
PS401-Mar. 17
... works until you have to fix it.” Disruptions of the gene can be either non-functional or “leaky”. Often the “leaky” phenotypes will really help you understand how to gene works. ...
... works until you have to fix it.” Disruptions of the gene can be either non-functional or “leaky”. Often the “leaky” phenotypes will really help you understand how to gene works. ...
GENETICS 310-PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
Oculocutaneous albinism type 1A
... codons 355 (thr to lys) and codon 365 (asp to asn). These mutations cause the tyrosinase activity to be disrupted, causing the lack of pigmentation seen in albinism. Both of these mutations occur in the copper binding region of the enzyme. ...
... codons 355 (thr to lys) and codon 365 (asp to asn). These mutations cause the tyrosinase activity to be disrupted, causing the lack of pigmentation seen in albinism. Both of these mutations occur in the copper binding region of the enzyme. ...
Mutations
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
Mutations Learning goals Mutation Where Mutations Occur
... • 1. Explain what a mutation is and how it can affect an organism. • 2. Name the two types of cells where mutations can occur and the affects. • 3. Describe the two types of gene mutations and give examples of each. ...
... • 1. Explain what a mutation is and how it can affect an organism. • 2. Name the two types of cells where mutations can occur and the affects. • 3. Describe the two types of gene mutations and give examples of each. ...
genetics Study Guide(fall 2016) - new book)
... When is the dominant phenotype expressed? When is the recessive phenotype expressed? solve multiple allele problems (eye colour in fruit flies – wild-type, honey, apricot, white), using the correct notation the difference between complete dominance, codominance, and intermediate inheritance solve in ...
... When is the dominant phenotype expressed? When is the recessive phenotype expressed? solve multiple allele problems (eye colour in fruit flies – wild-type, honey, apricot, white), using the correct notation the difference between complete dominance, codominance, and intermediate inheritance solve in ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
Evolution of genomes
... For the development of good models of molecular evolution it is useful to distinguish between different types of mutations. I will make here the major distinction between mutations on a local scale and mutations on a global scale, the former being ones that can be described by looking at a stretch o ...
... For the development of good models of molecular evolution it is useful to distinguish between different types of mutations. I will make here the major distinction between mutations on a local scale and mutations on a global scale, the former being ones that can be described by looking at a stretch o ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.