MUTATIONS
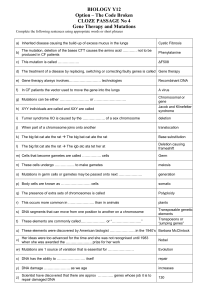
... – A frameshift mutation (another type of gene mutation) inserts or deletes a nucleotide in the DNA sequence. ...
... – A frameshift mutation (another type of gene mutation) inserts or deletes a nucleotide in the DNA sequence. ...
Cornell Notes Template
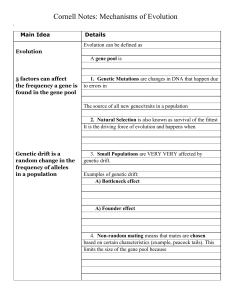
... The source of all new genes/traits in a population 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
... The source of all new genes/traits in a population 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
Bombay Phenotype
... be tolerated in the heterozygous state but may behave as a recessive lethal allele in the homozygous state, in which case homozygous recessive individuals will not ...
... be tolerated in the heterozygous state but may behave as a recessive lethal allele in the homozygous state, in which case homozygous recessive individuals will not ...
Warm-Up 2/26 and 2/27
... gene’ that causes a disorder – If this gene is ‘recessive’ they don’t have the disorder but are carriers – If this gene is ‘dominant’ they have the disorder – In chromosomal mutations, one parent gives an extra chromosome, mutant chromosome, or doesn’t give one at all ...
... gene’ that causes a disorder – If this gene is ‘recessive’ they don’t have the disorder but are carriers – If this gene is ‘dominant’ they have the disorder – In chromosomal mutations, one parent gives an extra chromosome, mutant chromosome, or doesn’t give one at all ...
Section 7.2 Reinforcement
... homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an example of both ...
... homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an example of both ...
Mutations - Choteau Schools
... DNA is changed by an outside force (such as radiation). This change may impair the function of the cell. The mutation is passed on to daughter cells when the original cell divides. ...
... DNA is changed by an outside force (such as radiation). This change may impair the function of the cell. The mutation is passed on to daughter cells when the original cell divides. ...
Heredity
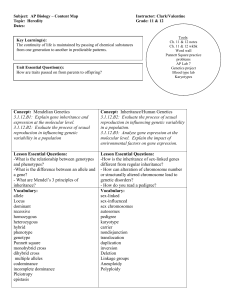
... 3.1.12.B2: Evaluate the process of sexual reproduction in influencing genetic variability in a population. 3.1.12.B3: Analyze gene expression at the molecular level. Explain the impact of environmental factors on gene expression. ...
... 3.1.12.B2: Evaluate the process of sexual reproduction in influencing genetic variability in a population. 3.1.12.B3: Analyze gene expression at the molecular level. Explain the impact of environmental factors on gene expression. ...
Life 101 - findyourtao2011
... Questions: 1. How can mutations lead to differences in gene frequency? 2. How do mutations cause evolutionary change? 3. Can you think of another positive mutation? 4. Create a short skit on how mutation drives evolution. ...
... Questions: 1. How can mutations lead to differences in gene frequency? 2. How do mutations cause evolutionary change? 3. Can you think of another positive mutation? 4. Create a short skit on how mutation drives evolution. ...
7.2
... between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an exam ...
... between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an exam ...
PPT 2.1M - CytoMaize.ORG
... Mutation: 1) The act or process of making a heritable change in the genetic material (DNA). Phenotype: 2) The appearance of an individual. Phenotypes can be normal (wild-type) or mutant. A mutant individual can have parents that are genetic carriers, but show a normal phenotype. Mutant phenotypes a ...
... Mutation: 1) The act or process of making a heritable change in the genetic material (DNA). Phenotype: 2) The appearance of an individual. Phenotypes can be normal (wild-type) or mutant. A mutant individual can have parents that are genetic carriers, but show a normal phenotype. Mutant phenotypes a ...
Slide 1
... deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein produced is. Figure 8.17a, d ...
... deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein produced is. Figure 8.17a, d ...
Smurfs, Trolls & Elves
... Changes In Frequency • As railroads and development swept through, the blue Fugates started moving out of Troublesome Creek and marrying other people • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
... Changes In Frequency • As railroads and development swept through, the blue Fugates started moving out of Troublesome Creek and marrying other people • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
Special Topics in Heredity
... Polygenic inheritance: The additive effect of two or more genes on a trait. Ex. Several genes are involved in skin color with an additive effect on the amount of pigment. ...
... Polygenic inheritance: The additive effect of two or more genes on a trait. Ex. Several genes are involved in skin color with an additive effect on the amount of pigment. ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.