Gene mutations
... codon after is changed These types of mutations cause Frameshift mutations Can cause major changes to the protein, to the point where it can’t perform its normal function ...
... codon after is changed These types of mutations cause Frameshift mutations Can cause major changes to the protein, to the point where it can’t perform its normal function ...
Mendelian Genetics III Exceptions
... the ABO gene. H protein attaches the A or B protein to the cell surface. hh genotype = no H protein. All ABO genotypes appear as type O. ...
... the ABO gene. H protein attaches the A or B protein to the cell surface. hh genotype = no H protein. All ABO genotypes appear as type O. ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... 3. Excluding the stop sequence, how many nucleotides are necessary to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long? a. 33 b. 66 c. 100 d. 300 ...
... 3. Excluding the stop sequence, how many nucleotides are necessary to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long? a. 33 b. 66 c. 100 d. 300 ...
Inheritance of a Trait - Introduction
... a different mix of the maternal and paternal chromosomes in each gamete, which produces variation in the population. The progeny can inherit different alleles from their parents, resulting in a particular genotype at that locus. The alleles can interact with each other in different ways – such as be ...
... a different mix of the maternal and paternal chromosomes in each gamete, which produces variation in the population. The progeny can inherit different alleles from their parents, resulting in a particular genotype at that locus. The alleles can interact with each other in different ways – such as be ...
principles of genetics
... Gene mutations, Chromosomal mutations: Deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation, aneuploidy and polyploidy; Induced versus spontaneous mutations; Backward and forward mutations; Suppressor mutations; Molecular basis of mutations in relation to UV light and chemical mutagens; Detection of muta ...
... Gene mutations, Chromosomal mutations: Deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation, aneuploidy and polyploidy; Induced versus spontaneous mutations; Backward and forward mutations; Suppressor mutations; Molecular basis of mutations in relation to UV light and chemical mutagens; Detection of muta ...
Amino Acid Substitution - UNT's College of Education
... nucleotide pairs in a gene; alters the ‘reading frame’ of triplets~frameshift mutation ...
... nucleotide pairs in a gene; alters the ‘reading frame’ of triplets~frameshift mutation ...
mutations - Université d`Ottawa
... t = mean conditional fixation time 1/K = mean time between 2 consecutive fixation events K = rate of substitution (# mutations fixed per unit time) ...
... t = mean conditional fixation time 1/K = mean time between 2 consecutive fixation events K = rate of substitution (# mutations fixed per unit time) ...
Mutations II
... to 10-9 mutations per gene per generation – Lenski’s E. coli: 8.9 x 10-11 per base pair per generation • Since E. coli’s genome is 4.6 x 106 base pairs, this works out to one mutation every 2442 generations ...
... to 10-9 mutations per gene per generation – Lenski’s E. coli: 8.9 x 10-11 per base pair per generation • Since E. coli’s genome is 4.6 x 106 base pairs, this works out to one mutation every 2442 generations ...
Mutations Justified True or False
... Yes, because we learned in the 4 PowerPoint’s that chemicals and smoke from buildings can cause, just like the birch trees, changes in the organisms. And the chemicals can also change genes inside the organism. I know this because Mr. Bormann told us to put it in our notes. The environment can alter ...
... Yes, because we learned in the 4 PowerPoint’s that chemicals and smoke from buildings can cause, just like the birch trees, changes in the organisms. And the chemicals can also change genes inside the organism. I know this because Mr. Bormann told us to put it in our notes. The environment can alter ...
Transposons_&_DNA_Mutations
... from one generation to the next Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
... from one generation to the next Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
Ch. 8 Mutations
... contains 3.2 billion base pairs. During DNA Replication, DNA makes an error every 100,000 base pairs and repairs it to an average of one error every 10 billion base pairs. That’s an average of 0.31 base pairs each time DNA is replicated. ...
... contains 3.2 billion base pairs. During DNA Replication, DNA makes an error every 100,000 base pairs and repairs it to an average of one error every 10 billion base pairs. That’s an average of 0.31 base pairs each time DNA is replicated. ...
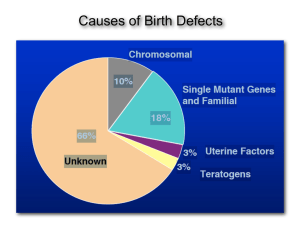
Causes of Birth Defects
... condition (due to genetics, development, chronic injury, etc.). pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the s ...
... condition (due to genetics, development, chronic injury, etc.). pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the s ...
Presentation
... causes partial loss of function in this pathway -Genes could be in parallel pathways that perform redundant functions -Genes can be in parallel pathways that do not have related functions, but one is required when other is missing (Ex. checkpoint mutation and DNA repair machinery). ...
... causes partial loss of function in this pathway -Genes could be in parallel pathways that perform redundant functions -Genes can be in parallel pathways that do not have related functions, but one is required when other is missing (Ex. checkpoint mutation and DNA repair machinery). ...
Natural Selection March , 2.009 * 103
... Natural selection is the process by which mutations that increase fitness become more common over time, and mutations that decrease fitness become less common over time. ...
... Natural selection is the process by which mutations that increase fitness become more common over time, and mutations that decrease fitness become less common over time. ...
Genes and Mutations 1. Define: Genetics – Genetics may be defined
... 11. One per 100 million copies of the DNA present/ at least one. The m-concentration for a bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence ...
... 11. One per 100 million copies of the DNA present/ at least one. The m-concentration for a bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence ...
Genetics and Heredity
... • Epistasis– a gene at one locus alters the expression of a separate gene • Pleiotropy– a gene with multiple phenotypic effects • Polygenic inheritance– an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotype ...
... • Epistasis– a gene at one locus alters the expression of a separate gene • Pleiotropy– a gene with multiple phenotypic effects • Polygenic inheritance– an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotype ...
lz(g) - Molecular and Cell Biology
... Cross the two mutants: get not a mix of phenotypes, but instead, either phenotype #1 or #2. The term “epistasis” refers to a phenomenon in which an allele of one gene masks (“stops”) the effects on the phenotype of an allele of a different gene. The discovery of epistatic interactions between gene p ...
... Cross the two mutants: get not a mix of phenotypes, but instead, either phenotype #1 or #2. The term “epistasis” refers to a phenomenon in which an allele of one gene masks (“stops”) the effects on the phenotype of an allele of a different gene. The discovery of epistatic interactions between gene p ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.