Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of RNA involved in protein synthesis. 6. Know how to use the genetic code to identify amino acids. 7. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than 1 kind of codon? 8. Genes con ...
... 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of RNA involved in protein synthesis. 6. Know how to use the genetic code to identify amino acids. 7. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than 1 kind of codon? 8. Genes con ...
sex
... or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks gene activity, causing a loss-of-function phenotype even in the presence of a normal copy of the gene. This phenomenon occurs when the mutant gene ...
... or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks gene activity, causing a loss-of-function phenotype even in the presence of a normal copy of the gene. This phenomenon occurs when the mutant gene ...
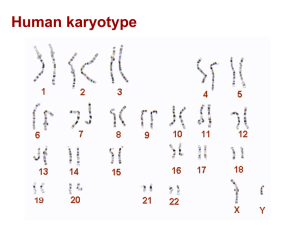
What Should I Know for the HUMAN GENOME TEST? Chapter 14
... Which of these is passed on to offspring? How can mutations be beneficial? What is a lethal mutation? What is a sex linked gene? How are twins made? How are the two kinds of twins different? What do we call twins that fail to completely separate and are born joined together? What’s the difference be ...
... Which of these is passed on to offspring? How can mutations be beneficial? What is a lethal mutation? What is a sex linked gene? How are twins made? How are the two kinds of twins different? What do we call twins that fail to completely separate and are born joined together? What’s the difference be ...
Gen_Week1 - life.illinois.edu
... Survival & reproduction of individuals are not random. Those that survive and reproduce are those with the most favorable variations. They are naturally selected. ...
... Survival & reproduction of individuals are not random. Those that survive and reproduce are those with the most favorable variations. They are naturally selected. ...
Campbell Ch 14 Reading guide
... to the F2 generations. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 6. When does the segregation of alleles occur? __________________________________ ...
... to the F2 generations. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 6. When does the segregation of alleles occur? __________________________________ ...
mutation PP
... DNA changes • Sometimes, a gene can be “turned on” (induced, or activated) and cause a protein to be made, while at other times it can be “turned off” (inhibited or repressed) to save energy - like a light bulb • Genes also change over time, like people do. A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. ...
... DNA changes • Sometimes, a gene can be “turned on” (induced, or activated) and cause a protein to be made, while at other times it can be “turned off” (inhibited or repressed) to save energy - like a light bulb • Genes also change over time, like people do. A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. ...
Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
... • Such a change might come about because – natural selection favored the gene – the population received new immigrants carrying the gene (gene flow) – nonresistant genes mutated into a resistant version of the gene – of random genetic drift from one generation to the next ...
... • Such a change might come about because – natural selection favored the gene – the population received new immigrants carrying the gene (gene flow) – nonresistant genes mutated into a resistant version of the gene – of random genetic drift from one generation to the next ...
lecture4 - ucsf biochemistry website
... The work of EB Lewis beginning in the 1940’s gave us an extraordinary view of genetic and of development. The scientific community is still trying to catch up with the implications of some of the things he found. I will mention two genetic phenomena that he described because they are especially mean ...
... The work of EB Lewis beginning in the 1940’s gave us an extraordinary view of genetic and of development. The scientific community is still trying to catch up with the implications of some of the things he found. I will mention two genetic phenomena that he described because they are especially mean ...
ppt
... melanogaster. When females heterozygous for these genes were crossed with scute bristled, ruby eyed males, the following classes and numbers of progeny (out of 1000) ...
... melanogaster. When females heterozygous for these genes were crossed with scute bristled, ruby eyed males, the following classes and numbers of progeny (out of 1000) ...
Review Questions: Gene Regulation and Expression
... “read” by a ribosome during translation. The ribosome puts together amino acids to make a protein based on the code from the gene. An RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA gene to make an mRNA to be translated by the ribosome. Genes give the instructions for the creation of proteins. Proteins give stru ...
... “read” by a ribosome during translation. The ribosome puts together amino acids to make a protein based on the code from the gene. An RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA gene to make an mRNA to be translated by the ribosome. Genes give the instructions for the creation of proteins. Proteins give stru ...
File
... Most mutations are automatically repaired by the organism’s enzymes, but those that are not repaired may result in altered chromosomes or genes. Mutant body cells are not passed on to offspring but mutant gametes may be inherited. In some cases, mutations are beneficial to organisms. A pedig ...
... Most mutations are automatically repaired by the organism’s enzymes, but those that are not repaired may result in altered chromosomes or genes. Mutant body cells are not passed on to offspring but mutant gametes may be inherited. In some cases, mutations are beneficial to organisms. A pedig ...
Genes and Inheritance
... Proteins either become part of the body (STRUCTURAL) …or they build other molecules, forming the body (FUNCTIONAL) ...
... Proteins either become part of the body (STRUCTURAL) …or they build other molecules, forming the body (FUNCTIONAL) ...
MUTATIONS
... EX: Cri du Chat is a deletion mutation. An affect person sounds like a cat when they cry. ...
... EX: Cri du Chat is a deletion mutation. An affect person sounds like a cat when they cry. ...
Study Guide: From Gene to Phenotype 1. Explain the different
... 5. According to the dominance hypothesis for heterosis, should it be possible to develop an inbred with the same phenotype as an F1 hybrid? 6. Is heterosis as important in natural ecosystems as it is in agroecosystems? 7. Why is F1 hybrid seed more commonly grown than F2 hybrid seed? 8. Why is under ...
... 5. According to the dominance hypothesis for heterosis, should it be possible to develop an inbred with the same phenotype as an F1 hybrid? 6. Is heterosis as important in natural ecosystems as it is in agroecosystems? 7. Why is F1 hybrid seed more commonly grown than F2 hybrid seed? 8. Why is under ...
Notes Guide
... Genes are _______________ from _______________ to their _______________. 2. Some forms of a gene (_____________) may be ______________ and others may be ______________________. 3. In most _______________ reproducing organisms, each adult has _______________copies of each gene—one from ______________ ...
... Genes are _______________ from _______________ to their _______________. 2. Some forms of a gene (_____________) may be ______________ and others may be ______________________. 3. In most _______________ reproducing organisms, each adult has _______________copies of each gene—one from ______________ ...
Oct 11 - University of San Diego
... Presence of certain alleles at one locus can alter expression of alleles at different locus Ex: Coat color in dogs ...
... Presence of certain alleles at one locus can alter expression of alleles at different locus Ex: Coat color in dogs ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.